Spectrum Of Antibiotics Chart
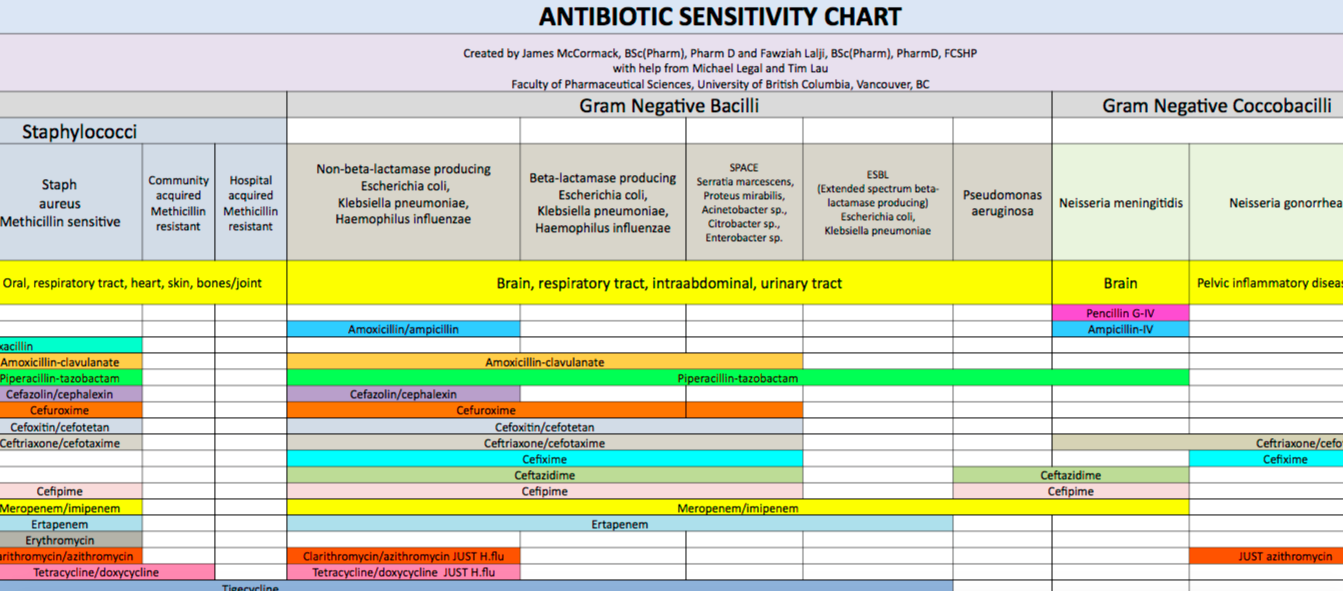
Spectrum Of Antibiotics Chart - The antibiotics listed are active against e.faecalis, but have limited activity for e.faecium cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than 40% activity for s.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local susceptibility data Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharmd and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm), pharmd, fcshp with assistance from tim lau faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, university of british columbia, vancouver, bc. Three new classes of antibacterial antibiotics have been brought into clinical use: Species with less than 30 isolates, susceptibilities should be interpreted with caution. Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those identified by standard antibiotic use metrics. Mandell, douglas, and bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. Coli., and either kill the bacteria (bactericidal) or keep it from reproducing and growing (bacteriostatic). Web antibiotics specifically treat infections caused by bacteria, such as staph., strep., or e. Web kucers' the use of antibiotics. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotic antibiotics can be divided into two classes based on their mechanism of action. Narrow spectrum antibiotis target specific bacteria such as gram positive or gram negative. Web broad spectrum antibiotics act against a larger group of bacteria. Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those identified by standard antibiotic use metrics. Grey boxes indicate organism has intrinsic resistance or susceptibilities are not published to. The antibiotics listed are active against e.faecalis, but have limited activity for e.faecium cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than 40% activity for s.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local susceptibility data Bacteriostatic antibiotics inhibit their growth or reproduction. Local antibiotic sensitivities & preferences will vary. Common uses include urinary tract infections (utis), strep throat (pharyngitis), pneumonia, ear infections (otitis media),. Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharm d and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm), pharmd, fcshp with help from michael legal and tim lau faculty of pharmaceugcal sciences, university of brigsh columbia, vancouver, bc. Web kucers' the use of antibiotics. Species with less than 30 isolates, susceptibilities should be interpreted with caution. Mandell, douglas, and bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. Grey. Grey boxes indicate organism has intrinsic resistance or susceptibilities are not published to corresponding antimicrobial. Narrow spectrum antibiotis target specific bacteria such as gram positive or gram negative. Species with less than 30 isolates, susceptibilities should be interpreted with caution. Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharm d and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm), pharmd, fcshp with help from michael legal and tim. Cyclic lipopeptides (such as daptomycin), glycylcyclines (such as tigecycline), and oxazolidinones. Web the antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of microorganisms it can kill or inhibit. Species with less than 30 isolates, susceptibilities should be interpreted with caution. Common teaching often explains that bactericidal antibiotics kill bacteria and bacteriostatic antibiotics prevent the growth of bacteria. Web antibiogram &. Species with less than 30 isolates, susceptibilities should be interpreted with caution. Coli., and either kill the bacteria (bactericidal) or keep it from reproducing and growing (bacteriostatic). Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those identified by standard antibiotic use metrics. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotic antibiotics can be divided into two. Narrow spectrum antibiotis target specific bacteria such as gram positive or gram negative. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotic antibiotics can be divided into two classes based on their mechanism of action. Web the antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of microorganisms it can kill or inhibit. Web the data in the spectra of activity table are intended to serve. Narrow spectrum antibiotis target specific bacteria such as gram positive or gram negative. Local antibiotic sensitivities & preferences will vary. Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those identified by standard antibiotic use metrics. Bacteriostatic antibiotics inhibit their growth or reproduction. Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharmd and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm),. Three new classes of antibacterial antibiotics have been brought into clinical use: The antibiotics listed are active against e.faecalis, but have limited activity for e.faecium cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than 40% activity for s.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local susceptibility data Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those. Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharmd and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm), pharmd, fcshp with assistance from tim lau faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, university of british columbia, vancouver, bc. By definition, antibiotics are medications used to fight bacterial infections. Web the spectra listed here reflect general antibiotic use and may not relate to your patient’s pathogen(s) or reflect the antibiogram of your. Local antibiotic sensitivities & preferences will vary. Common uses include urinary tract infections (utis), strep throat (pharyngitis), pneumonia, ear infections (otitis media), some sinus. Web an antibiotic spectrum index identified differences in prescribing practice patterns among three nicus unique from those identified by standard antibiotic use metrics. Mandell, douglas, and bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. Created by james mccormack, bsc(pharm), pharmd and fawziah lalji, bsc(pharm), pharmd, fcshp with assistance from tim lau faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, university of british columbia, vancouver, bc. By definition, antibiotics are medications used to fight bacterial infections. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotic antibiotics can be divided into two classes based on their mechanism of action. The true definition is not so simple. Recognize antibiotics that specifically cover mrsa (optional objective in the additional learning section) teaching instructions. Web the antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of microorganisms it can kill or inhibit. Bacteriostatic antibiotics inhibit their growth or reproduction. Web this review will discuss the place in therapy, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and other pharmacologic considerations encountered when prescribing commonly used antibiotics in. Web compare the two classes of antibiotics: Web the data in the spectra of activity table are intended to serve as a general guide to antibacterial usefulness based on treatment guidelines and recommendations, in vitro activity, predominant patterns of susceptibility or. Cyclic lipopeptides (such as daptomycin), glycylcyclines (such as tigecycline), and oxazolidinones. Web antibiogram & 1st line agents by species.
Image result for antibiotic spectrum chart Antibiotic, Chart, Flow sheet

Abx Coverage Antibiotics chart, Antibiotics pharmacology
Antibiotic Spectrum Chart Phartoonz vrogue.co

Winding Spiral Case A Day in the Life General Internal Medicine
Antibiotic Spectrum

Antibiotics Classification According To Spectrum
![[Serious] Updated Pocket Size Antibiotic Chart Sheet medicalschool](https://external-preview.redd.it/qVbOdA8FToY0cVLrN5L1lf6v_j0ioHG2XsHWNZJpdUA.png?width=1200&height=602&auto=webp&s=582bf7b0e895012f7dec1ebfa21b48c290326337)
[Serious] Updated Pocket Size Antibiotic Chart Sheet medicalschool
Spectrum Of Antibiotics Chart
Antibiotic Rainbow Chart
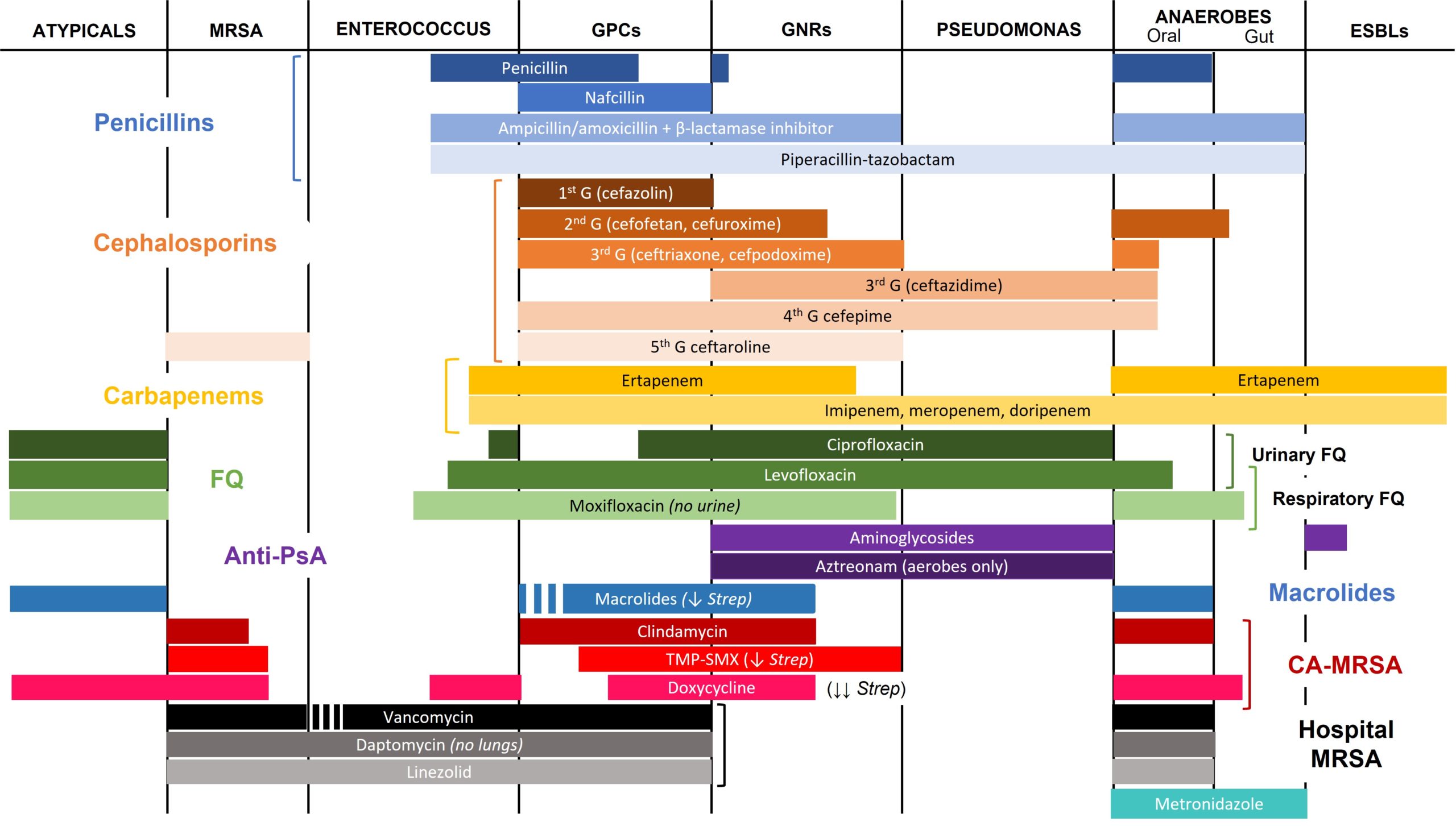
Antibiotics Part 1 Spectrum teachIM
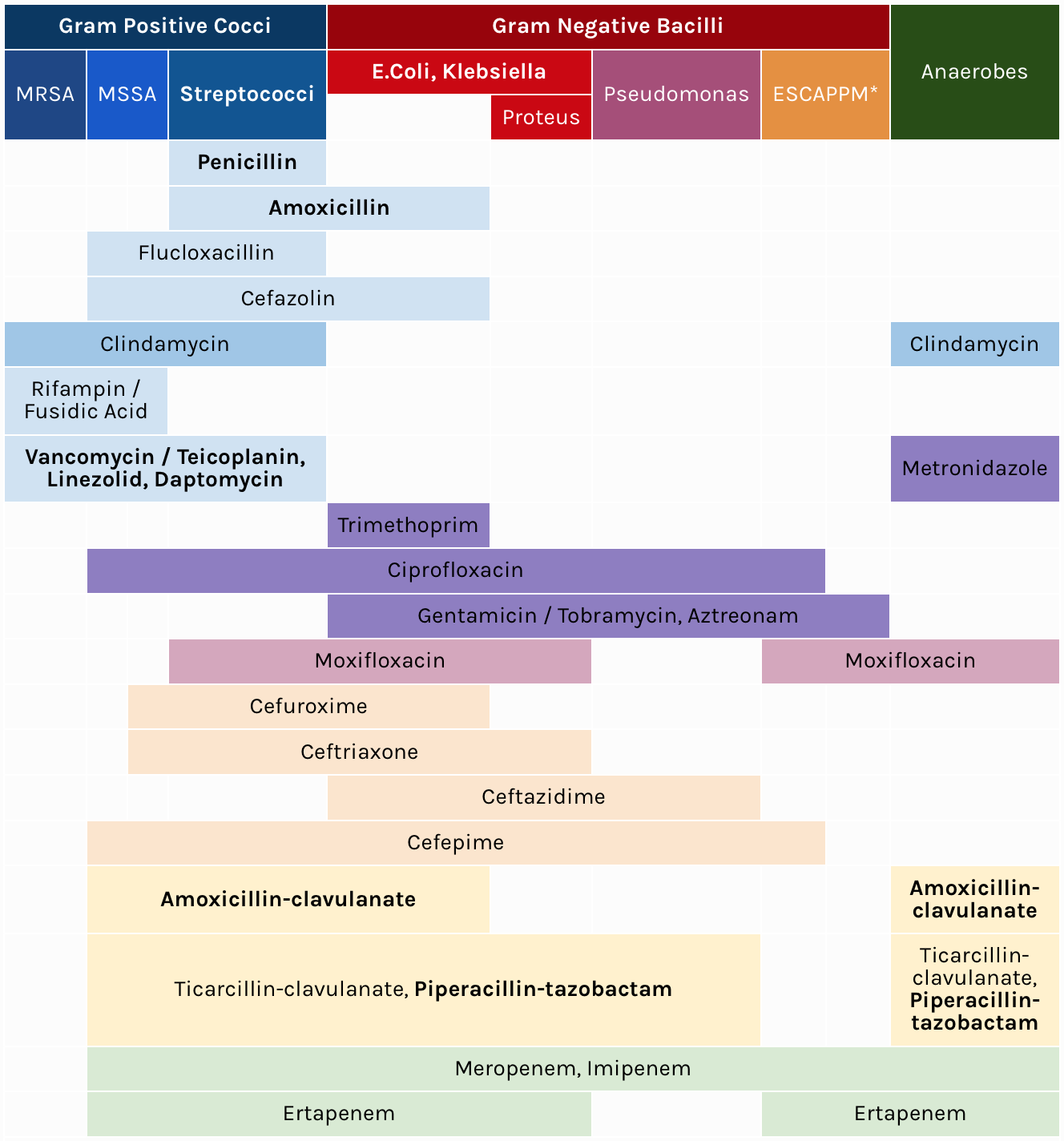
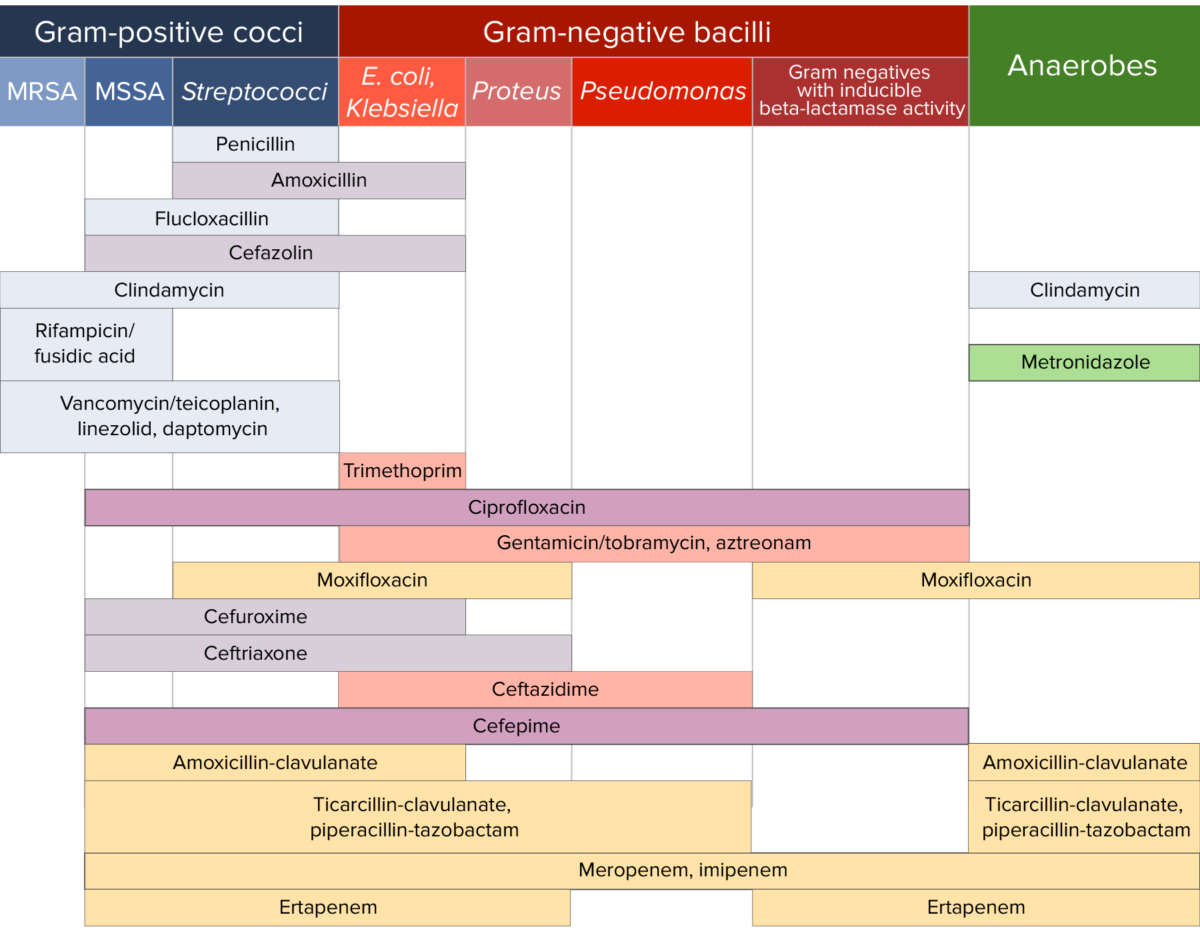
Created By James Mccormack, Bsc(Pharm), Pharm D And Fawziah Lalji, Bsc(Pharm), Pharmd, Fcshp With Help From Michael Legal And Tim Lau Faculty Of Pharmaceugcal Sciences, University Of Brigsh Columbia, Vancouver, Bc.
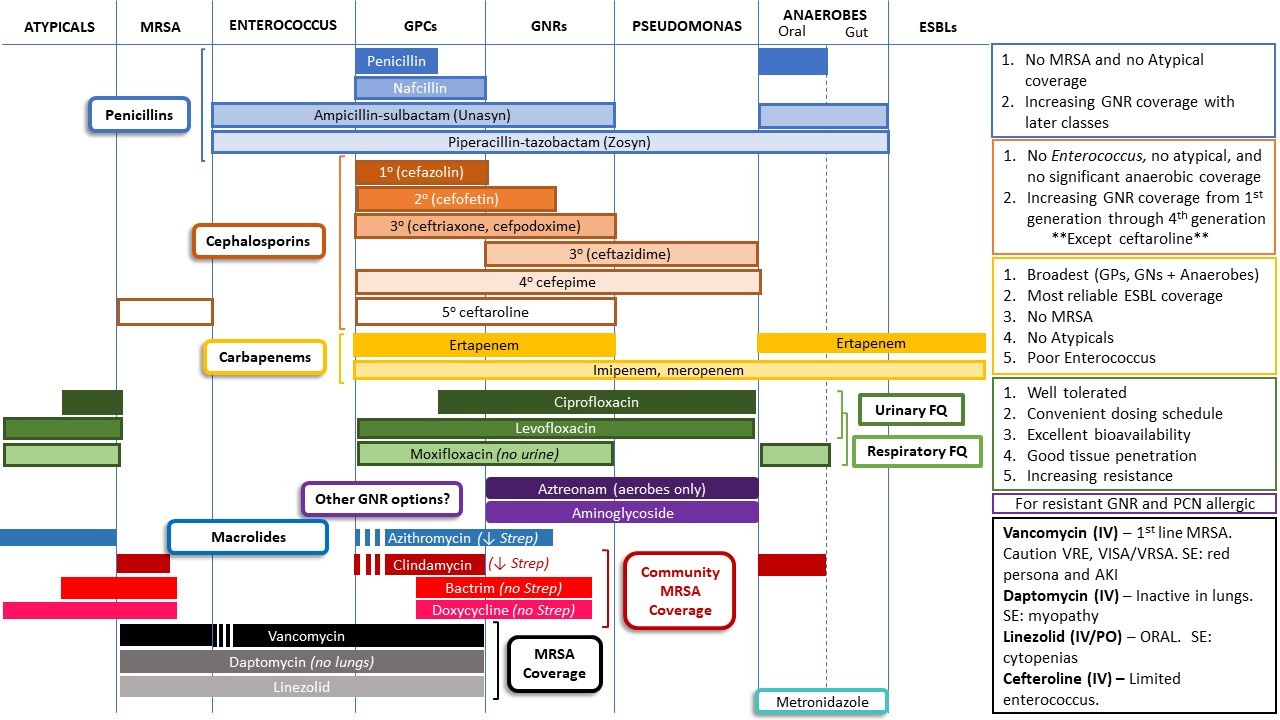
Web Antimicrobial Agents Are Classically Grouped Into Two Main Categories Based On Their In Vitro Effect On Bacteria:
Grey Boxes Indicate Organism Has Intrinsic Resistance Or Susceptibilities Are Not Published To Corresponding Antimicrobial.
Three New Classes Of Antibacterial Antibiotics Have Been Brought Into Clinical Use:
Related Post: