Specific Heat Drawing
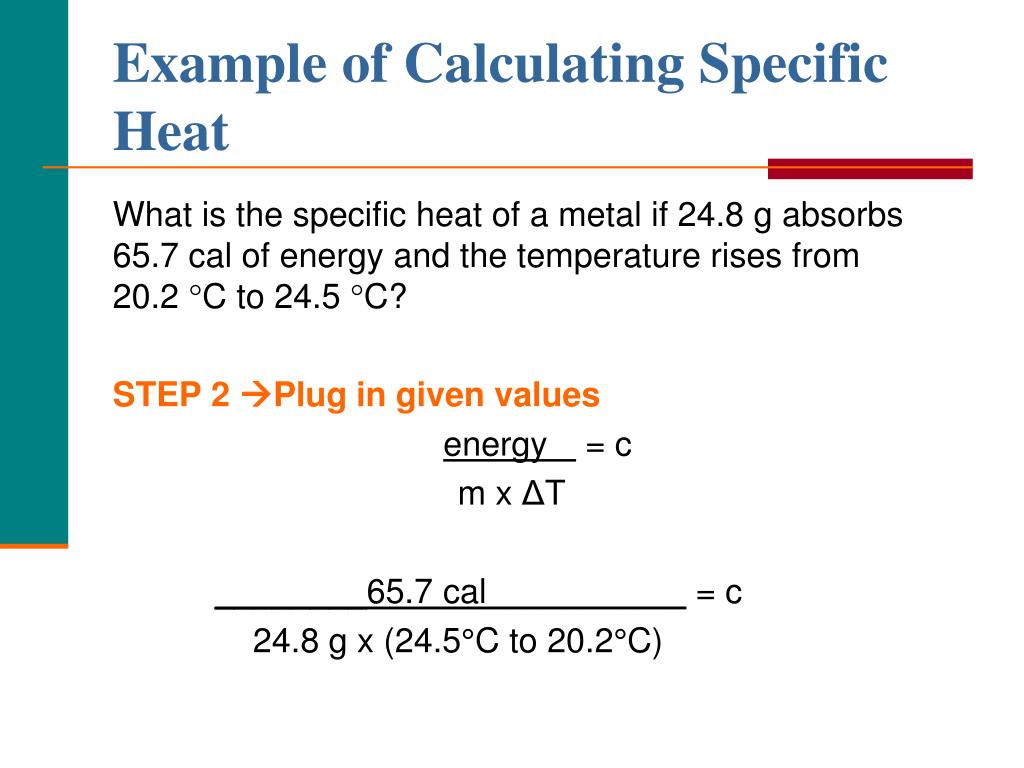
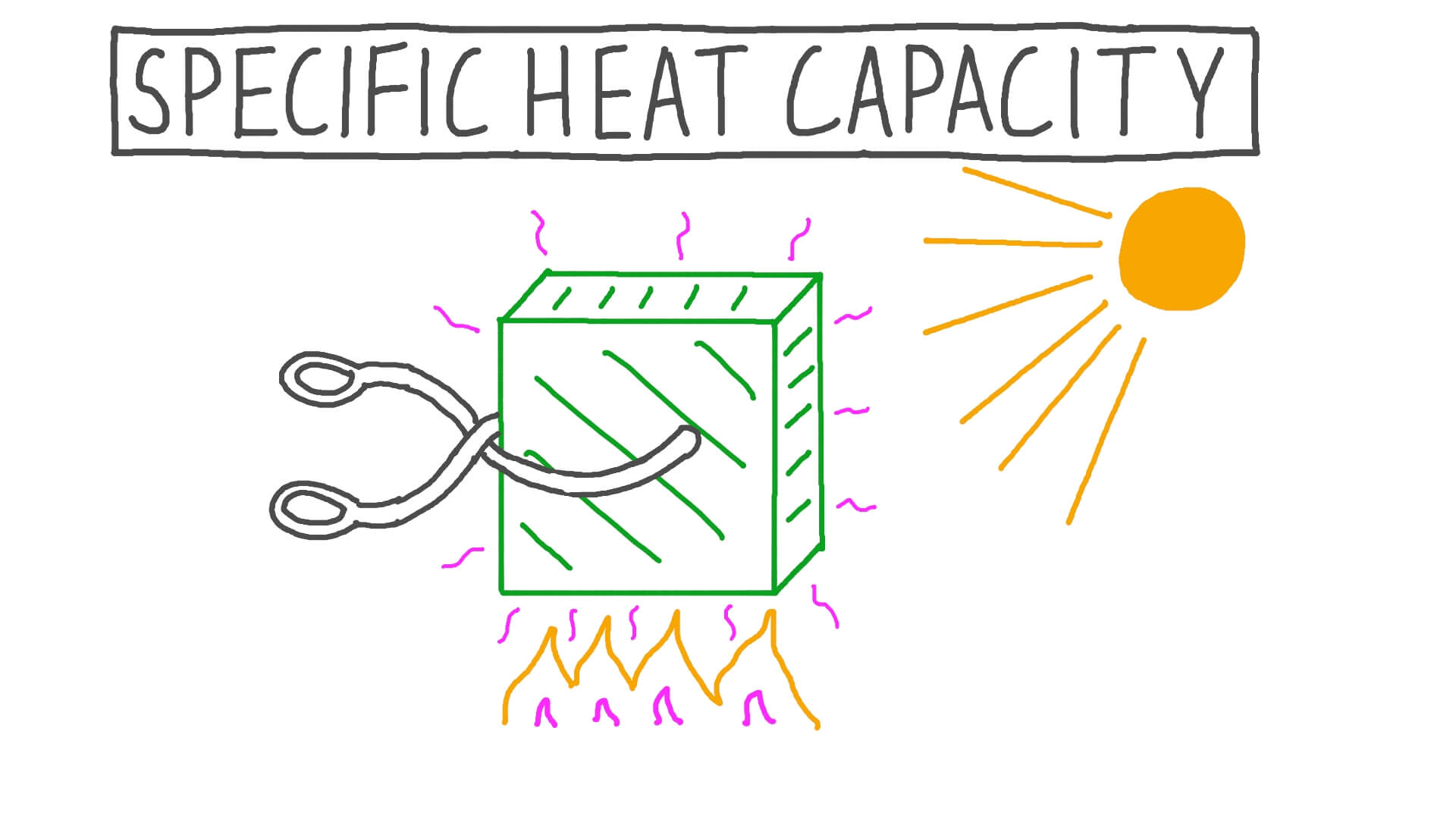
Specific Heat Drawing - Where q is the heat gained or lost, m is the mass of the object, c is its specific heat, and δt is the change in. Q q is the amount of supplied or subtracted heat (in joules), m m is the mass of the sample, and \delta t δt is the difference between the initial and final temperatures. The choice is yours 路 ♂️ most of us have either been there or still stuck there. Web the formula for specific heat looks like this: Web the specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of mass by 1.00 ºc. C 2 h 6 o(l) 2.376: Web the specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled. Web the symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase. The equation that relates heat (q) ( q) to specific heat (cp) ( c p), mass (m) ( m), and temperature change (δt) ( δ t) is shown below. Web specific heat online unit converter. Q q is the amount of supplied or subtracted heat (in joules), m m is the mass of the sample, and \delta t δt is the difference between the initial and final temperatures. The amount of heat absorbed or released by a substance depends directly on the type of substance, its mass, and the. Web the si unit for specific. Web specific heat 8/4/2018 2revised joule (j): Web sal was explaining the intuition behind the formula for thermal conductivity, he was not solving for specific heat ratios. The units of specific heat are usually calories or joules per gram per celsius degree. Namely, by measuring the heat capacity of a sample of the substance, usually with a calorimeter, and dividing. Q = cp × m × δt q = c p × m × δ t. Web the specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of mass by 1.00 ºc. Web the specific heat of aluminum is 903 j/kg•k. 1.00 cal = 4.184 j specific heat (c s): Web specific heat 8/4/2018. Web specific heat 8/4/2018 2revised joule (j): Web specific heat online unit converter see also tabulated values for gases, food and foodstuff, metals and semimetals, common liquids and fluids and common solids, as well as values of molar specific heat for common organic substances and inorganic substances. Web specific heat, the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of. Web specific heat, the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one celsius degree. The specific heat of water is 1 calorie (or 4.186 joules) per gram per celsius degree. Web this chemical property, known as specific heat, is defined as the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of. Web the symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase. The specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of mass by 1.00ºc. Its si unit is j/ (kg ⋅ ⋅ k) or j/ (kg ⋅ ⋅ °c °c ). Specific heat is temperature (and phase) dependent. The. Specific heat is temperature (and phase) dependent. Web the symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase. Web the symbol c stands for specific heat and depends on the material and phase. Unit of heat most commonly used in the si system. The amount of heat gained or lost by an object when its temperature. Web specific heat 8/4/2018 2revised joule (j): Web sal was explaining the intuition behind the formula for thermal conductivity, he was not solving for specific heat ratios. Web specific heat capacity (often just called specific heat) is the amount of heat energy (usually in joules) necessary to increase the temperature of one gram of substance by one degree celsius or. The units of specific heat are usually calories or joules per gram per celsius degree. The specific heat c is a property of the substance; Web specific heat and heat capacity are measures of the energy needed to change the temperature of a substance or object. Q q is the amount of supplied or subtracted heat (in joules), m m. Q = cp × m × δt q = c p × m × δ t. Web the specific heat capacity of a substance is typically determined according to the definition; Web the formula for specific heat looks like this: Namely, by measuring the heat capacity of a sample of the substance, usually with a calorimeter, and dividing by the. Unit of heat most commonly used in the si system. Think about your question then watch the video again and you will see that sal is reenforcing your point using generalized intuition as opposed to specifics. Metals and semimetals common liquids and fluids c) = 5/9 [t ( c)] (9/5) + 32 the energy required to heat a product can be calculated as m dt (1) q = heat required (kj) = specific heat (kj/kg k, kj/kg dt = temperature difference (k, Web by following these steps and standards, you can create a mechanical drawing with specific heat treatment requirements, that conveys your design intent and specifications clearly and. Web specific heat capacity (often just called specific heat) is the amount of heat energy (usually in joules) necessary to increase the temperature of one gram of substance by one degree celsius or one kelvin. The quantity of heat liberated or absorbed when the temperature of 1.00 gram of a substance falls or rises 1.00 c. Specific heat is temperature (and phase) dependent. Web the symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase. Web the si unit for specific heat is j / (kg × k) or j / (kg ×oc). C = \frac {q} {m \delta t} c = mδt q. Web the formula for specific heat looks like this: Q = cp × m × δt q = c p × m × δ t. (recall that the temperature change δt is the same in units of kelvin and degrees celsius.) values of specific heat must generally be measured, because there. Web specific heat and heat capacity are measures of the energy needed to change the temperature of a substance or object. Web specific heat, the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one celsius degree. The temperature change ( δt δ t) is the same in units of kelvins and degrees celsius (but not degrees fahrenheit).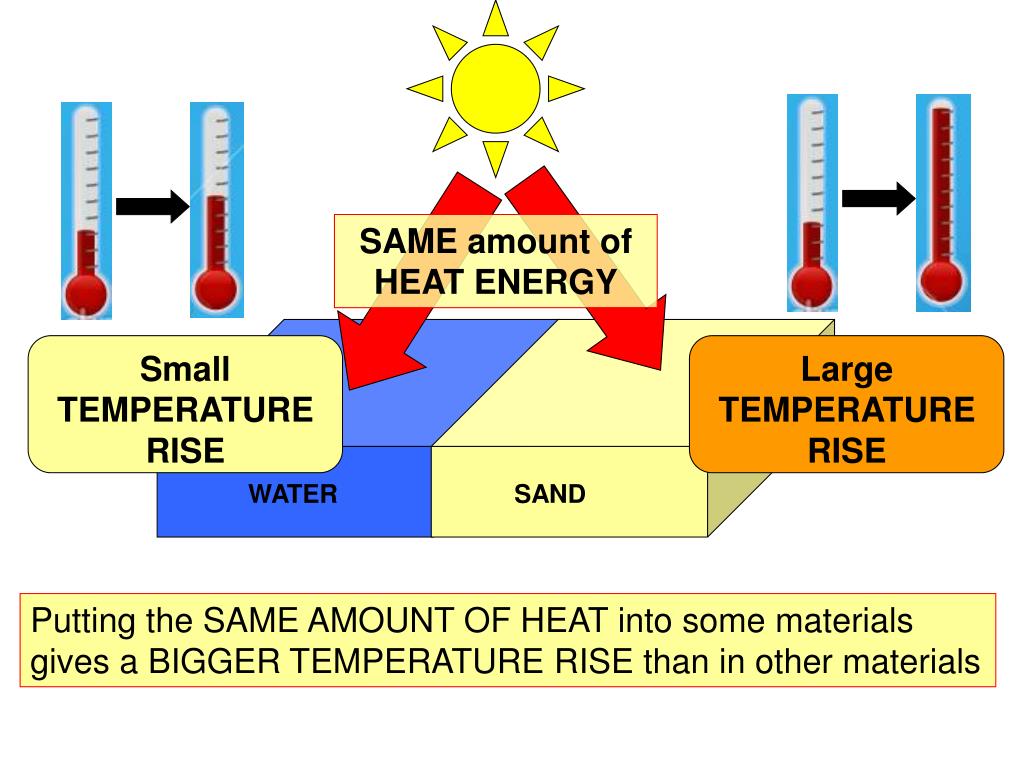
PPT SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY PowerPoint Presentation, free download

AQA A Level Physics Year 2 /IB Physics Specific Heat Capacity
Finding a material's specific heat capacity GCSE Science Marked by
How To Calculate Specific Heat Of Metal Haiper
Lesson Video Specific Heat Capacity Nagwa
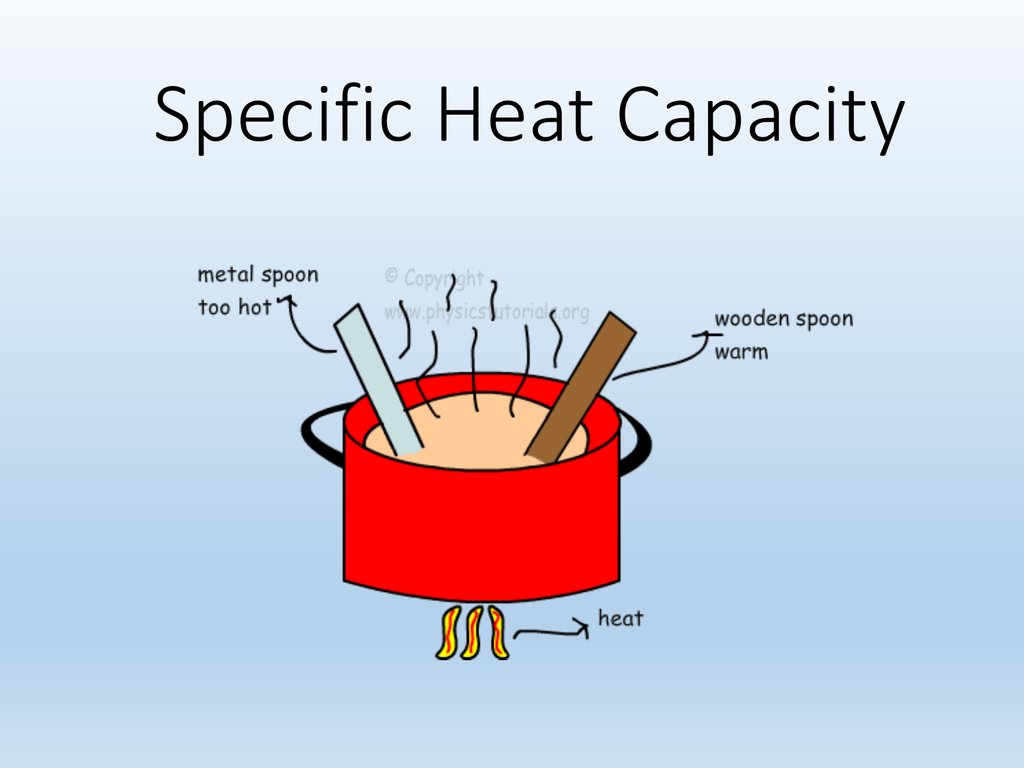
1.3 Specific Heat Capacity
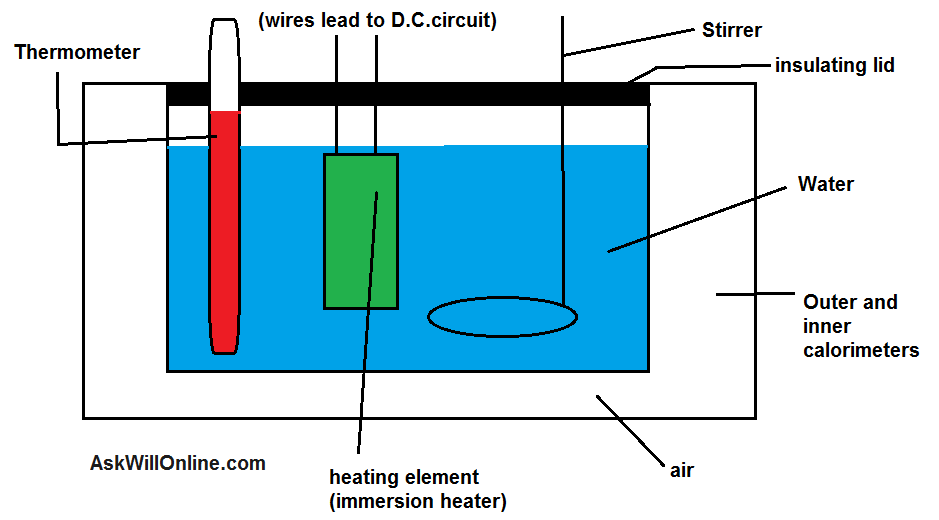
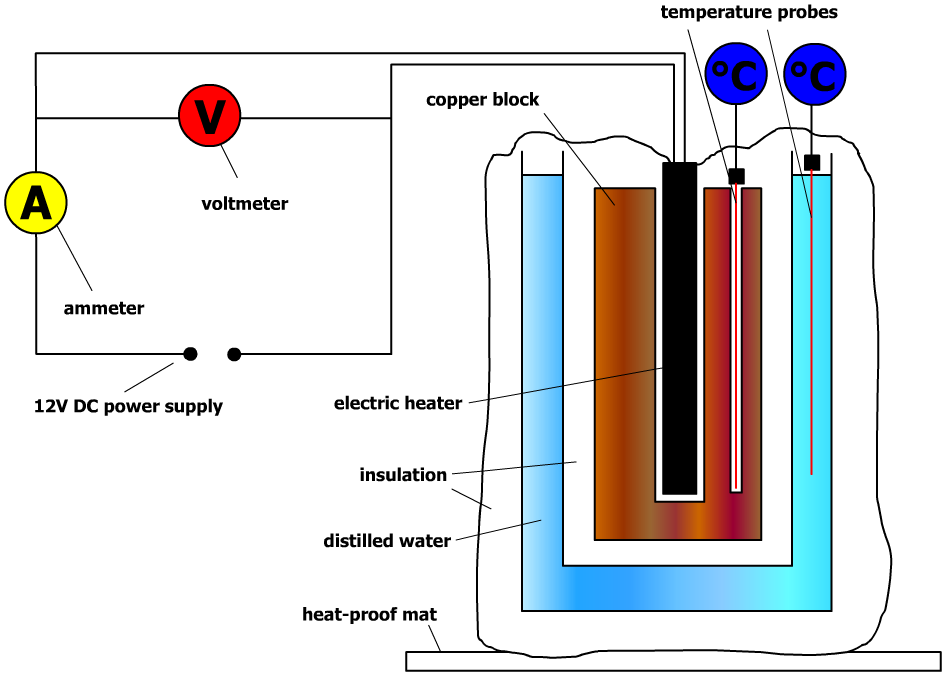
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Experiments In Physics Ask
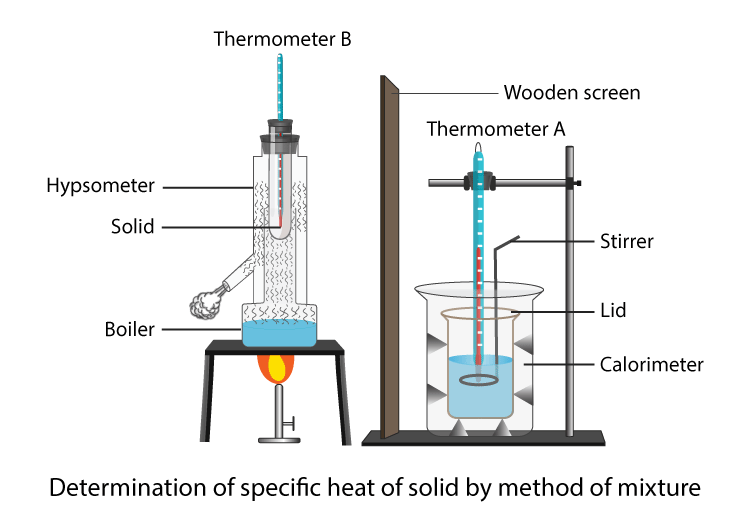
To Determine Specific Heat Capacity Of A Given Solid Physics Practical

Lesson 10 Specific Heat YouTube
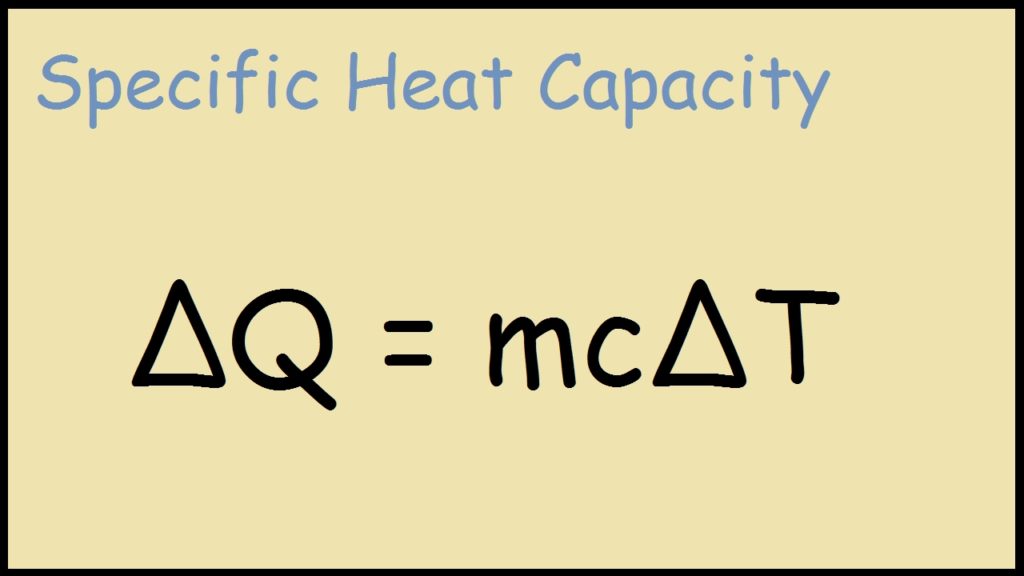
Specific Heat Formula Definition, Equations, Examples
Q = \(Mc\Delta T\) Derivation Of Specific Heat Formula
The Specific Heat C Is A Property Of The Substance;
Web Sal Was Explaining The Intuition Behind The Formula For Thermal Conductivity, He Was Not Solving For Specific Heat Ratios.
Web Specific Heat Online Unit Converter.
Related Post: