Smooth Muscle Tissue Drawing
Smooth Muscle Tissue Drawing - One unique feature of neural crest cells is that their migration occurs. They range from about 30 to 200 μ m (thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers), and they produce their own connective tissue, endomysium. Introduction smooth muscle is found throughout the body where it serves a variety of functions. Web smooth muscle can be confused with cardiac muscle because the cells are often running in different directions, just as they are in cardiac muscle. Also, smooth muscle tissue is mostly cellular (and therefore more nuclei are present), whereas the connective tissue is mostly extracellular collagen fibers with fewer cells. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells do not exhibit striations since their actin and myosin (thin and thick) protein filaments are not organized as sarcomeres. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. Web smooth muscle derives from both mesoderm and neural crest cells; Web smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and blood vessels. Web how to draw a muscle tissues/how to draw striated smooth and cardiac muscles.it is very easy drawing. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly draw their true shapes and directions. They range from about 30 to 200 μ m (thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers), and they produce their own connective tissue, endomysium. One unique feature of neural crest cells is that their. In the histology of hollow organs like the esophagus, intestine, you will find two concentric layers of smooth muscles in the same section of that particular tissue. Web smooth muscle derives from both mesoderm and neural crest cells; It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and blood vessels. It is. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly draw their true shapes and directions. You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways , including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular system. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly draw their true shapes and directions. Web smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways , including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular system. Web smooth. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. View the slide on an appropriate objective. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Web smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. Smooth muscle fibers are often found forming sheets of tissue and function in a coordinated fashion. Web smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, uterus and stomach. Diagrammatic view of three types of. The table below compares the differences in the morphology of the three types of. How to draw a muscle tissue,straight muscles,smooth muscles,cardiac muscles ══🅒🅛🅐🅢🅢 11th. Fill out the blanks next to your. Web smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly draw their true shapes and directions. Smooth muscle fibers are often found forming sheets of tissue and function in a coordinated fashion due to the presence of. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells do not exhibit striations since their actin and myosin (thin and thick) protein filaments are not organized as sarcomeres. One unique feature of neural crest cells is that their migration occurs. Also, smooth muscle tissue is mostly cellular (and therefore more nuclei are present), whereas the connective tissue is mostly extracellular. It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and blood vessels. Web smooth muscles are widely distributed in the animal’s body and predominantly found in the visceral hollow organs and blood vessels. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. This is because smooth muscle contributes to many different tissues throughout the body. Smooth muscle tissue, skeletal muscle tissue and, cardiac muscles tissue of body (types of muscle), heart muscle tissue, epicardium, myocardium cells of heart , bone muscles, human muscular system. The area inside the box is enlarged in the next image. Web smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs. Web obtain a slide of smooth muscle tissue from the slide box. They range from about 30 to 200 μ m (thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers), and they produce their own connective tissue, endomysium. You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways , including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular system. Also, smooth muscle tissue is mostly cellular (and therefore more nuclei are present), whereas the connective tissue is mostly extracellular collagen fibers with fewer cells. Smooth muscle fibers are often found forming sheets of tissue and function in a coordinated fashion due to the presence of gap junctions between the cells. How to draw a muscle tissue,straight muscles,smooth muscles,cardiac muscles ══🅒🅛🅐🅢🅢 11th. It is found in numerous bodily systems, including the ophthalmic, reproductive, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems, where it functions to contract. Web smooth muscle derives from both mesoderm and neural crest cells; Web smooth muscle is one of three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. View the slide on an appropriate objective.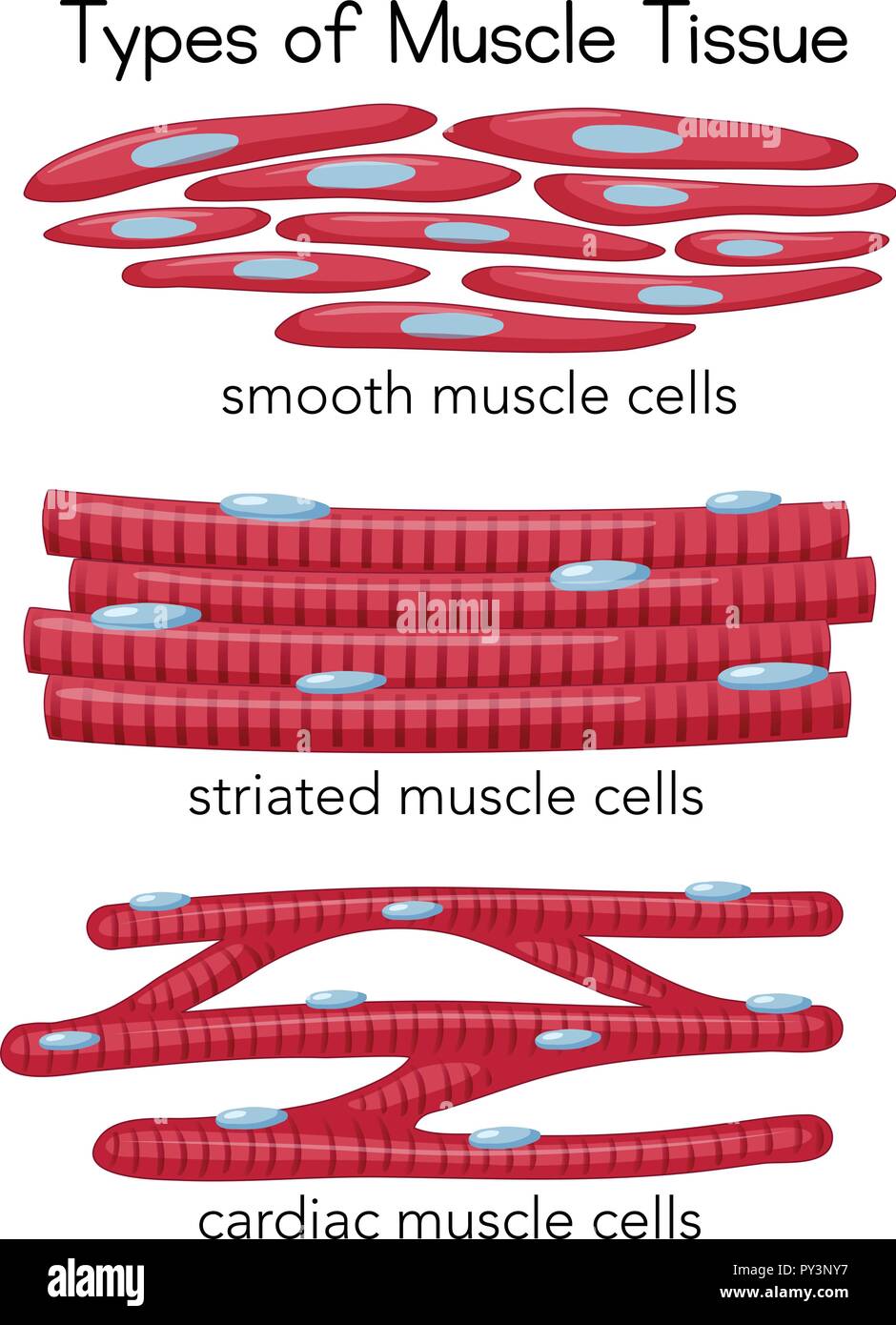
Types of Muscle Tissue illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy

LM of a section through human smooth muscle tissue Stock Image P154

How To Draw Muscle Fibers at How To Draw
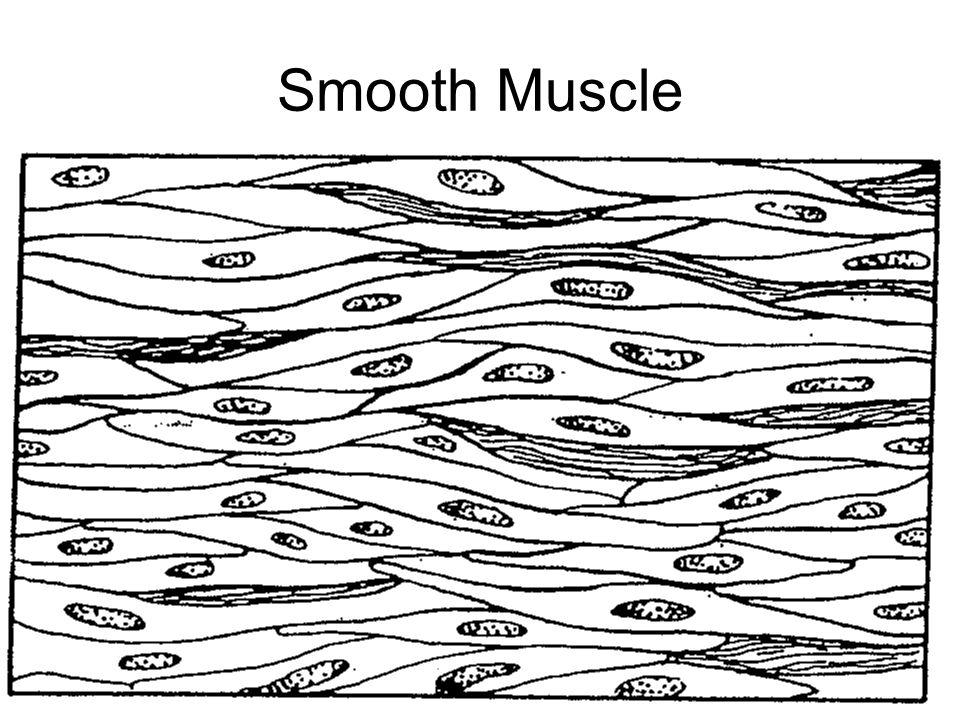
Smooth Muscle Diagram Drawing Smooth Muscle Structure Function
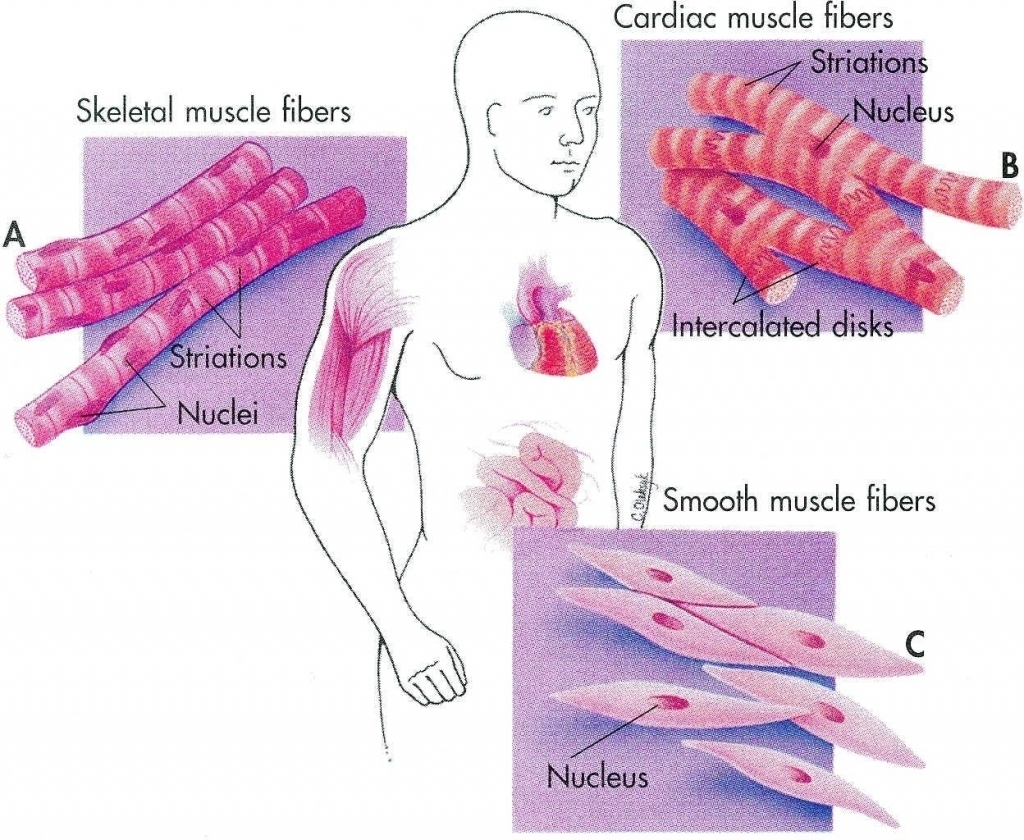
Smooth Muscle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
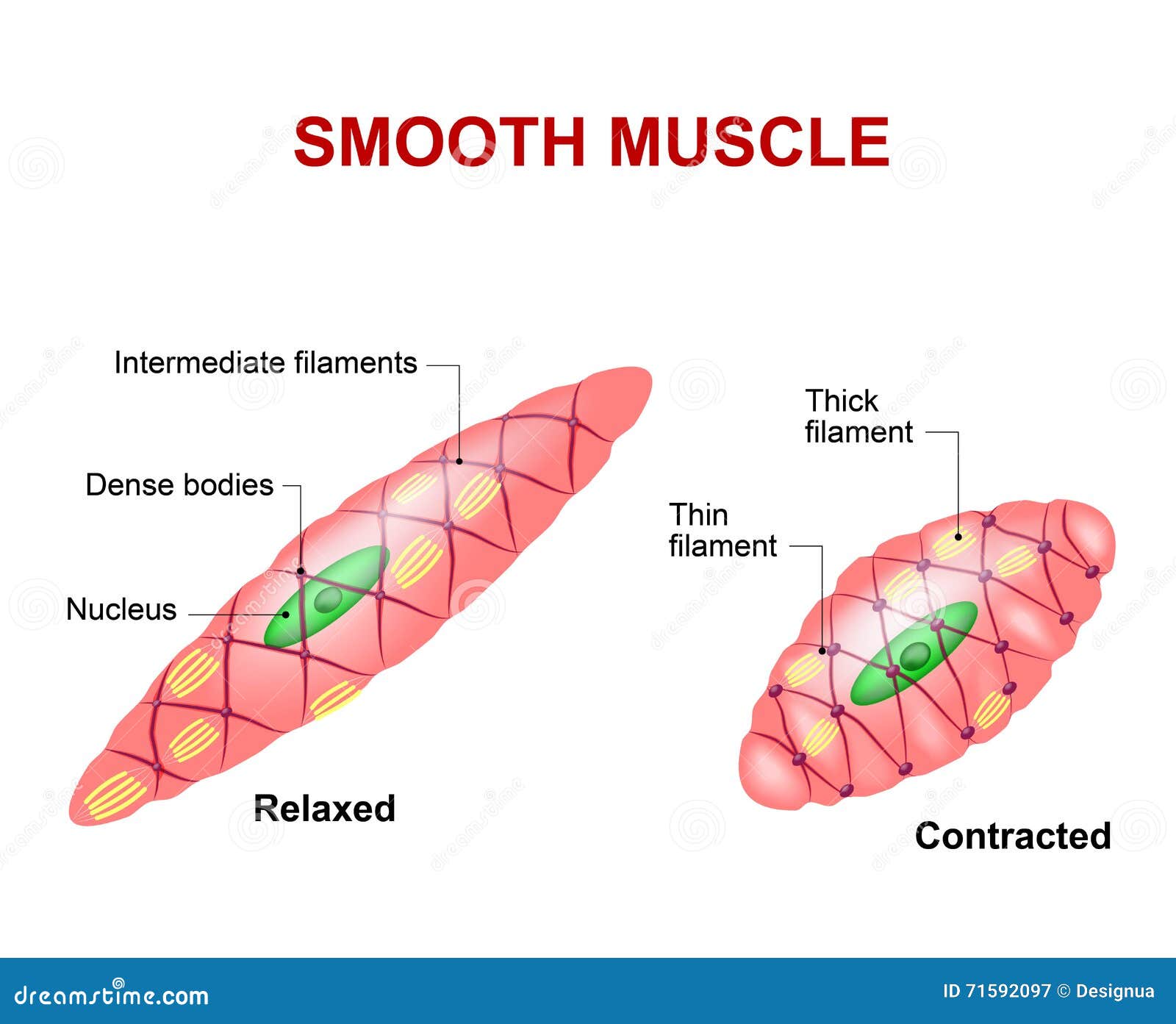
Smooth muscle tissue stock vector. Illustration of autonomic 71592097

Smooth Muscle Diagram Smooth Muscle Examples And Function
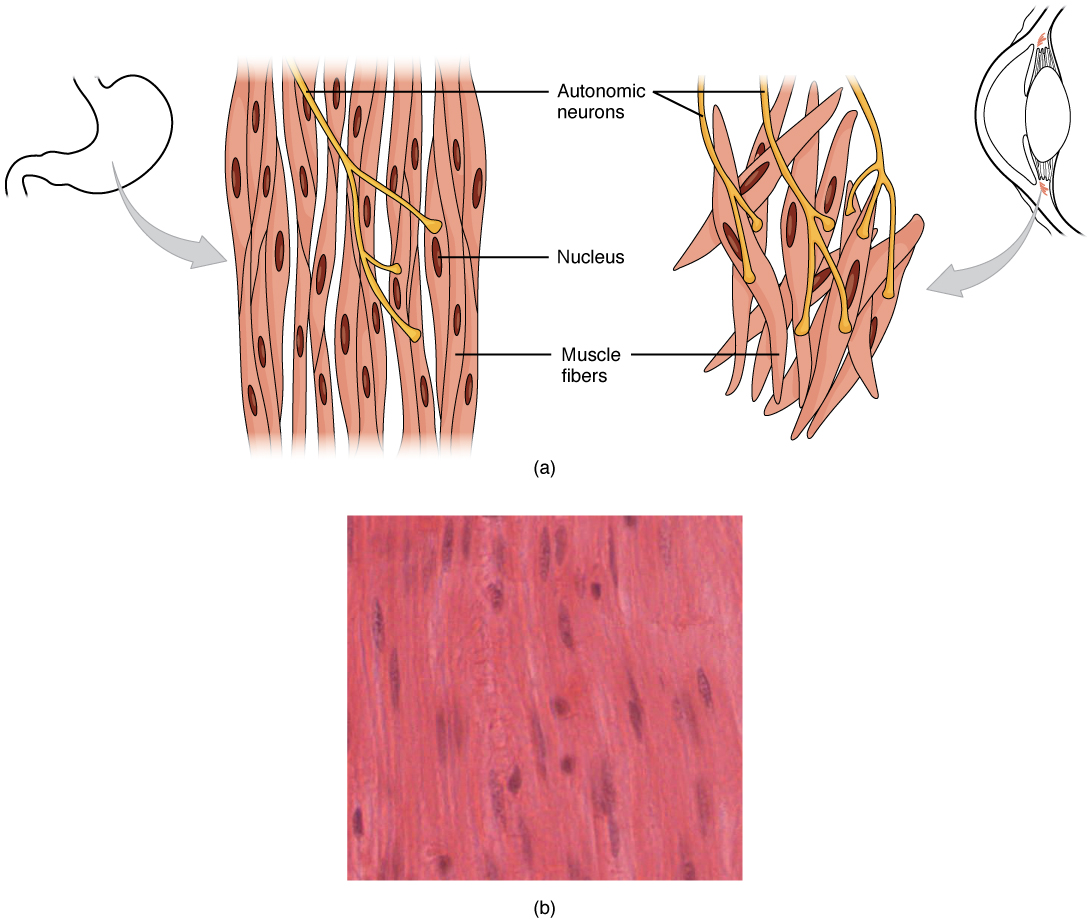
Smooth Muscle Anatomy and Physiology I
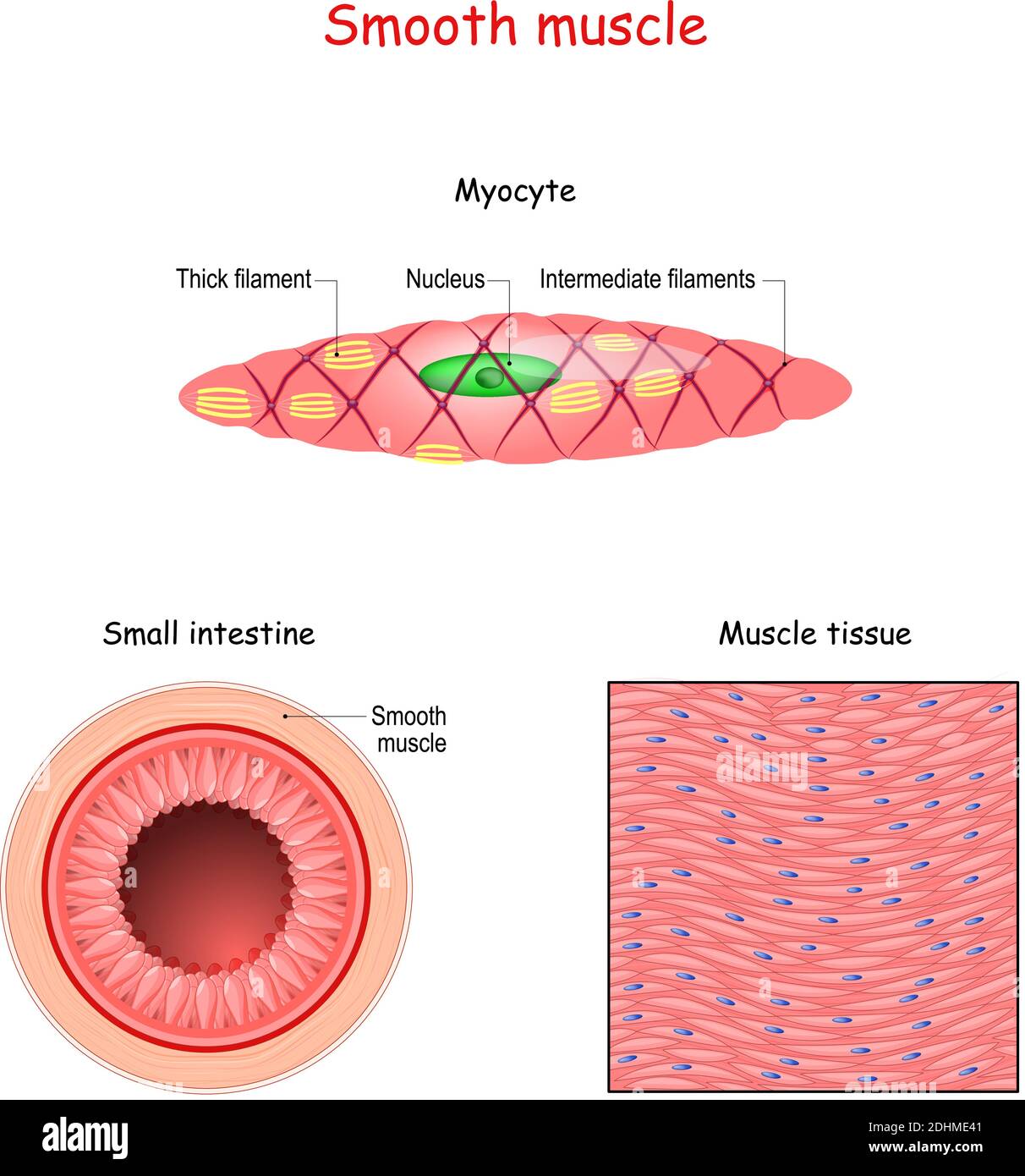
Structure of smooth muscle fibers. anatomy of Myocyte. Background of
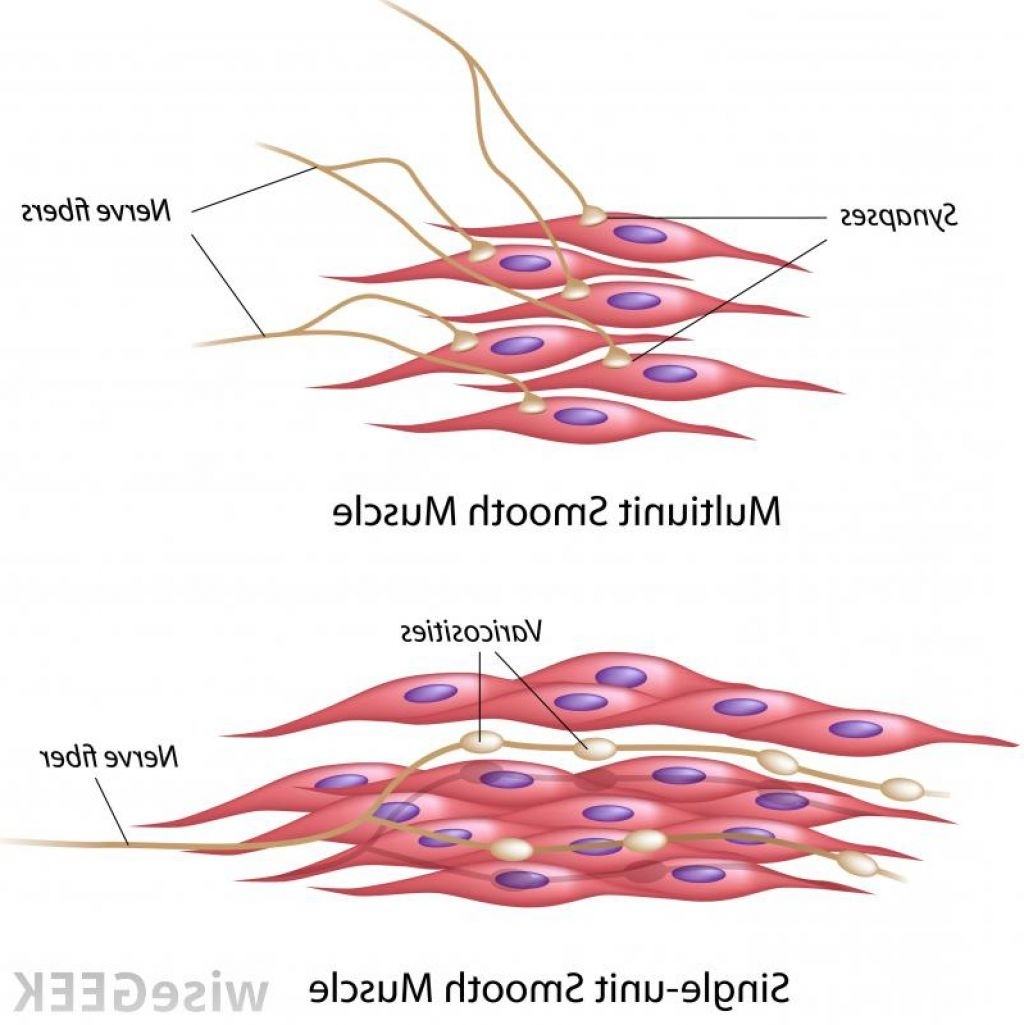
Smooth Muscle Diagram / Smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle tissue
Smooth Muscle Cells Are A Lot Smaller Than Cardiac Muscle Cells, And They Do Not Branch Or Connect End To End The Way Cardiac Cells Do.
Web Smooth Muscle Is Found Throughout The Body Around Various Organs And Tracts.
Web Smooth Muscles Are Widely Distributed In The Animal’s Body And Predominantly Found In The Visceral Hollow Organs And Blood Vessels.
These Cells Have Fibers Of Actin And Myosin Which Run Through The Cell And Are Supported By A Framework Of Other Proteins.
Related Post: