Sacral Torsion Chart
Sacral Torsion Chart - With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. Web learn about the anatomy, biomechanics, and clinical implications of pelvic and sacral osteopathy with amboss, a comprehensive medical knowledge platform for doctors and students. A frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named sacral torsion about an oblique axis, which is also known as sacral torsion, or simply as torsion. Web sacral motion within the si joint can produce several dysfunctions: The test is also known as: The left sacral base palpates and visualizes as posterior. Web torsions are typically classified as: Flex the knees until motion is felt. Don't even ask me what that means), and in a left posterior torsion (called left on right); Web sacral torsions encompass anterior (l on l / r on r) or posterior (l on r / r on l) torsion dysfunctions of the sacrum. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. In relation to the skull have their own mobility. Patient is in the sims position. In the most common torsion, the left lower sacral quadrant is prominent. This technique involves the patient actively contracting and relaxing specific muscles attached to the sacrum to improve the range of motion and reduce pain. Torsions do meet the above definition of sijd, and are the focus of this chapter. A frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named sacral torsion about an oblique axis, which is also known as sacral torsion, or simply as torsion. Web sacral rocking (articulation) is one type of osteopathic technique that can be used to correct sacral dysfunctions. Web sacral. The test is also known as: With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. Clinically, this disruption presents with a mobility limitation relative to baseline and sharp pain inferolateral to the posterior superior iliac spine. Web in the most common torsion, the left lower sacral quadrant is prominent. Identify common. Web how to identify and treat sacral torsion, sacral shear, and related mechanical chronic low back pain and buttock pain. Have patient hug the table until motion felt, if needed utilize respiratory assist to fully engage barrier. With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. One single positive test does. Patient is in the sims position. Right on right (left sacral base moving anterior around the right axis of rotation); In relation to the skull have their own mobility. A frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named sacral torsion about an oblique axis, which is also known as sacral torsion, or simply as torsion. Left on right (left sacral base. This technique involves the patient actively contracting and relaxing specific muscles attached to the sacrum to improve the range of motion and reduce pain. Web sacral motion within the si joint can produce several dysfunctions: Flex the knees until motion is felt. Sacroiliac joint pain and sacroiliac joint mimics create a broad differential, adding difficulty to diagnosis. The left sacral. After years of study, research, and manipulation, he concluded that the cranial bones, sacrum. This technique involves the patient actively contracting and relaxing specific muscles attached to the sacrum to improve the range of motion and reduce pain. This activity outlines sacral rocking and explains the role of the interprofessional team in patients who undergo sacral rocking. Web sacrum muscle. In the most common torsion, the left lower sacral quadrant is prominent. The test is also known as: Web sacral rocking (articulation) is one type of osteopathic technique that can be used to correct sacral dysfunctions. A frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named sacral torsion about an oblique axis, which is also known as sacral torsion, or simply as. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid evidence for sacroiliac dysfunction. The craniosacral technique was established by dr. This activity outlines sacral rocking and explains the role of the interprofessional team in patients who undergo sacral rocking. Web a frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named. Anterior torsion, posterior torsion, and unilateral flexion or extension dysfunctions. Identify common symptoms of sacral somatic dysfunctions. Clinically, this disruption presents with a mobility limitation relative to baseline and sharp pain inferolateral to the posterior superior iliac spine. In relation to the skull have their own mobility. Web the sacral thrust test is a pain provocation test used to diagnose. With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. Clinically, this disruption presents with a mobility limitation relative to baseline and sharp pain inferolateral to the posterior superior iliac spine. This technique involves the patient actively contracting and relaxing specific muscles attached to the sacrum to improve the range of motion and reduce pain. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid evidence for sacroiliac dysfunction. The left sacral base palpates and visualizes as posterior. Continuously monitor lumbosacral junction as patient is moved into sims position. A physiologic function occurring in the sacrum during ambulation and forward bending. Web in both cases, both in a left anterior torsion (called left on left; This article will discuss how to diagnose such sacral dysfunctions and describe muscle energy techniques used to correct such dysfunctions. Web sacrum muscle energy treatment (met) is a technique used in manual therapy to improve mobility in the sacrum. Web this usually indicates l5 is anterior to s1. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. Web how to identify and treat sacral torsion, sacral shear, and related mechanical chronic low back pain and buttock pain. The left ila is more prominent in both of these lesions. Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of somatic dysfunction (torsions, unilateral shears or. In the most common torsion, the left lower sacral quadrant is prominent.
sacral torsion lesions Diagram Quizlet

Sacral Torsion L5 diagnosis YouTube
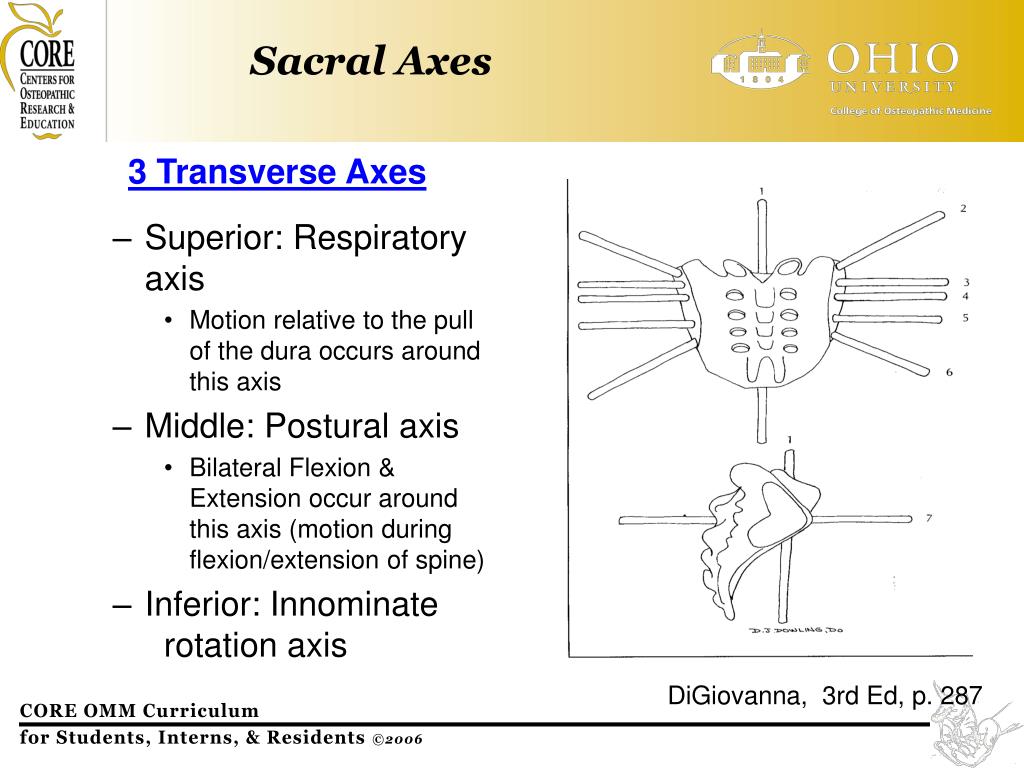
PPT CORE OMM Curriculum Board Review PowerPoint Presentation, free

Sacral Torsion Diagnosis YouTube
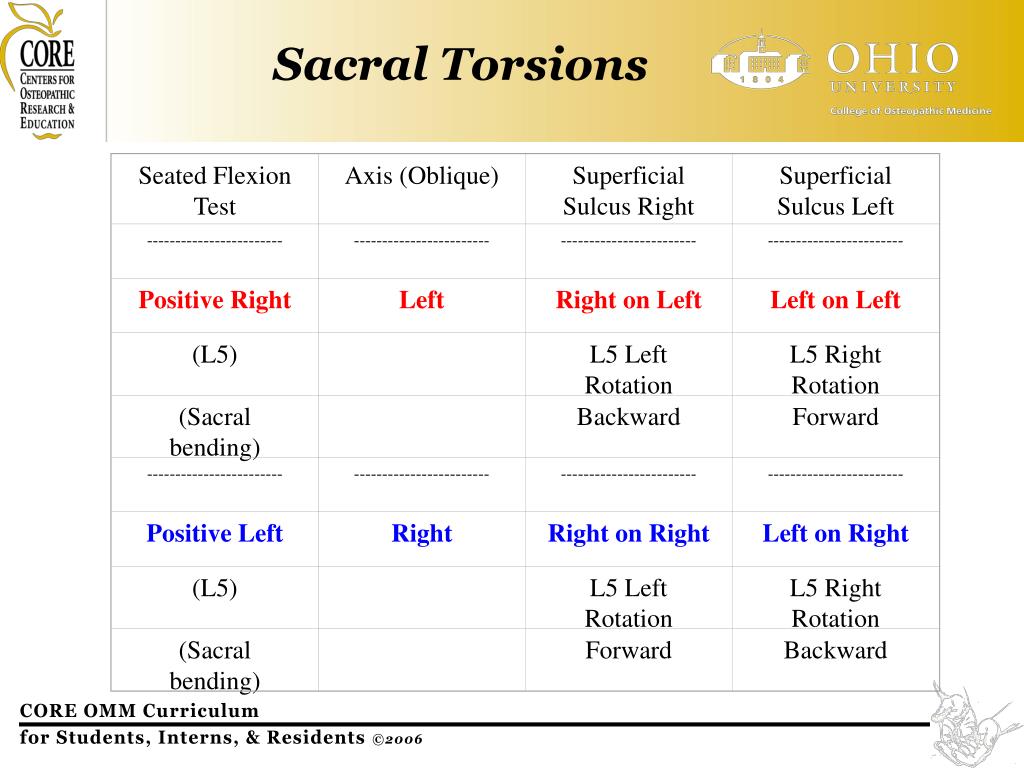
PPT CORE OMM Curriculum Board Review PowerPoint Presentation, free

Sacral Torsion Chart

torsions sacrum Anatomie médicale, Anatomie du corps, Etude medecine

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Sacral Diagnosis Chart

Sacral Torsion What Is It, Causes, Treatment, and More Osmosis
Web A Frequently Reported Sacral Movement Dysfunction Is Named Sacral Torsion About An Oblique Axis, Which Is Also Known As Sacral Torsion, Or Simply As Torsion.
Sacroiliac Joint Pain And Sacroiliac Joint Mimics Create A Broad Differential, Adding Difficulty To Diagnosis.
The Craniosacral Technique Was Established By Dr.
Right On Left ( Right Sacral Base Moving Posterior Around The Left Axis Of Rotation);
Related Post: