Sediment Size Chart
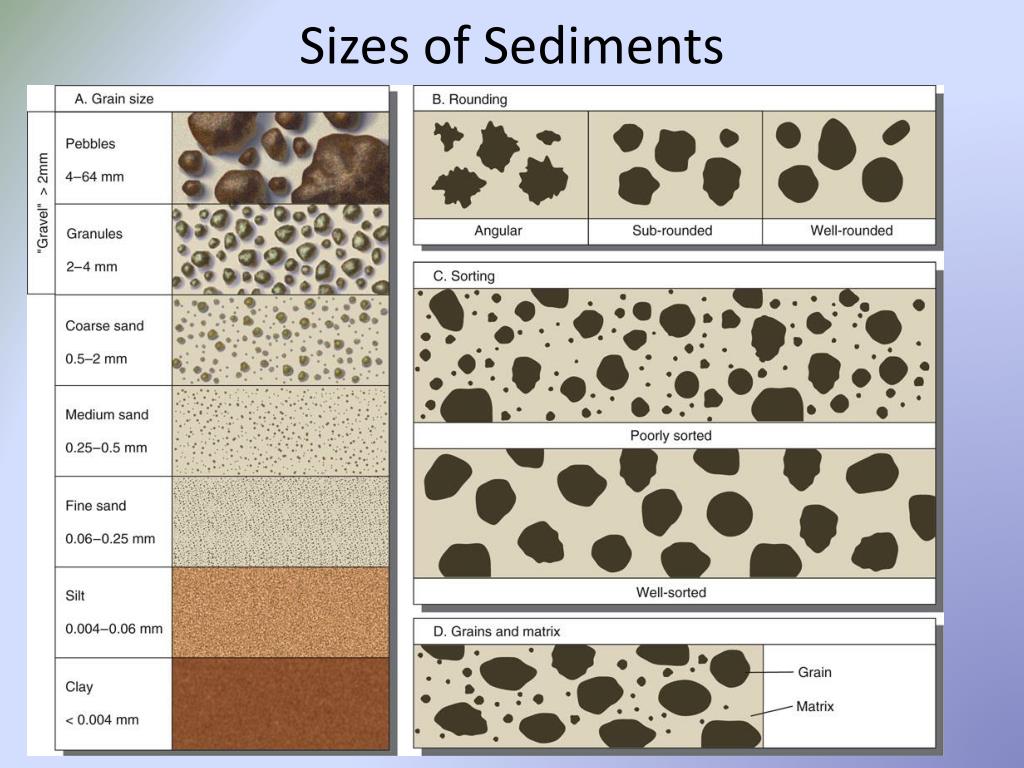
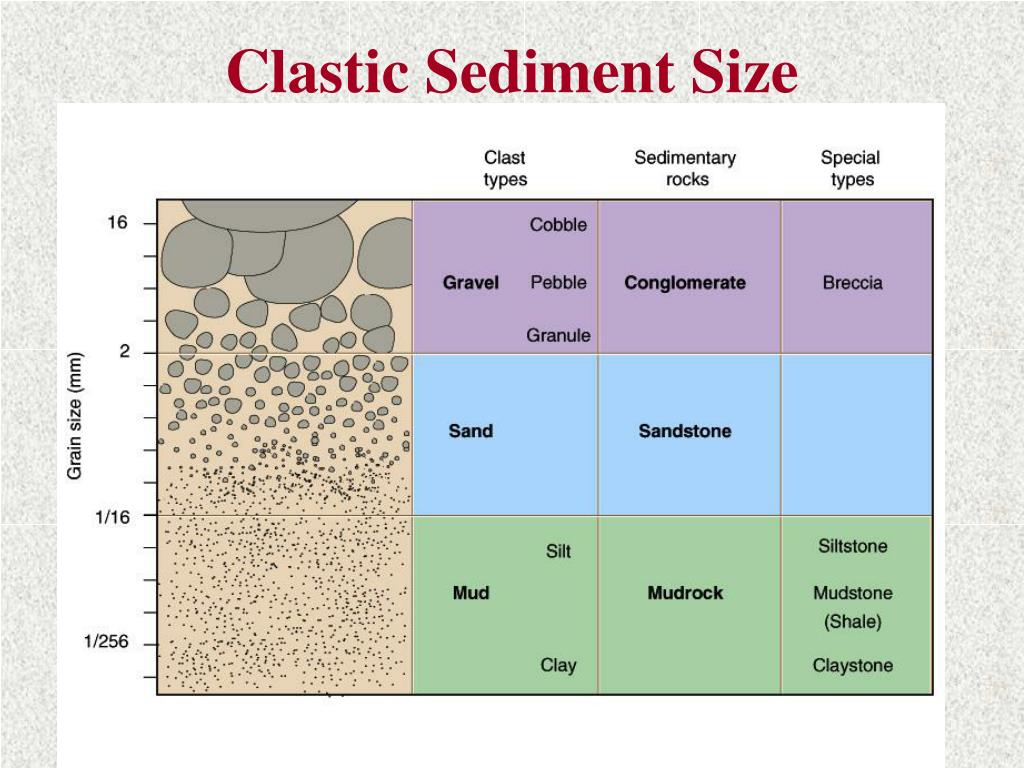
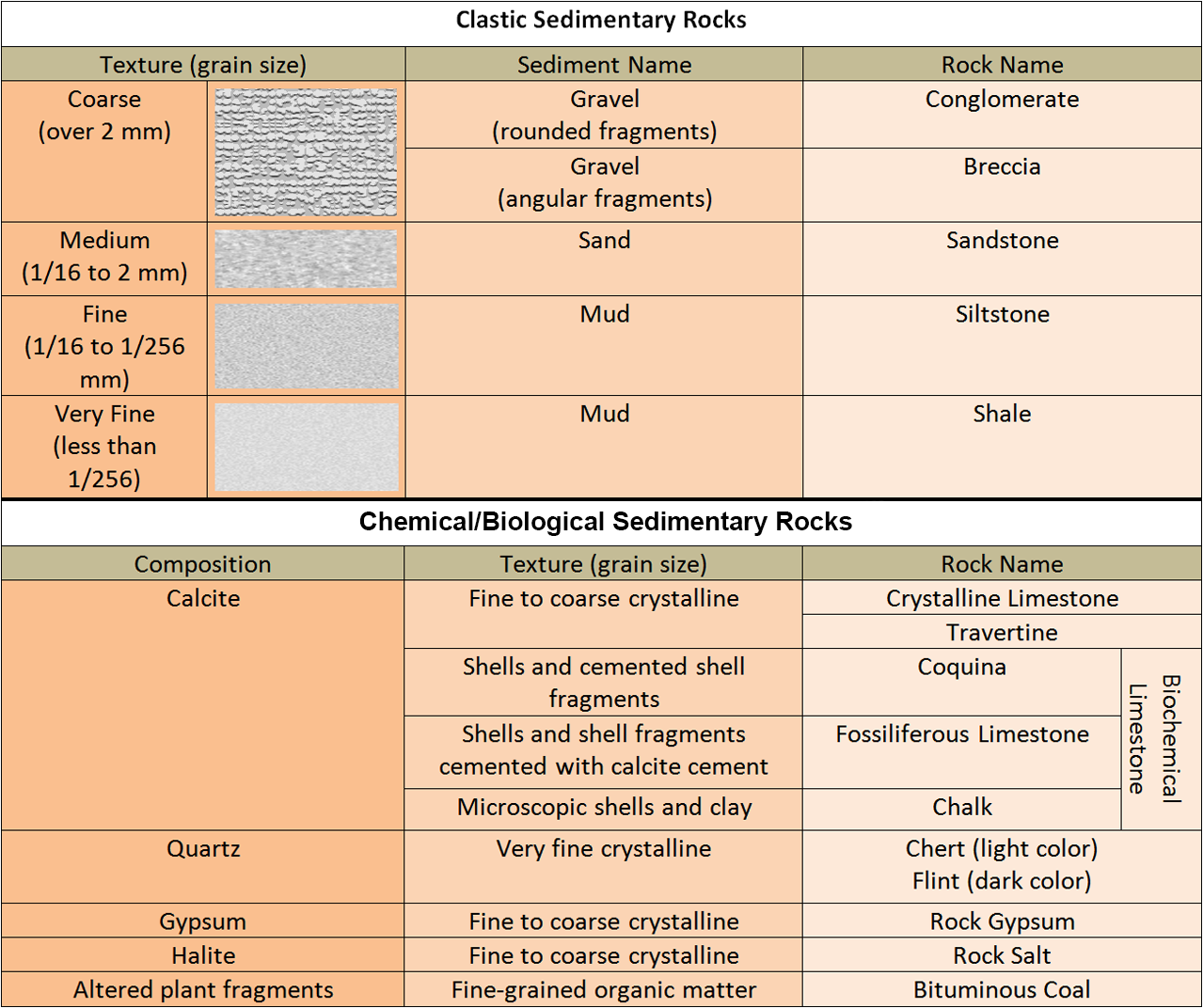
Sediment Size Chart - Sediment texture can be examined through several variables. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. © university of hawai‘i, 2015. Mm, which can be expressed as 2 0, 2 −1, 2 −2, 2 −3. Two important parameters for sediment transport are the median particle diameter d50 d 50 and the grading, for example, d90/d10 d 90 / d 10. If you are a beginner geologist, or using these in a ks2 classroom, we would recommend starting with the ‘bite size’ card. Figure 6.39 shows the technical definition of sediment particles. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of. Among other things, grain size represents the conditions under which the sediment was deposited. The first is grain size. They key thing to remember about this is that the bigger the phi. A visual reference for descriptions of sorting (top) and roundness (bottom) of sediments and grains in clastic sedimentary rocks. This is different from the crystallite size, which is the size of a single crystal inside the particles or grains. Quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments. Sediments are solid. Figure 6.39 shows the technical definition of sediment particles. Discuss how composition and/or grain size is used to classify sedimentary rocks and provide examples. Exploring our fluid earth, a product of the curriculum research & development group (crdg), college of education. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. And here's a couple of classification schemes for sediment. The first is grain size. Figure 6.39 shows the technical definition of sediment particles. Sediments are solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of rock and soil erosion, and are carried and deposited by wind, water, or ice. Quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments. Grain size is the average diameter of clasts (particles) of clastic sediments. The scale was developed specifically as a statistical device to permit the direct application of conventional statistical practices to sedimentary data. Two important parameters for sediment transport are the median particle diameter d50 d 50 and the grading, for example, d90/d10 d 90 / d 10. A visual reference for descriptions of sorting (top) and roundness (bottom) of sediments and. Grain size, density and bulk properties. Where n = phi (φ) value. And here's a couple of classification schemes for sediment using these terms: Web sediments are classified by particle size, ranging from the finest clays (diameter <0.004 mm) to the largest boulders (> 256 mm) (figure 12.1.2). © university of hawai‘i, 2015. The size limits for each grade vary from scale to scale. Web sediments classification based on grain size. Mm, which can be expressed as 2 0, 2 −1, 2 −2, 2 −3. The scale was developed specifically as a statistical device to permit the direct application of conventional statistical practices to sedimentary data. Two important parameters for sediment transport are. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Dx d x is defined as the sediment particle diameter (in metres) for which x x % by weight is finer. To avoid negative values of the derivative (phi), a minus sign was. Web sediments are classified by particle size, ranging from the finest clays (diameter <0.004 mm) to the. Figure 6.39 shows the technical definition of sediment particles. Sediments are solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of rock and soil erosion, and are carried and deposited by wind, water, or ice. Use these grain size cards in your observations of sedimentary rocks. Web on most scales, the finest particles are designated clay, followed. Grain size, density and bulk properties. Grain size is the average diameter of clasts (particles) of clastic sediments and rocks. And here's a couple of classification schemes for sediment using these terms: They range in size from large blocks to microscopic particles. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean sediments, and some of the most common distinctions are based on the sediment texture, the sediment composition, and the sediment’s origin. Sediments are solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of rock and soil erosion, and are carried and deposited by wind, water,. They range in size from large blocks to microscopic particles. This is different from the crystallite size, which is the size of a single crystal inside the particles or grains. They key thing to remember about this is that the bigger the phi. Web particle size (grain size) chart. The first is grain size. Figure 6.39 shows the technical definition of sediment particles. Web the graphical display and statistical analysis of sediment grain size became a popular pursuit of sedimentologists in the 1950s and 60s, particularly those who studied modern sediments. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean sediments, and some of the most common distinctions are based on the sediment texture, the sediment composition, and the sediment’s origin. Web wentworth (1922) grain size classification detailed chart the canonical definition of sediment grain sizes as defined by geologist chester k. If you are a beginner geologist, or using these in a ks2 classroom, we would recommend starting with the ‘bite size’ card. Convert between millimeters and phi units. Describe grains using sorting and rounding terminology. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to conglomerate, and soil depending on their grain size. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Sediment texture can be examined through several variables. Web phi size values for the sediment class limits range from −5 phi (for a diameter of 32 mm, or very coarse pebble size) down to +10 phi (for a diameter of 1/1,024 mm, or clay size).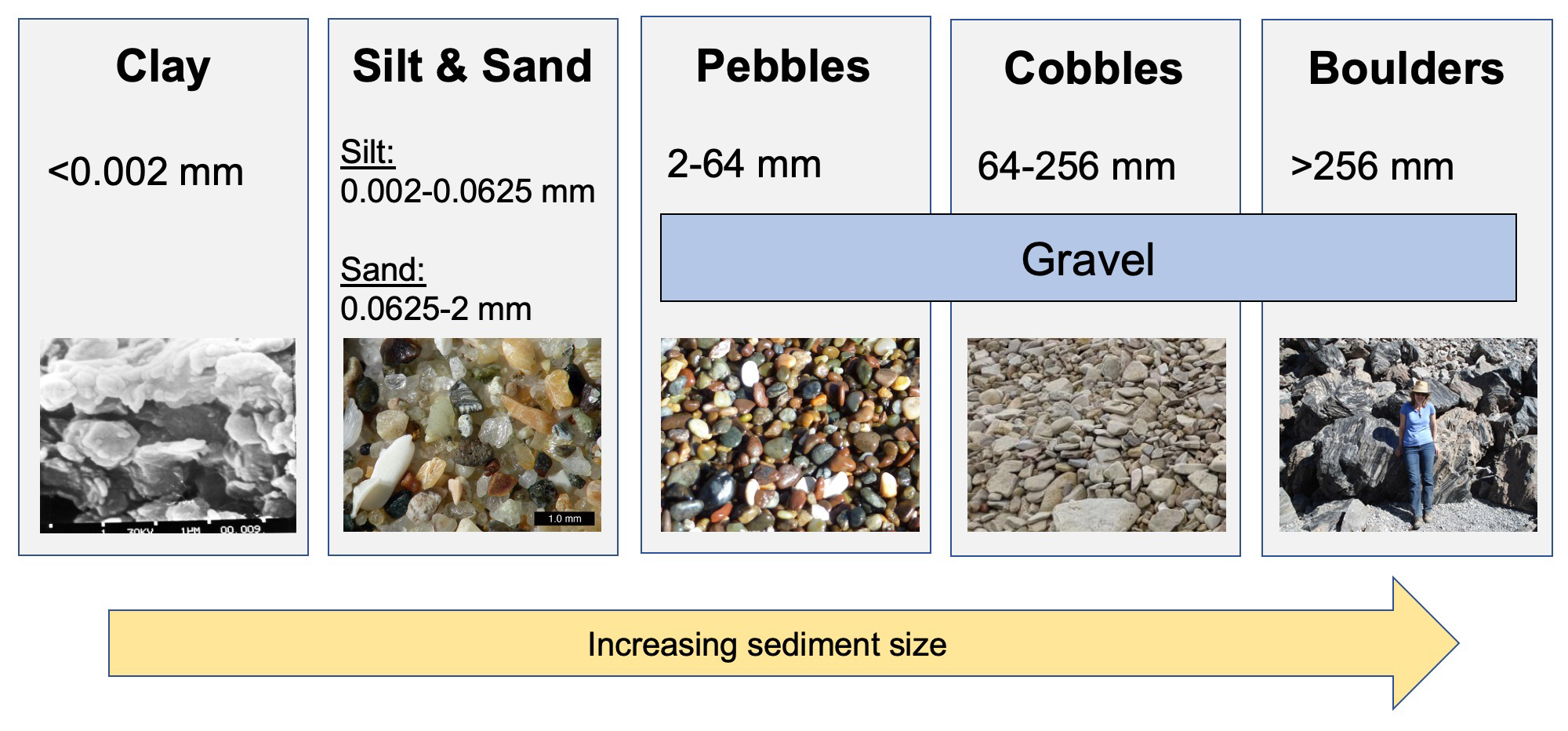
Sediment Grain Size Chart

Sedimentary rock Grain Size, Stratification, Deposition Britannica
PPT Sedimentary Rocks PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2247029
PPT Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks PowerPoint Presentation, free

1 Sediment size classification. Download Table

Comparison of grain sizes to soils and loess sediment classification

Sediment grainsize scale Download Table

Sediment size scales and classes Download Table

Sediment Grain Size Chart
Types of sedimentary rocks The Society
Web Wentworth (1922) Grain Size Classification Detailed Chart The Canonical Definition Of Sediment Grain Sizes As Defined By Geologist Chester K.
Web Grain Size (Or Particle Size) Is The Diameter Of Individual Grains Of Sediment, Or The Lithified Particles In Clastic Rocks.
Discuss How Composition And/Or Grain Size Is Used To Classify Sedimentary Rocks And Provide Examples.
Web Sediments Classification Based On Grain Size.
Related Post: