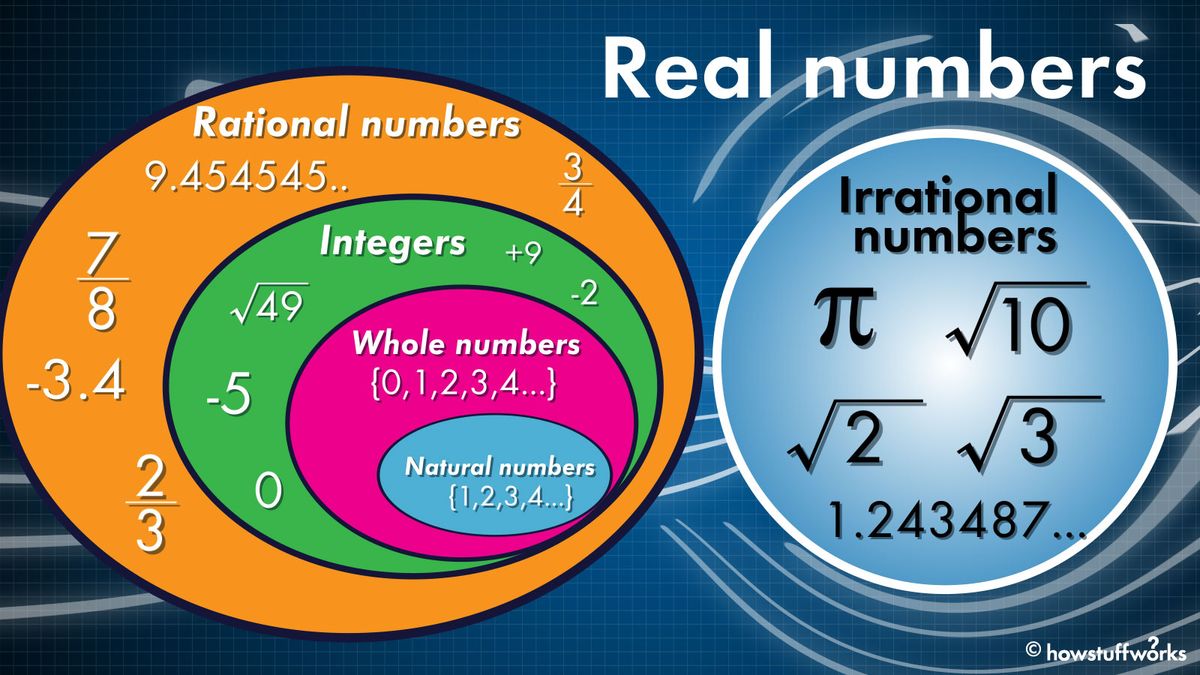
Rational Numbers And Irrational Numbers Chart
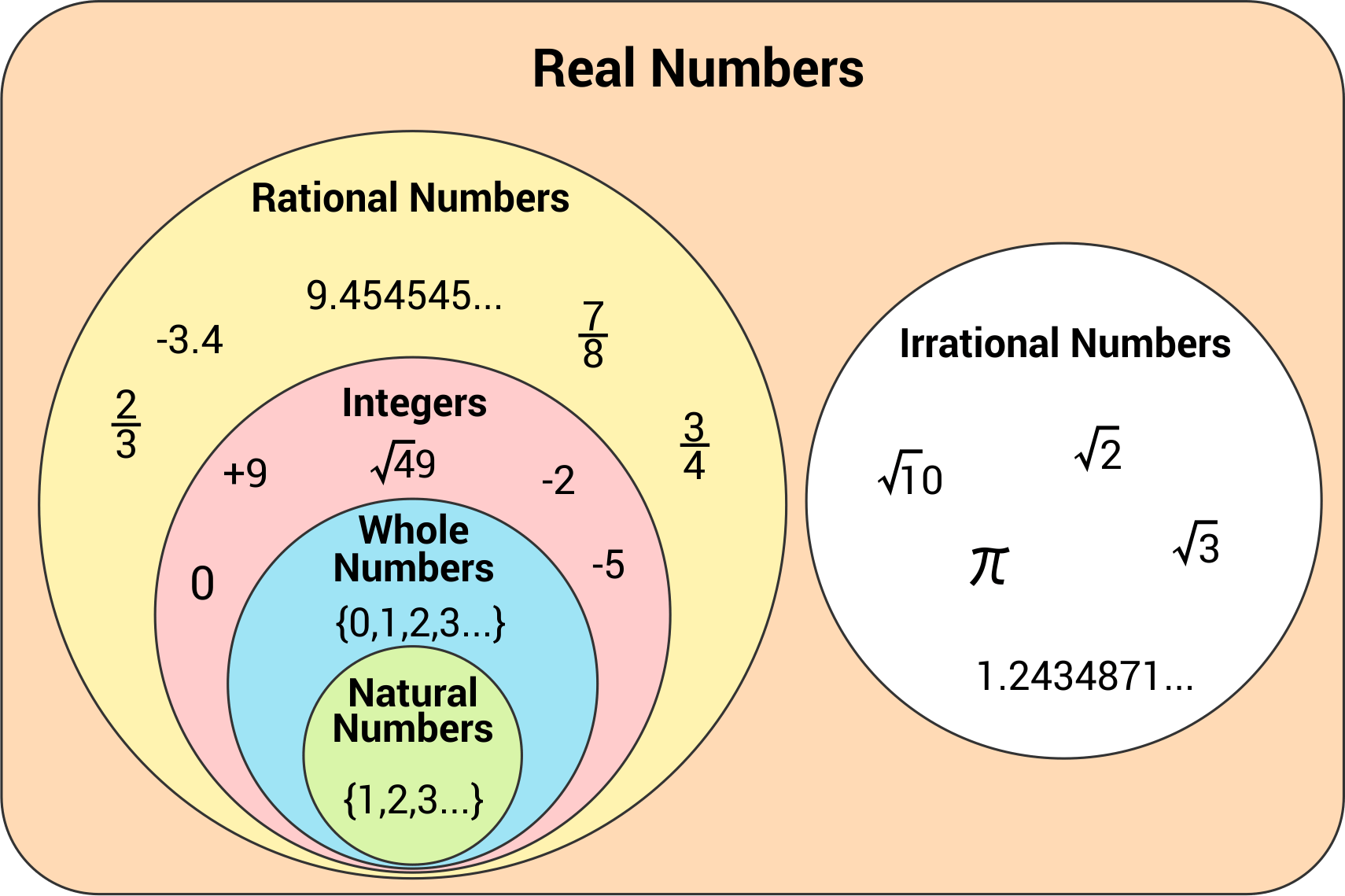
Rational Numbers And Irrational Numbers Chart - Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal, they continue indefinitely without repeating. Web we can write any rational number as the ratio of two integers. Product of rational & irrational is irrational. A funnel represents each group or set of numbers. Web let's summarize a method we can use to determine whether a number is rational or irrational. As per the definition, rational numbers include all integers, fractions and repeating decimals. The venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. Description of each set of real numbers. For an irrational number x, and a rational number y, their result, x+y = an irrational number. Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational number and an irrational number. Web what is the difference between rational and irrational numbers, how to identify rational and irrational numbers, examples and step by step solutions, gcse maths Web rational and irrational numbers. Locate fractions on the number line. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a repeating block of digits. How to classify real numbers. Learn the definitions, more differences and examples based on them. Web let us see how to identify rational and irrational numbers based on the given set of examples. Sum & product of two rationals is rational. The “stack of funnels” diagram below will help us easily classify any real numbers. For an irrational number x, and a rational number y,. Web rational numbers and irrational numbers. If the decimal form of a number. Web learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are actually irrational. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 720 mastery points. A rational. The rational number is a quotient of this ratio. How to classify real numbers. For an irrational number x, and a rational number y, their result, x+y = an irrational number. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? There are five subsets within the set of real numbers. Web many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. Description of each set of real numbers. Sum of rational & irrational is irrational. Stops or repeats, the number is rational. Let’s go over each one of them. Irrational numbers are also a subset of the real numbers. Web let us see how to identify rational and irrational numbers based on the given set of examples. Classify different types of real numbers We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do. Web a rational number is a number that can be written in the form of a common fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not 0. If the decimal form of a number. The rational number is a quotient of this ratio. Explain how the sets of numbers (counting, whole, integer, rational, irrationals, reals) are related to each other.. All the numbers mentioned in this lesson belong to the set of real numbers. 1.5 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 3/2. How to classify real numbers. As per the definition, rational numbers include all integers, fractions and repeating decimals. In this example, both p and q must be integers, which. Learn the definitions, more differences and examples based on them. A more thorough introduction to the topics covered in this section can be found in the prealgebra chapters, decimals and properties of real numbers. Real numbers hold some crucial properties in mathematics: Five (5) subsets of real numbers. Definition of rational and irrational numbers. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a repeating block of digits. Stops or repeats, the number is rational. Formally, a rational number is a number that can be expressed in the form. There are five subsets within the set of real numbers. Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational. Web let's summarize a method we can use to determine whether a number is rational or irrational. Learn other forms, such as decimals, in which these types of numbers can appear. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 720 mastery points. Web identify integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. Description of each set of real numbers. Home » arithmetic » irrational numbers. Web a rational number is a number that can be written in the form of a common fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not 0. Sums and products of irrational numbers. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? Definition of rational and irrational numbers. Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be written as a simple fraction or ratio. Five (5) subsets of real numbers. The “stack of funnels” diagram below will help us easily classify any real numbers. A more thorough introduction to the topics covered in this section can be found in the prealgebra chapters, decimals and properties of real numbers. As per the definition, rational numbers include all integers, fractions and repeating decimals. Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal, they continue indefinitely without repeating.
Worksheets On Rational And Irrational Numbers

Rational vs. Irrational Numbers 4 Key Differences, Definition
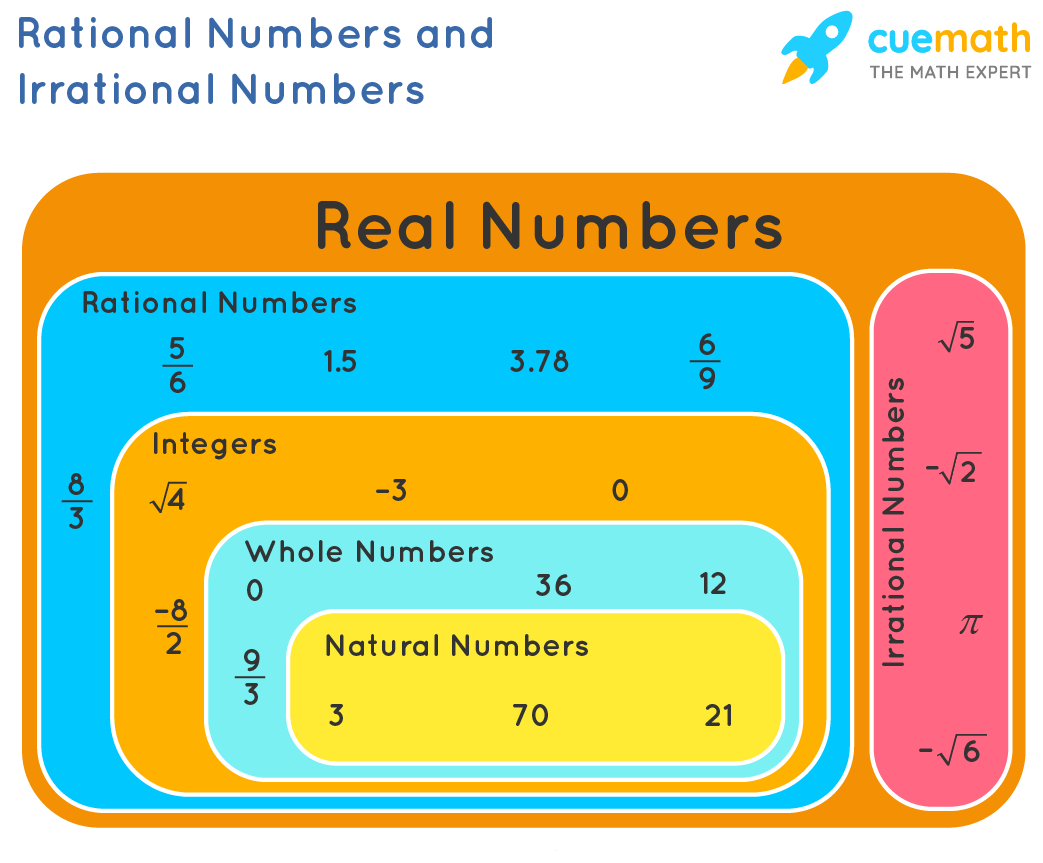
Rational Numbers Definition Examples What are Rational Numbers?
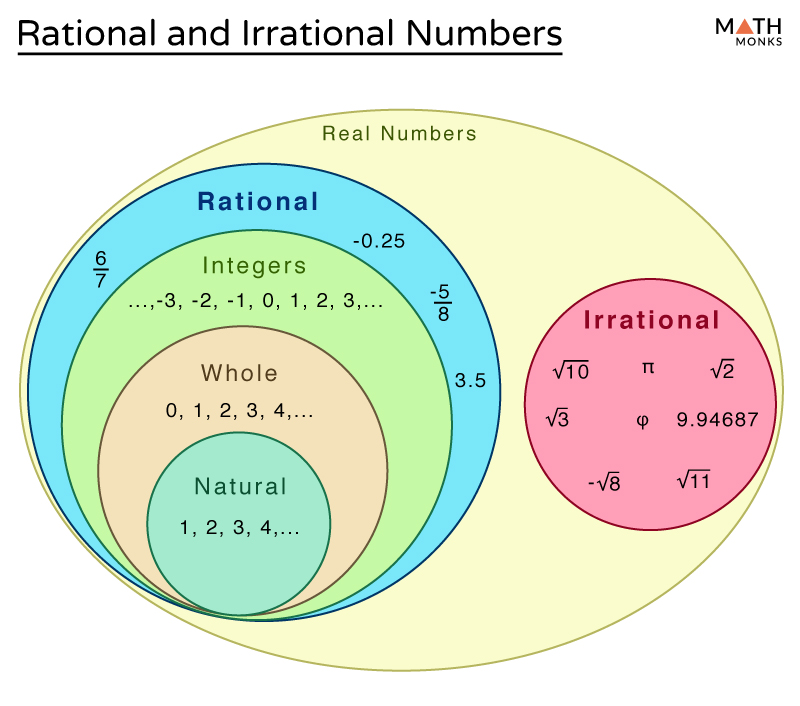
Rational and Irrational Numbers Differences & Examples
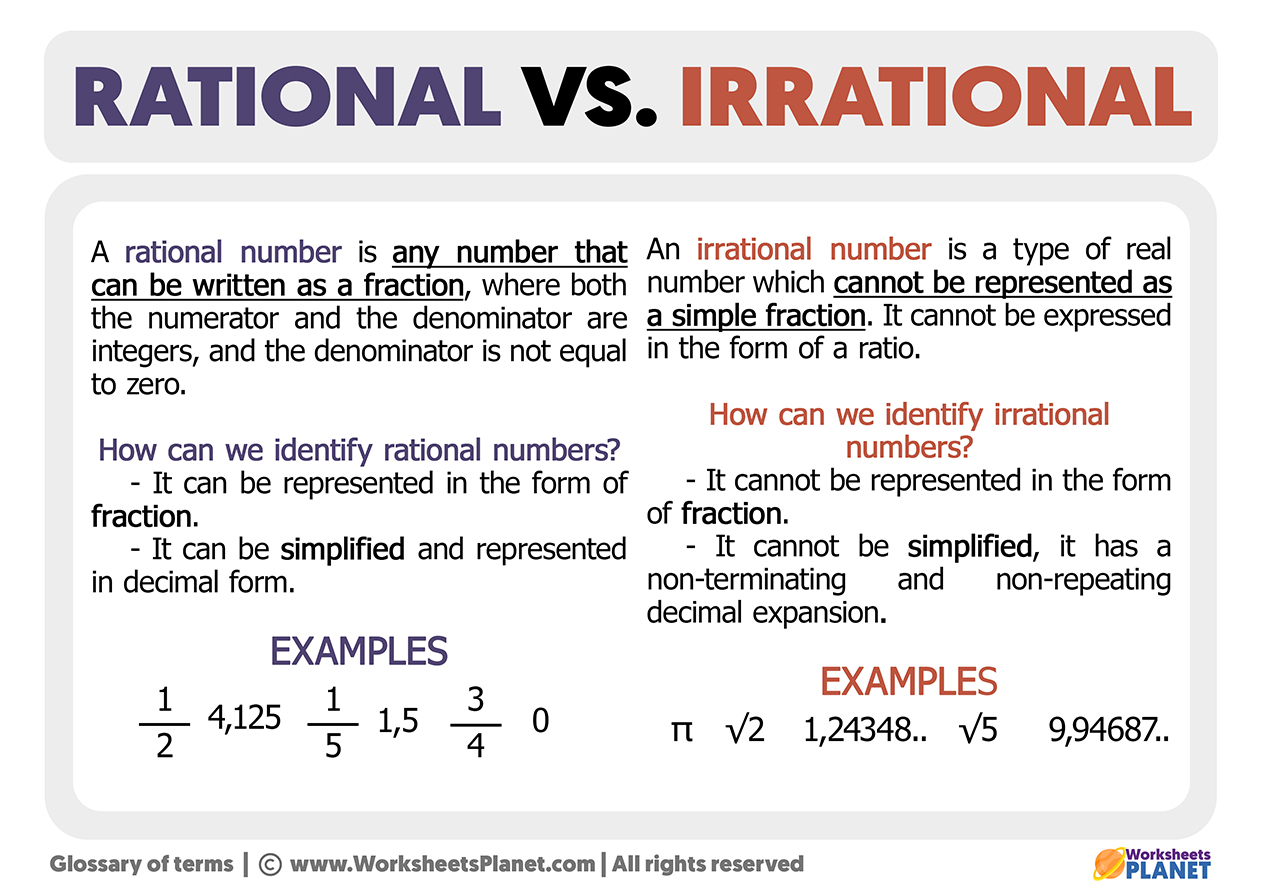
Rational And Irrational Numbers
Rational And Irrational Numbers Examples
Printables Rational vs. Irrational Numbers HP® United Kingdom

Rational Irrational Numbers Chart

Image result for rational or irrational numbers chart
What's the Difference Between Rational and Irrational Numbers? Flipboard
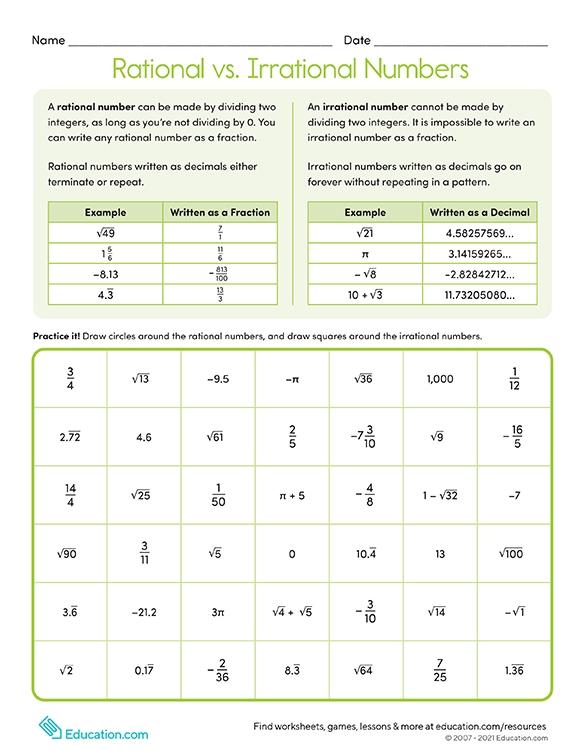
We Cannot Write Irrational Numbers, Such As The Square Root Of 8 And Pi, In This Way.
Rational Numbers Can Be Written As A Ratio That Compares Two Numbers Or Quantities, Giving A Simple Fraction Or Mixed Fraction P/Q.
Explain How The Sets Of Numbers (Counting, Whole, Integer, Rational, Irrationals, Reals) Are Related To Each Other.
There Are Five Subsets Within The Set Of Real Numbers.
Related Post: