Smith Chart With Admittance
Smith Chart With Admittance - In our case, \[y_{0} = \frac{1}{z_{0}} = \frac{1}{50} = 0.02\] Web this free online interactive smith chart tool is a calculator which can help you design matching networks and obtain maximum power transfer between your source and load. 2/17/2010 example admittance calculations with the smith chart 3/9 jim stiles the univ. Web impedance smith charts also known as z charts are the polar graphs that show the normalized line impedance in the complex reflection coefficient plane. Move the mouse around the chart. In the next section, we will learn to use impedance/admittance (z/y) smith chart, where both impedance and admittance circles are shown. That is, we are looking at the impedance of an antenna, or load (z_l). The admittance smith chart has loci for discrete constant susceptances ranging from \(−∞\) to \(∞\), and for discrete constant conductance ranging from \(0\) to \(∞\), see figure \(\pageindex{7}\). It uses a bilinear moebius transformation, projecting the complex impedance plane onto the complex γ plane: Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. This video describes how to. You can toggle between impedance and admittance charts. In the next section, we will learn to use impedance/admittance (z/y) smith chart, where both impedance and admittance circles are shown. Move the mouse around the chart. Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. For example, the impedance z = 0.5 + j2 is marked as point a in the above figure. Recall that on the standard or impedance smith chart, the circles and curves related to constant resistance and constant reactance. Move the mouse around the chart. 9.1k views 3 years ago emp microwave engineering. We can calculate this complex value—or we can. A less dense form is shown in figure \(\pageindex{8}\)(a). 9.1k views 3 years ago emp microwave engineering. Impedances, admittances, reflection coefficients, scattering parameters, noise figure circles, constant gain contours and regions for unconditional stability, and mechanical vibrations analysis, all at the same time. Enter load and characteristic impedances to calculate vswr and reflection coeffecients. The admittance smith chart has loci. Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. Web impedance smith charts also known as z charts are the polar graphs that show the normalized line impedance in the complex reflection coefficient plane. A less dense form is shown in figure \(\pageindex{10}\)(a). It is made of circles that represent different values. Web the smith chart can be used to simultaneously display multiple parameters. That is, we are looking at the impedance of an antenna, or load (z_l). A horizontal line through the center of the. Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. This tool is javascript so it works on windows, mac, ios,. Web the smith chart provides a graphical representation of γ that permits the determination of quantities such as the vswr or the. Move the mouse around the chart. Web the smith chart is made up of multiple circles, and segments of circles arranged in a way to plot impedance values in the form of r ± jx (fig. Instead of considering its impedance directly, you express its reflection coefficient γ l , which is used to characterize a load (such as admittance,. That is, we are looking at the impedance of an antenna, or load (z_l). 2/17/2010 example admittance calculations with the smith chart 3/9 jim stiles the univ. In the next section, we will learn to use impedance/admittance (z/y) smith chart, where both impedance and admittance circles are shown. The admittance smith chart has loci for discrete constant susceptances ranging from. In our case, \[y_{0} = \frac{1}{z_{0}} = \frac{1}{50} = 0.02\] 2/17/2010 example admittance calculations with the smith chart 3/9 jim stiles the univ. Web we can use this smith chart to read off the values for the impedance, and reflection coefficient. These graphs are used for visualizing the impedance at any point on the transmission line or any input in. Move the mouse around the chart. Web the moebius transform that generates the smith chart provides also a mapping of the complex admittance plane (y = 1 z or normalized y = 1 z) into the same chart: Web the smith chart can be used to simultaneously display multiple parameters including impedances, admittances, reflection coefficients, scattering parameters, noise figure circles,. Web this free online interactive smith chart tool is a calculator which can help you design matching networks and obtain maximum power transfer between your source and load. Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. Web smith chart can be used to display several parameters including; Enter load and characteristic impedances to calculate vswr and reflection coeffecients. It is made of circles. Web a smith chart is developed by examining the load where the impedance must be matched. Click anwhere inside the chart to see the corresponding circles. Web the moebius transform that generates the smith chart provides also a mapping of the complex admittance plane (y = 1 z or normalized y = 1 z) into the same chart: Impedances, admittances, reflection coefficients, scattering parameters, noise figure circles, constant gain contours and regions for unconditional stability, and mechanical vibrations analysis, all at the same time. Web smith chart can be used to display several parameters including; Web 8.3.2 admittance smith chart. First, we express the load z.j. The admittance smith chart has loci for discrete constant susceptances ranging from \(−∞\) to \(∞\), and for discrete constant conductance ranging from \(0\) to \(∞\), see figure \(\pageindex{9}\). A less dense form is shown in figure \(\pageindex{8}\)(a). For example, the impedance z = 0.5 + j2 is marked as point a in the above figure. Instead of considering its impedance directly, you express its reflection coefficient γ l , which is used to characterize a load (such as admittance, gain, and transconductance). Web the smith chart can be used to simultaneously display multiple parameters including impedances, admittances, reflection coefficients, scattering parameters, noise figure circles, constant gain contours and regions for unconditional stability. Web the smith chart is made up of multiple circles, and segments of circles arranged in a way to plot impedance values in the form of r ± jx (fig. In our case, \[y_{0} = \frac{1}{z_{0}} = \frac{1}{50} = 0.02\] Enter load and characteristic impedances to calculate vswr and reflection coeffecients. Web impedance smith charts also known as z charts are the polar graphs that show the normalized line impedance in the complex reflection coefficient plane.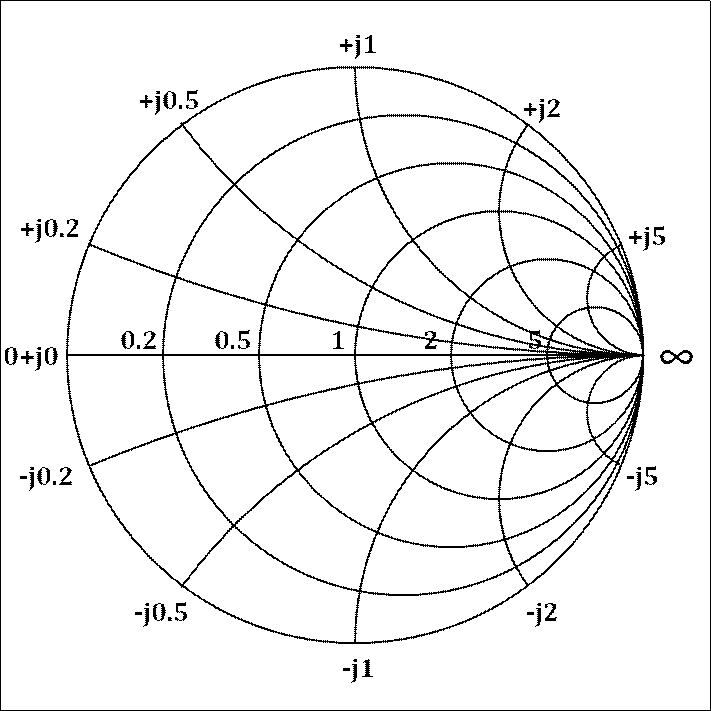
What is Smith Chart and how to use it for Impedance Matching

Impedance Matching by Using Smith Chart A StepbyStep Guide, Part II
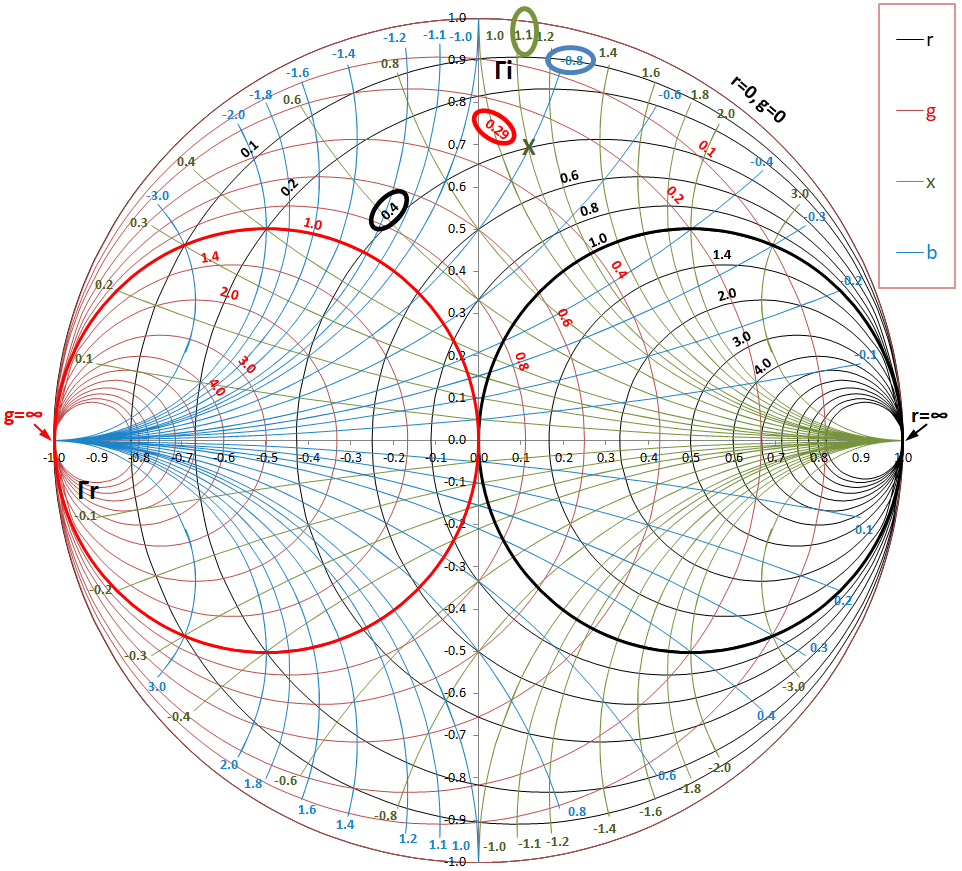
Impedance Matching by Using Smith Chart A StepbyStep Guide, Part II
Free Admittance Smith Chart PDF 956KB 1 Page(s)
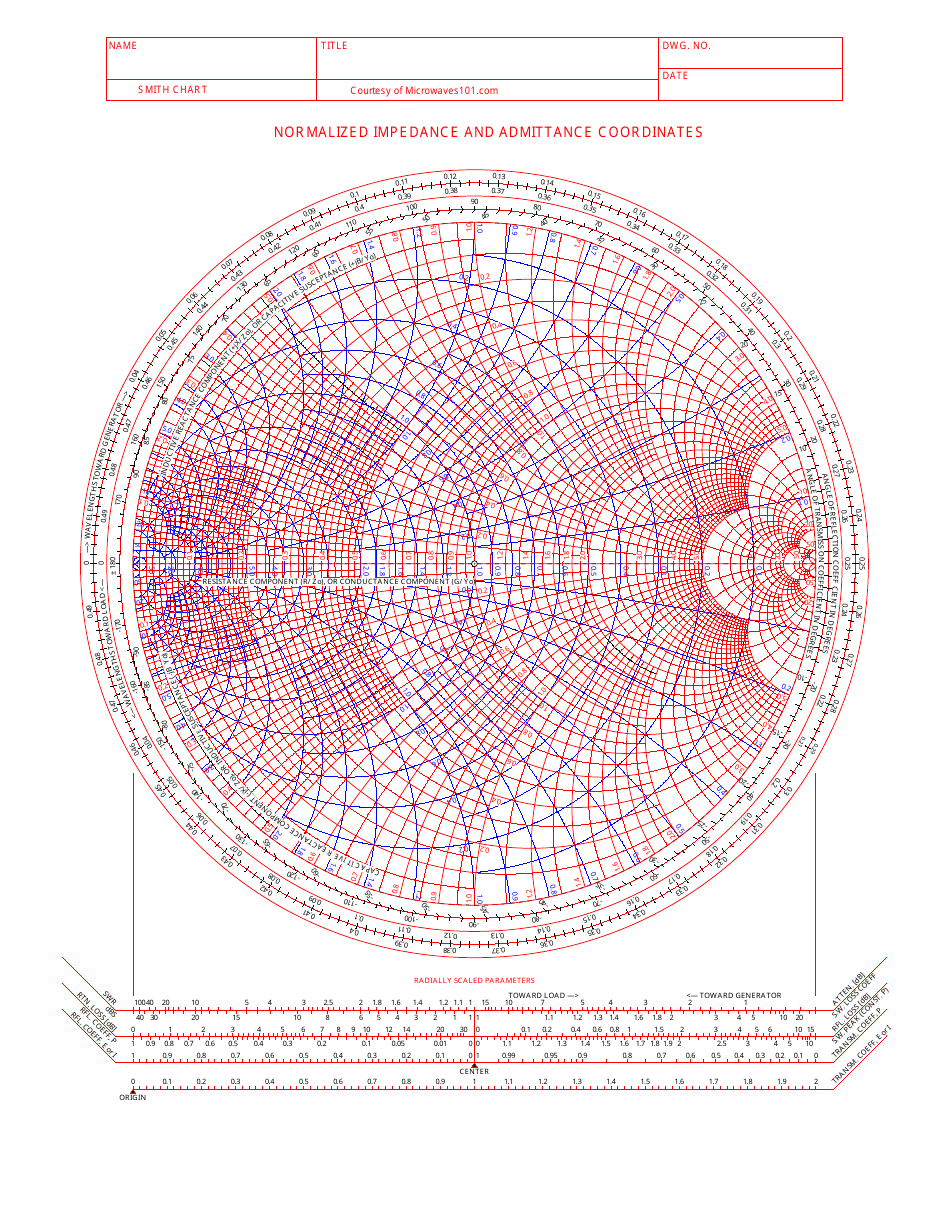
Normalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates Smith Chart Download
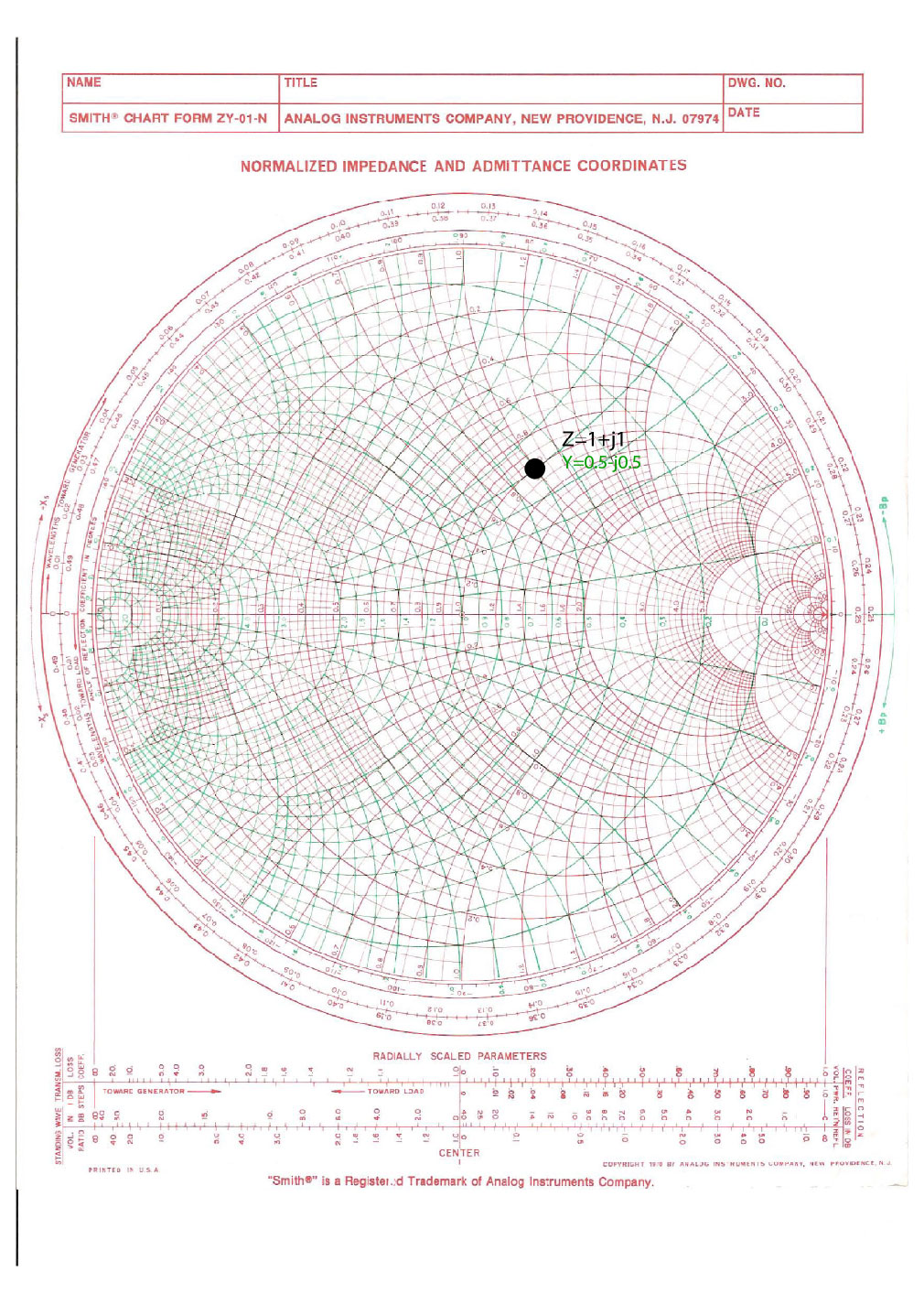
Impedance and Admittance on Smith Chart Ximera
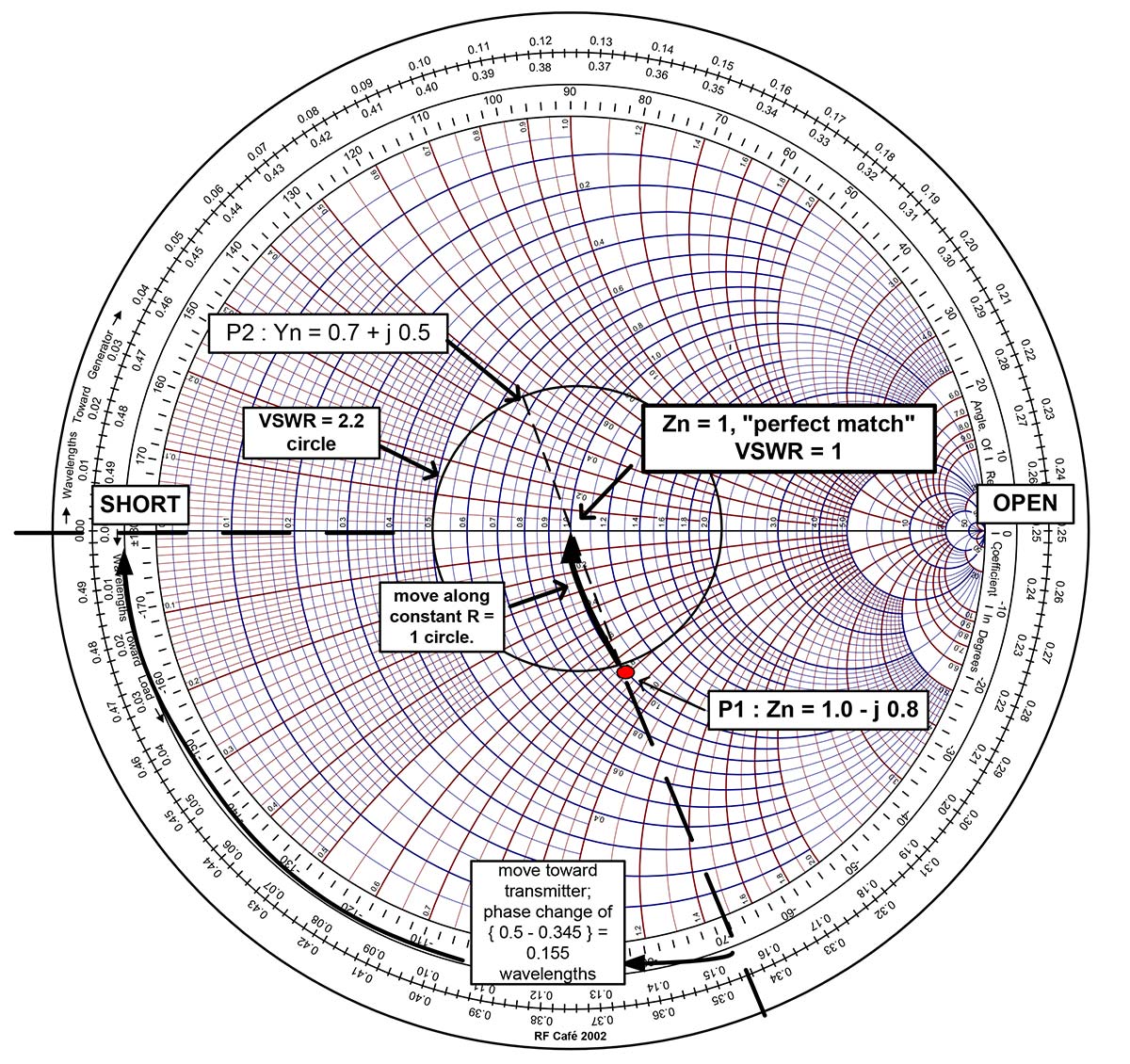
how to use a smith chart Jude Misaid

Free Admittance Smith Chart PDF 956KB 1 Page(s)
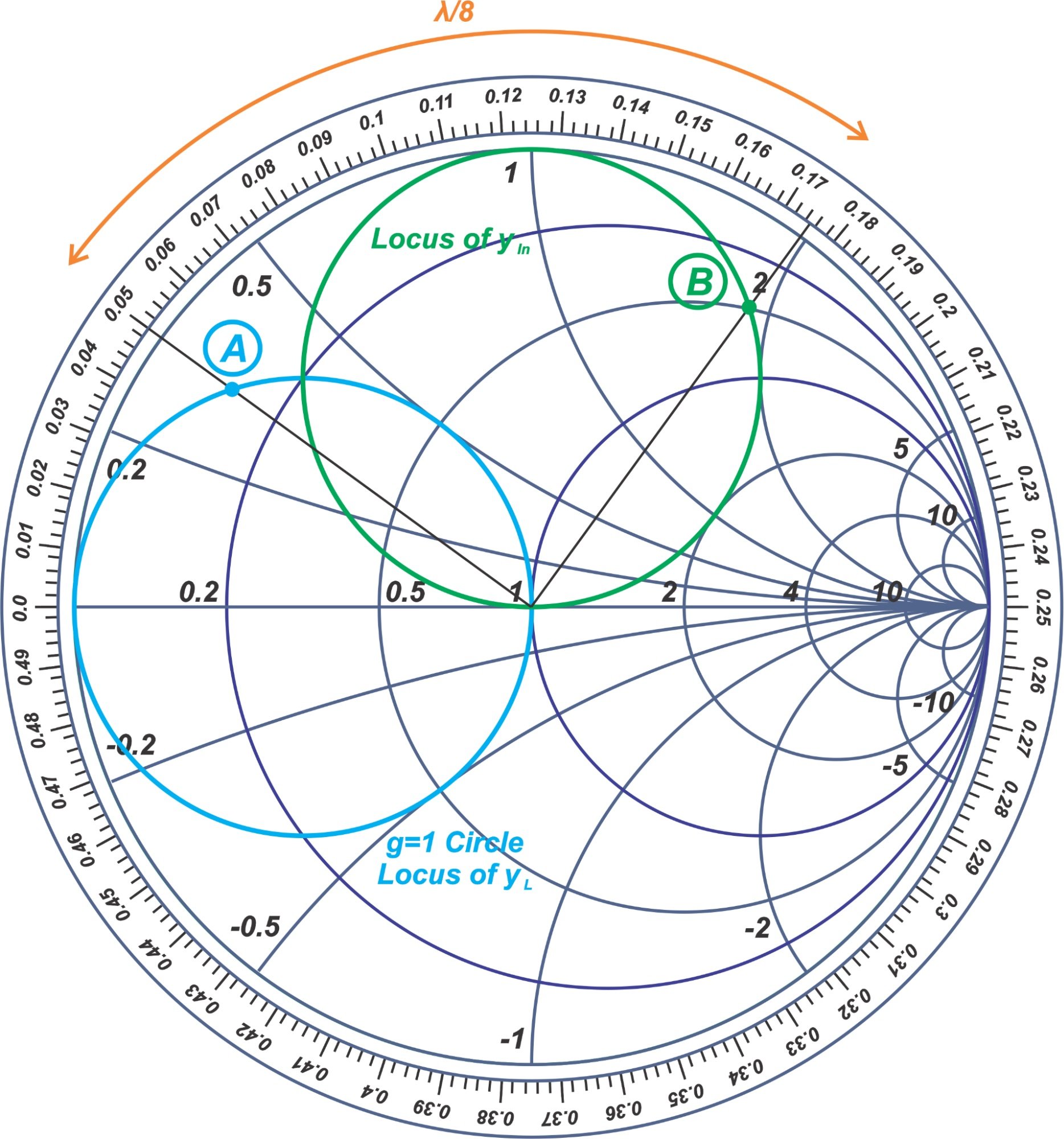
Learn Stub Tuning With a Smith Chart Technical Articles
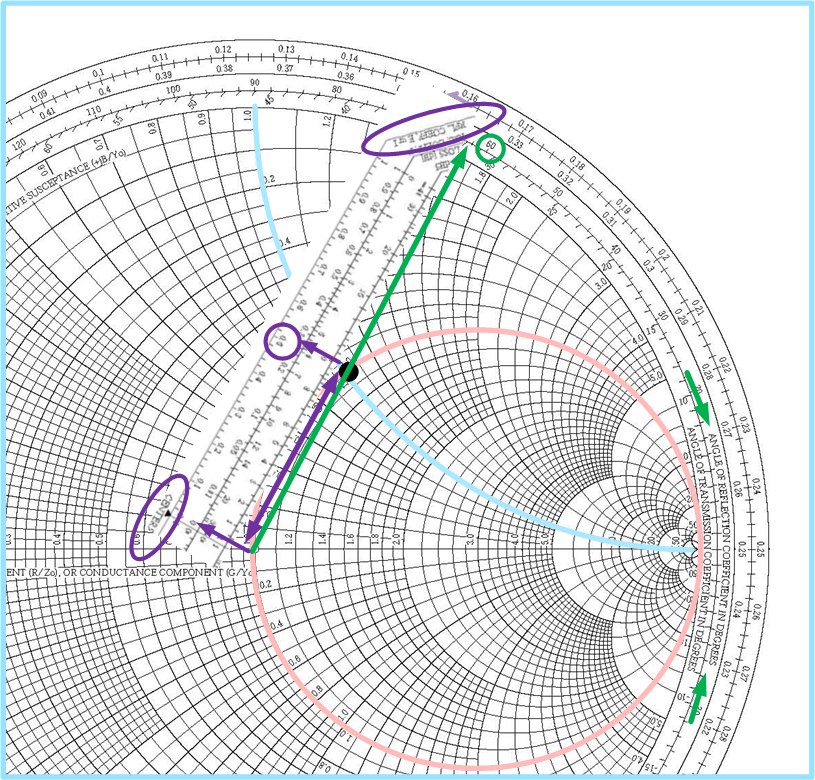
Impedance and Admittance on Smith Chart Ximera
The Admittance Smith Chart Has Loci For Discrete Constant Susceptances Ranging From \(−∞\) To \(∞\), And For Discrete Constant Conductance Ranging From \(0\) To \(∞\), See Figure \(\Pageindex{7}\).
It Uses A Bilinear Moebius Transformation, Projecting The Complex Impedance Plane Onto The Complex Γ Plane:
Recall That On The Standard Or Impedance Smith Chart, The Circles And Curves Related To Constant Resistance And Constant Reactance.
Web The Smith Chart Provides A Graphical Representation Of Γ That Permits The Determination Of Quantities Such As The Vswr Or The Terminating Impedance Of A Device Under Test (Dut).
Related Post: