Sedimentary Rock Identification Chart
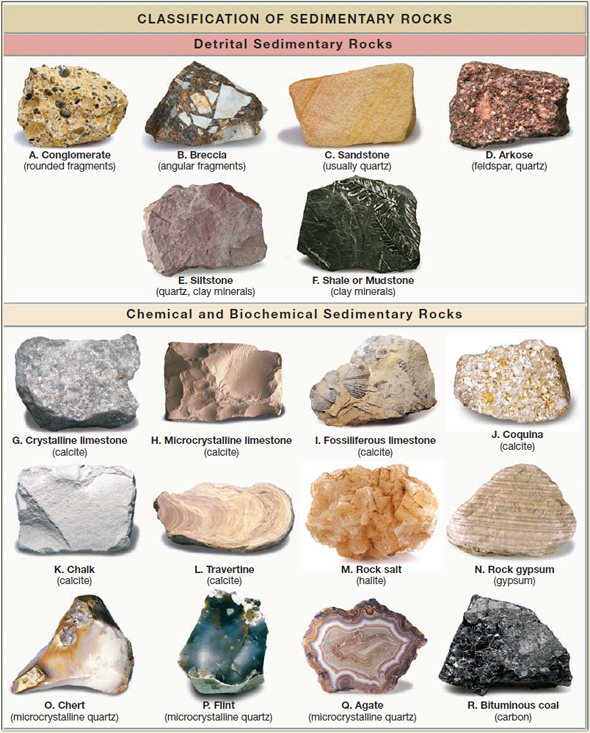
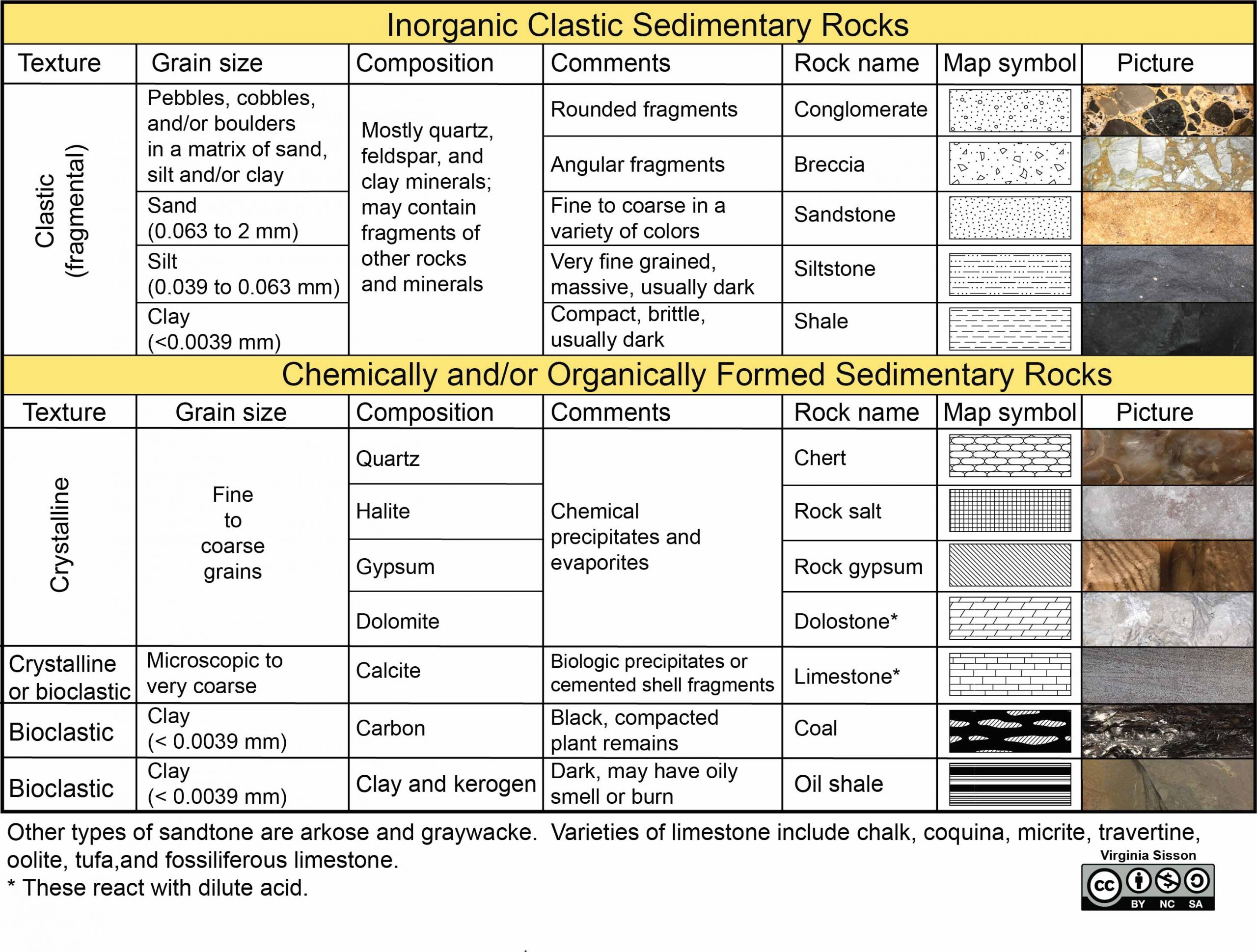
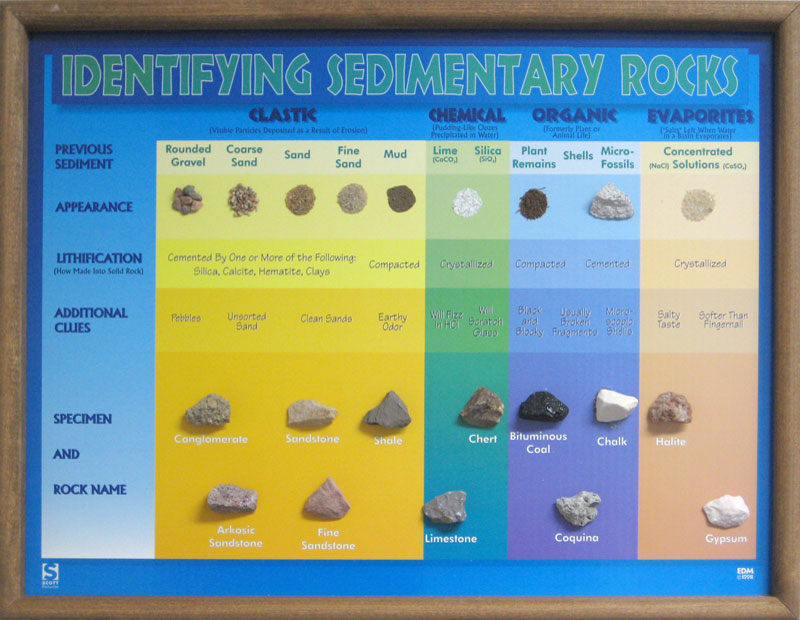
Sedimentary Rock Identification Chart - Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. They are the mountains and the bottom of the ocean. Print a sedimentary identification flow chart or sedimentary rock dichotomous key to use with mini me geology sedimentary rock kits. If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. Web the size, shape, and composition of the clasts varies widely based upon the source rock and the length of time the sediment has been moving through the system. Photos and facts about clastic, chemical and organic sedimentary rocks. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. These include igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic types. Chalk is soft, friable, porous, and effervesces vigorously in contact with hydrochloric acid. Web key properties include: Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. Web you are a true mini me geologist! Photos and facts about clastic, chemical and organic sedimentary rocks. Sediment is deposited in a number of environments of deposition, by both moving air and moving water. Web photos and brief descriptions of some common sedimentary rock types are shown. Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. Chalk is a type of limestone made up of the microscopic calcium carbonate shells of marine organisms. If it is organic or chemical, determine the rock’s composition and look for unique characteristics to arrive at an identification. Web here's how to identify 44 of the most common igneous,. The classification of sedimentary rocks is largely based on differentiating the processes that lead to their formation. The clastic sedimentary rocks are identified and named. These include igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic types. The most important geological processes that lead to the creation of sedimentary rocks are erosion, weathering, dissolution, precipitation, and lithification. Web sedimentary rocks form by the accumulation and. Sedimentary rocks are rocks composed of sediment. If it is organic or chemical, determine the rock’s composition and look for unique characteristics to arrive at an identification. Web it’s a practical, logical and robust system for classifying and naming geological materials as they appear at the scale of a single exposure, hand specimen or thin section. Grain size is the. They are the mountains and the bottom of the ocean. Sedimentary rock identification is primarily based on composition. Sediment is deposited in a number of environments of deposition, by both moving air and moving water. A visual reference for descriptions of sorting (top) and roundness (bottom) of sediments and grains in clastic sedimentary rocks. Print a sedimentary identification flow chart. Most sedimentary rocks exhibit visible layers or beds, a result of different periods or conditions of sediment deposition. Sedimentary rocks are rocks composed of sediment. The clastic sedimentary rocks are identified and named. The classification and description of the various clastic sedimentary rock types appears in the top section of the chart below. Web sedimentary rocks form by the accumulation. Web you are a true mini me geologist! Web earth science lab. A visual reference for descriptions of sorting (top) and roundness (bottom) of sediments and grains in clastic sedimentary rocks. Web it’s a practical, logical and robust system for classifying and naming geological materials as they appear at the scale of a single exposure, hand specimen or thin section.. Sediment is deposited in a number of environments of deposition, by both moving air and moving water. Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. Grain size is the average diameter of sediment fragments in sediment or rock. Web to identify a sedimentary rock, first determine if it is clastic, organic, or chemical. Web here's how. Print a sedimentary identification flow chart or sedimentary rock dichotomous key to use with mini me geology sedimentary rock kits. Most sedimentary rocks exhibit visible layers or beds, a result of different periods or conditions of sediment deposition. Web basalt, diabase, diorite, gabbro, granite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria. Web the size, shape, and composition of the clasts varies widely based. Web sedimentary rocks form by the accumulation and cementation of mineral or organic particles on the earth’s surface, often in water bodies. Web key properties include: Finally, compare the properties of your rock to those of known rock types while looking for other identifying characteristics. Web rock sediments magma metamorphic rock sedimentary rock 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1.0 10.0 100.0. Rocks are what the crust of the earth is made of. The resulting particles settle out of water or air (clastic rocks such as sandstone and mudstone) or the resulting chemicals precipitate from concentrated solutions (non‑clastic rocks such as limestone and salt). Web key properties include: The classification and description of the various clastic sedimentary rock types appears in the top section of the chart below. The first step to identify a rock is to try to categorize the rock into one of the three main types or groups of rocks. Web it’s a practical, logical and robust system for classifying and naming geological materials as they appear at the scale of a single exposure, hand specimen or thin section. Sedimentary rocks are formed on or near the earth’s surface, in contrast to metamorphic and igneous rocks, which are formed deep within the earth. A rock, three things must be considered: These rocks usually have layers that hold important clues to earth’s history. Gneiss, marble, quartzite, schist, serpentinite, slate. If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. Sediment is deposited in a number of environments of deposition, by both moving air and moving water. Classification helps to place materials in a wider geological context, and allows unambiguous and informative formal names to be assigned. Sedimentary rocks are rocks composed of sediment. Web detrital rock is classified according to sediment grain size, which is graded from large to small on the wentworth scale (see figure). Web earth science lab.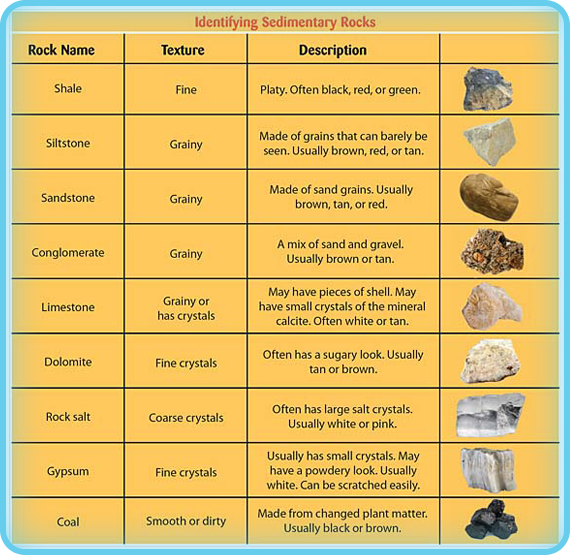
Rocks and minerals images
Solved Carefully examine the common sedimentary rocks shown in

Image result for chart Classification of chemical sedimentary rocks
Chapter 2 Earth Materials The Story of Earth An Observational Guide
Sedimentary Rock Identification Chart

Rocks And Minerals Chart Identification

Sedimentary Rock Identification Chartgoing in nature journal great

Overview of Sedimentary Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science

Sedimentary Rock Types Chart

Rock Collection And ID Chart 18 Rocks Igneous, Metamorphic, Sedimentary
Web Sedimentary Rocks Are Derived From Pre‑Existing Rocks By Weathering And Erosion.
Web To Identify Your Rock, First Take Note Of Its Physical Properties Like Color, Luster, Banding, Layering, And Grain Size.
Finally, Compare The Properties Of Your Rock To Those Of Known Rock Types While Looking For Other Identifying Characteristics.
Web Sedimentary Rocks Form By The Accumulation And Cementation Of Mineral Or Organic Particles On The Earth’s Surface, Often In Water Bodies.
Related Post: