Spongy Bone Drawing
Spongy Bone Drawing - The names imply that the two types differ in density, or how tightly the tissue is packed together. Also shown are red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and a blood stem cell. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Web the walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. Internal circumferential lamellae of compact bone #2. Compact bone is enclosed, except where it's covered by articular cartilage, and is covered by the periosteum. A cross section of the bone shows compact bone and blood vessels in the bone marrow. You will also find the spongy bone histology slide drawing tutorial at the end of this article. The expanded drawing displays the internal structure. Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Internal circumferential lamellae of compact bone #2. Diagram illustrating the anatomy of a long bone. Instead, it consists of trabeculae, which are lamellae that are arranged as rods or plates. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone; Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric. Drawing shows spongy bone, red marrow, and yellow marrow. Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone; Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Web basically, in kindergarten when you drew skeletons, you were drawing compact bone. External circumferential lamellae of compact. Identify the shape of the bones shown below as: Instead, it consists of trabeculae, which are lamellae that are arranged as rods or plates. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Write your answers on the spaces provided. Inside the compact bone is the periosteum (outer fibrous layer and inner osteogenic layer), interstitial lamellae,. Drawing shows spongy bone, red marrow, and yellow marrow. Whereas compact bone tissue forms the outer layer of all bones, spongy bone or cancellous bone forms the inner layer of all bones. Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone; It is highly vascularized and contains red bone marrow. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms. Concentric lamellae of osteon or haversian system #6. Long, short, flat, sesamoid or irregular. They primarily serve to protect tendons from excess wear. There are two types of bone tissue: Describe the histology of bone tissue; Web figure 6.3.1 6.3. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Identify the shape of the bones shown below as: Spongy bone is usually located at the ends of the long bones (the epiphyses), with the harder compact bone surrounding it. Define and list examples of bone markings; Overall osteon or haversian system of bone #4. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Web the walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. Name five. Spongy bone is usually located at the ends of the long bones (the epiphyses), with the harder compact bone surrounding it. Diagram illustrating the anatomy of a long bone. Web the bone drawing on the left side of the poster displays the following from outside to inside structure: Periosteum, medullary cavity, compact bone, and spongy bone. Identify the structures that. Periosteum, medullary cavity, compact bone, and spongy bone. 459 views 1 year ago. Compact bone is enclosed, except where it's covered by articular cartilage, and is covered by the periosteum. Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Ditki is the ideal resource for. The periosteum is a thick fibrous membrane covering the entire surface of a bone and serving as an attachment for muscles and tendons. Web spongy bone tissue. The names imply that the two types differ in density, or how tightly the tissue is packed together. Center canal or haversian canal of an osteon #5. 459 views 1 year ago. Write your answers on the spaces provided. Lacunae in concentric lamellae of haversian system #7. Name five bones of the axial skeleton and five bones of the appendicular skeleton. Compact bone is enclosed, except where it's covered by articular cartilage, and is covered by the periosteum. External circumferential lamellae of compact bone #3. Web the walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. Web here in this article, you will find a short but essential description of spongy bone with slide images. So, if you are interested to learn spongy bone histology a then continue this article till the end. Overall osteon or haversian system of bone #4. Diagram illustrating the anatomy of a long bone. Web like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Web identify the anatomical features of a bone; Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Whereas compact bone tissue forms the outer layer of all bones, spongy bone or cancellous bone forms the inner layer of all bones. Also shown are red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and a blood stem cell.
Spongy Bone (Cancellous Bone) Definition & Function Biology

Spongy bone, illustration Stock Image F017/2392 Science Photo Library
Healthy Bone Structure Spongy Cancellous Bone. A Bone Is Composed Of
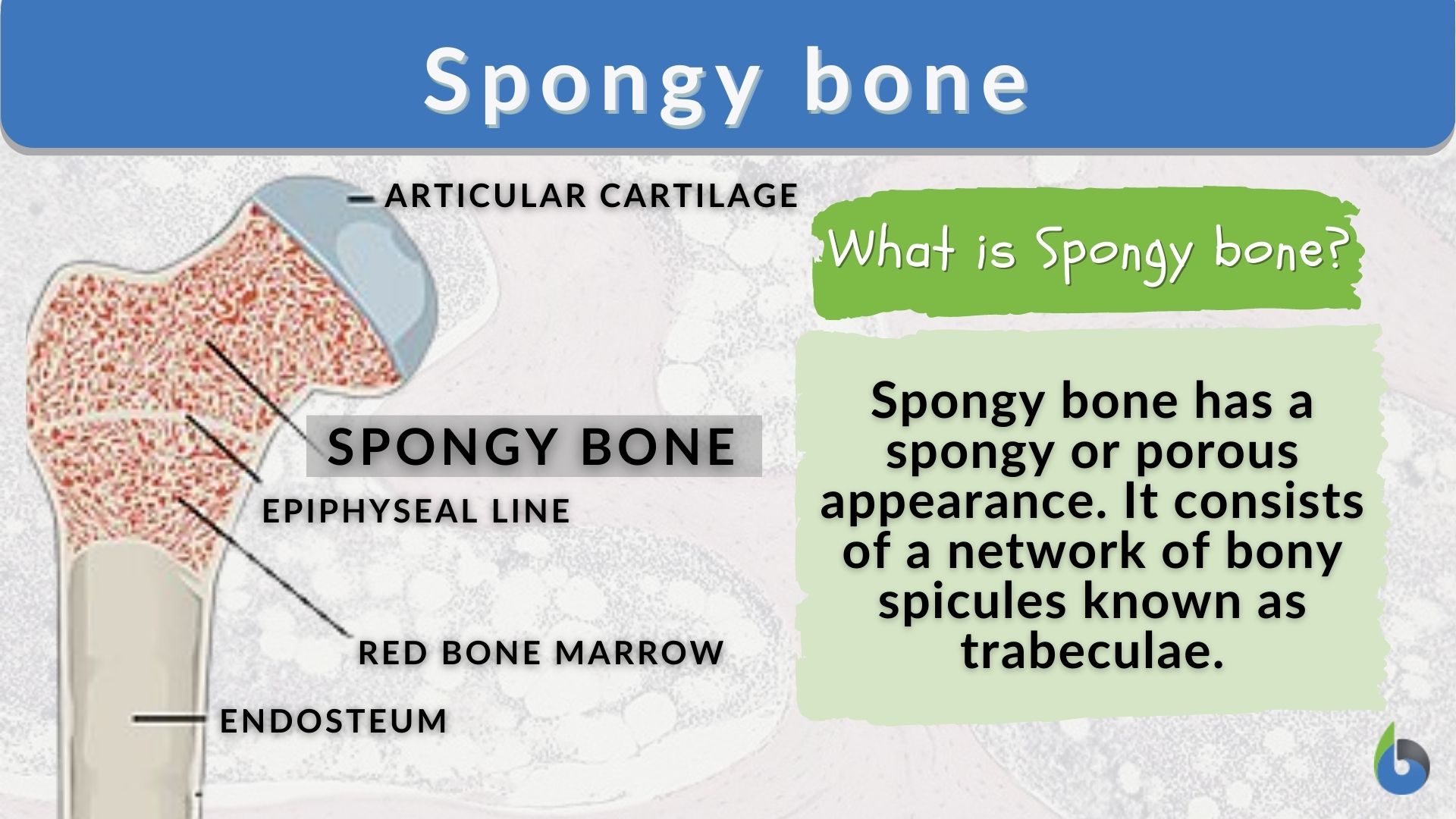
Spongy bone Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Histology Glossary Histology Spongy Bone Draw It to Know It

Spongy Bone Containg Red Bone Marrow Anatomy bones, Basic anatomy and

Explanation of bone structure. Two main types of bone include spongy

Structure of Spongy Bone

Histology of Spongy Bone YouTube
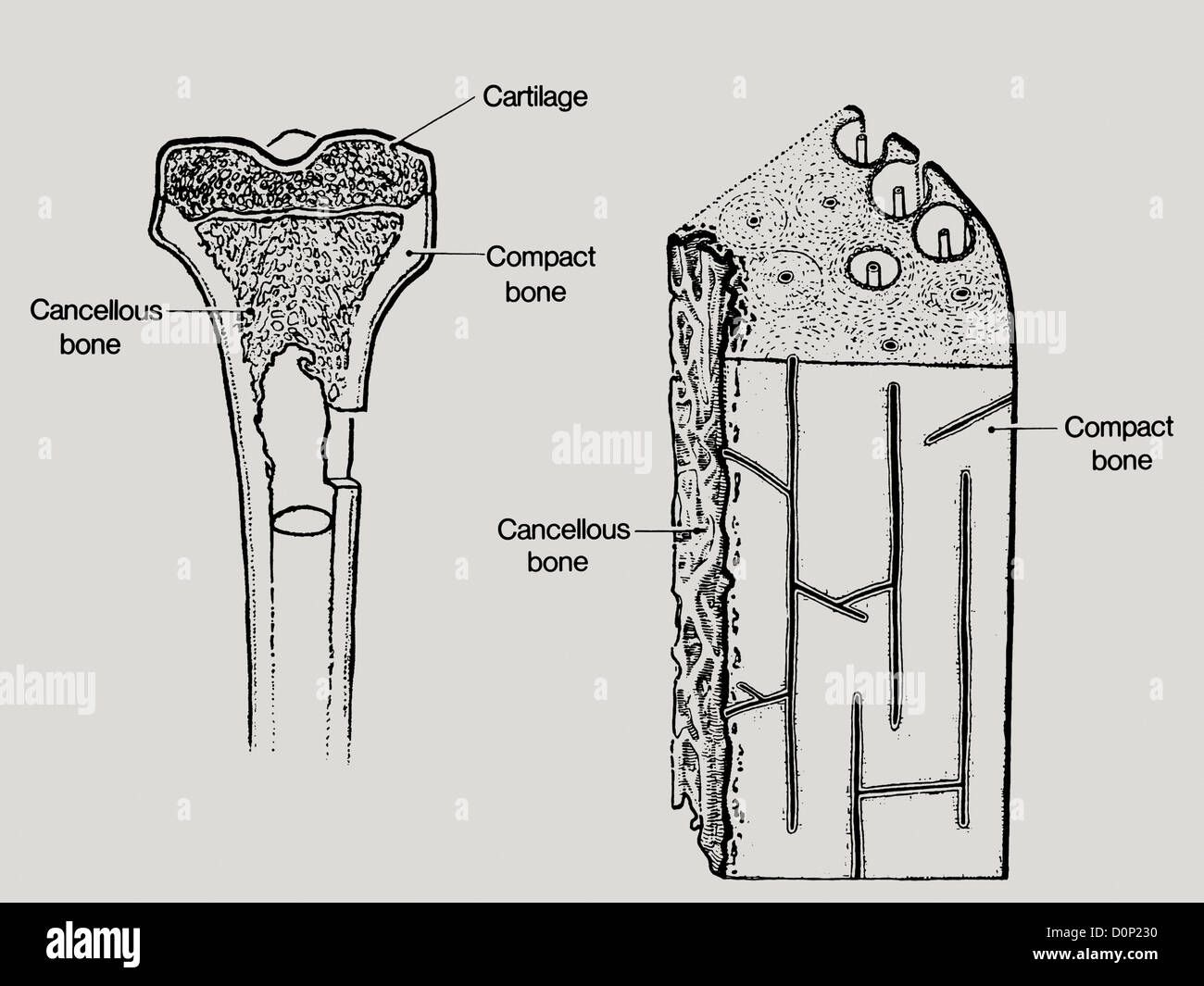
A line drawing showing the structure in bone, including cancellous or
Spongy Bone Is Usually Located At The Ends Of The Long Bones (The Epiphyses), With The Harder Compact Bone Surrounding It.
The Names Imply That The Two Types Differ In Density, Or How Tightly The Tissue Is Packed Together.
There Are Two Types Of Bone Tissue:
Long, Short, Flat, Sesamoid Or Irregular.
Related Post:
