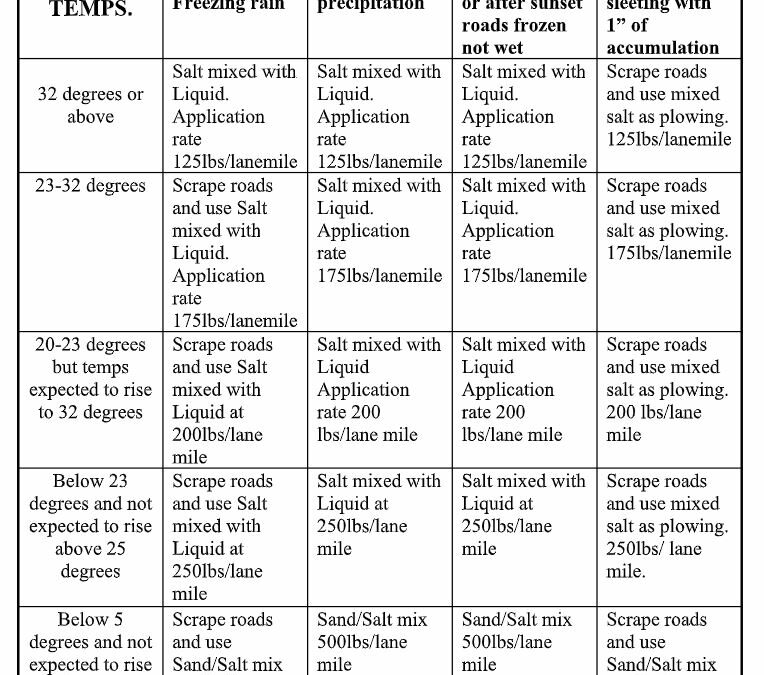
Road Salt Application Rate Chart
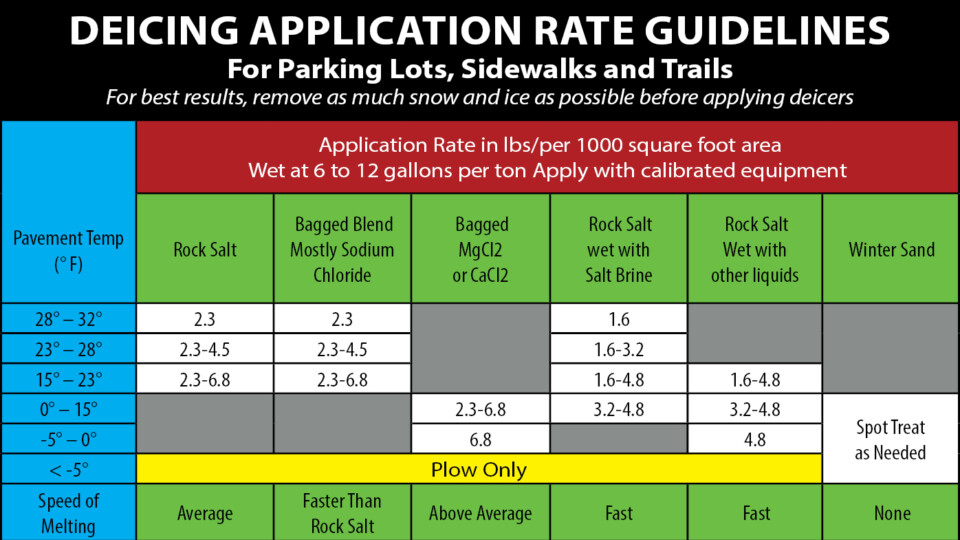
Road Salt Application Rate Chart - Web deicing application rate guidelines. Graph of decadal shift in radium concentration compared in road salt usage rates ( lindsay real others, 2021 ). The colder it gets or the more snow that falls, the more salt is needed. (°f) and trend (↑↓) weather maintenance application rate (lbs/per 1000 sq.ft.) pretreated with salt brine pretreated with other blends dry salt winter sand >30 ↑ snow plow, treat intersections only 4.5 4 Web where temperature categories overlap, select the rate most applicable to your situation. Annual estimates of road salt application were developed for the conterminous united states for the calendar years 1992 through 2015. Web for light snow or ice, 2.3 pounds or more of salt per 1000 square feet at a pavement temperature of 30°f should work (see chart below). It will not melt snow or ice. The salt application rate in either the solid or liquid form. Web the following chart is from minnesota pollution control agency. (°f) and trend (↑↓) weather maintenance application rate (lbs/per 1000 sq.ft.) pretreated with salt brine pretreated with other blends dry salt winter sand >30 ↑ snow plow, treat intersections only 4.5 4 Annual estimates of road salt application were developed for the conterminous united states for the calendar years 1992 through 2015. Benchmarking is also a good way to reduce. Many factors go into this calculation including: Web where temperature categories overlap, select the rate most applicable to your situation. Reacting to a snow and ice event and applying road salts after a bond has formed requires significantly more salt to be used. Web deicing application rate guidelines. Web the wisconsin salt wise partnership developed a winter maintenance application rates. Reacting to a snow and ice event and applying road salts after a bond has formed requires significantly more salt to be used. Graph of decadal shift in radium concentration compared in road salt usage rates ( lindsay real others, 2021 ). Pavement temperature (measured with an ir thermometer) snow/ice remaining on the surface after plowing (measured in inches) anticipated. * dry rock salt is not recommended. (°f) and trend (↑↓) weather maintenance application rate (lbs/per 1000 sq.ft.) pretreated with salt brine pretreated with other blends dry salt winter sand >30 ↑ snow plow, treat intersections only 4.5 4 For liquid applications it is the volume (gallons) of brine applied per lane mile. Adding brine to salt before it is. Pavement temperature (measured with an ir thermometer) snow/ice remaining on the surface after plowing (measured in inches) anticipated future snow fall. **winter sand contains ≤ 5% salt. For an interactive version of this chart visit: Adding brine to salt before it is applied will jump start the melting process and help keep the salt in place by reducing bounce and. It will not melt snow or ice. (°f) and trend (↑↓) weather maintenance application rate (lbs/per 1000 sq.ft.) pretreated with salt brine pretreated with other blends dry salt winter sand >30 ↑ snow plow, treat intersections only 4.5 4 Web treating paved areas with road salts. Benchmarking is also a good way to reduce salt use over time. Web getting. For example, roadway managers can log application rates per degrees below 32°f or inch of snow and set reduction goals each year (mpca, 2020). **winter sand contains ≤ 5% salt. To determine the optimal application rates review these variables: Determining how much salt you need for a parking lot, road, or any other area can be confusing. For solid applications. Web treating paved areas with road salts. For liquid applications it is the volume (gallons) of brine applied per lane mile. Web for light snow or ice, 2.3 pounds or more of salt per 1000 square feet at a pavement temperature of 30°f should work (see chart below). Develop your own application rates using the guidelines as a starting point. * dry rock salt is not recommended. For solid applications it is simply the weight of the salt applied per lane mile. Pavement temperature (measured with an ir thermometer) snow/ice remaining on the surface after plowing (measured in inches) anticipated future snow fall. The colder it gets or the more snow that falls, the more salt is needed. 2.0, august. Web you can save up to the following percentages of salt (compared to a standard deicing strategy) by using the following practices. Direct liquid application (dla) has been shown to be effective at clearing snow and ice while using less salt than granular salt application. The salt application rate in either the solid or liquid form. Web the wisconsin salt. For example, roadway managers can log application rates per degrees below 32°f or inch of snow and set reduction goals each year (mpca, 2020). Direct liquid application (dla) has been shown to be effective at clearing snow and ice while using less salt than granular salt application. (°f) and trend (↑↓) weather maintenance application rate (lbs/per 1000 sq.ft.) pretreated with salt brine pretreated with other blends dry salt winter sand >30 ↑ snow plow, treat intersections only 4.5 4 For solid applications it is simply the weight of the salt applied per lane mile. Annual estimates of road salt application were developed for the conterminous united states for the calendar years 1992 through 2015. Overtime pay and the increased cost of fuel caused by the oil embargo prompted a change in the bare pavement policy in 1973. How much snow, surface material, and rate of application. Web deicing application rate guidelines. Reacting to a snow and ice event and applying road salts after a bond has formed requires significantly more salt to be used. Web application rates should correspond with vehicles speed. Adding brine to salt before it is applied will jump start the melting process and help keep the salt in place by reducing bounce and scatter. For subsequent passes use 1⁄2 rate to the full initial rate. Pavement temperature (measured with an ir thermometer) snow/ice remaining on the surface after plowing (measured in inches) anticipated future snow fall. It will not melt snow or ice. Develop your own application rates using the guidelines as a starting point and modify them incrementally over time Benchmarking is also a good way to reduce salt use over time.
Adjustment Factor for Salt Application Rates for Parking Lots 9
Salt Conversion Chart Morton Salt, 45 OFF

Application Rates Salt Smart Collaborative
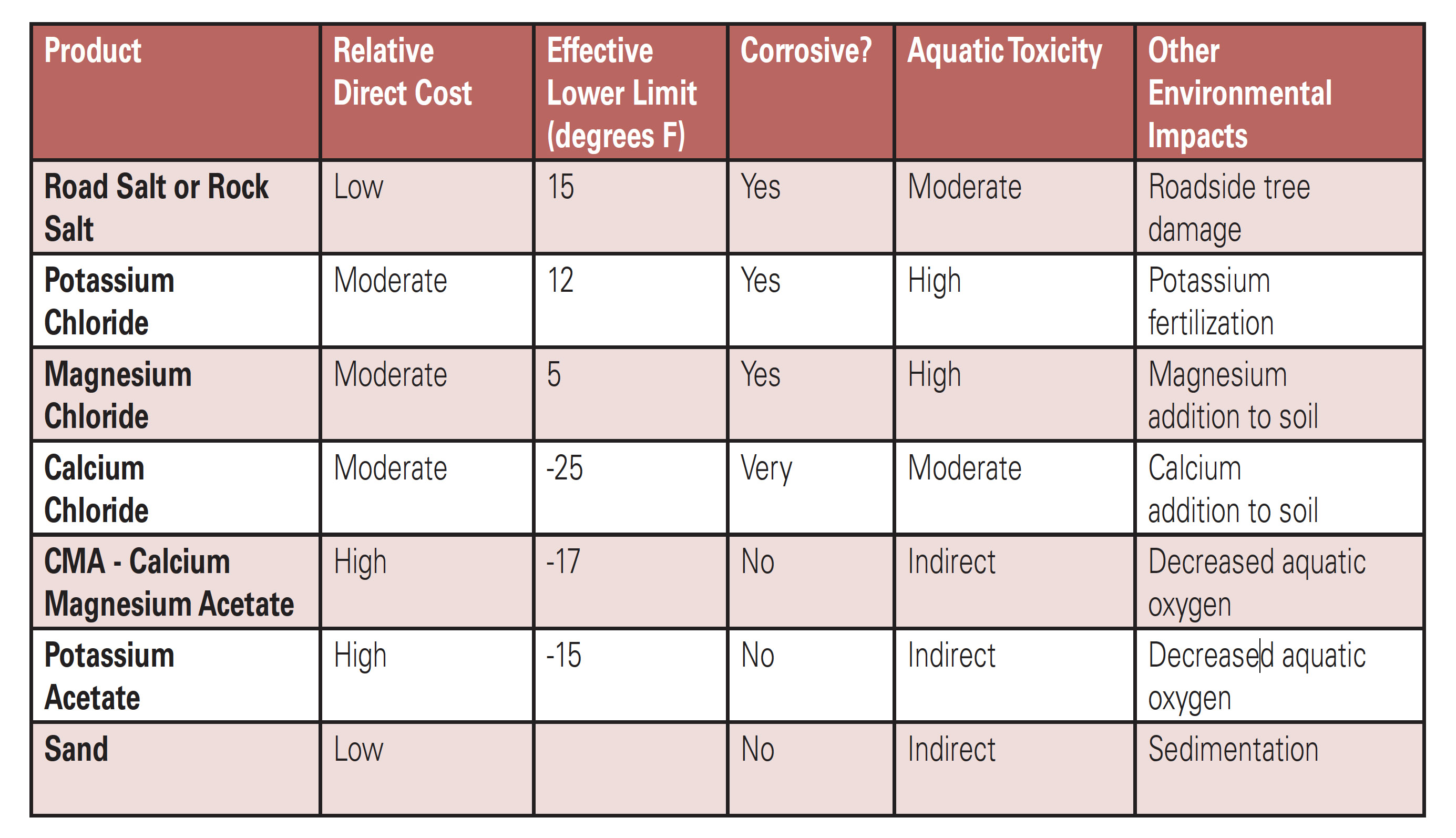
Eco Friendly Alternatives to Road Salt
Salt Application Basics to Help You Vanquish Snow & Ice The Rop Shop

Annual road salt application in the United States (data from Salt

Road salt application rates for the Hauver Branch and Hunting Creek

Resources for Public Road Agencies Salt Smart Collaborative

Road Salt NJ Watershed Watch Network

Best Application Rates For Rock Salt
Web Nh Road Salt Application Rates For Deicing Parking Lots (Pounds Per 1000 Sq.ft.) Pavement Temp.
Web Treating Paved Areas With Road Salts.
For An Interactive Version Of This Chart Visit:
Graph Of Decadal Shift In Radium Concentration Compared In Road Salt Usage Rates ( Lindsay Real Others, 2021 ).
Related Post: