Stoichiometry Chart Conversions Chart
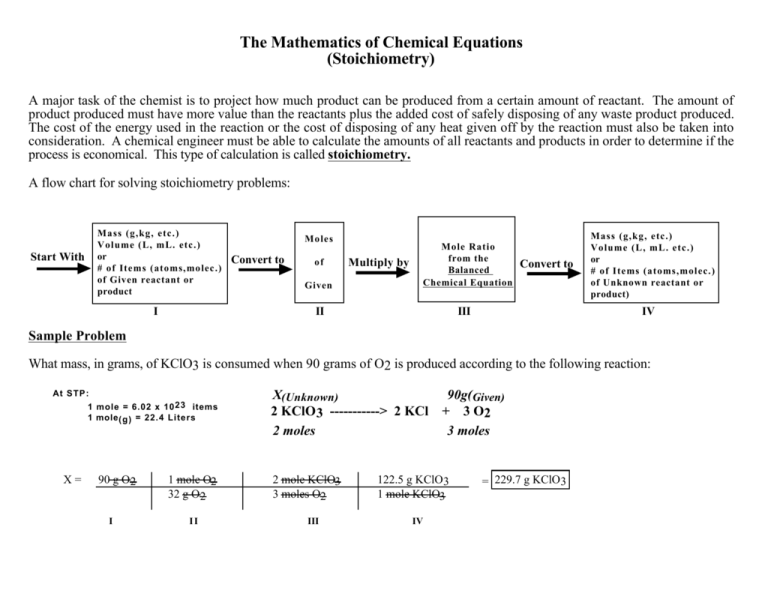
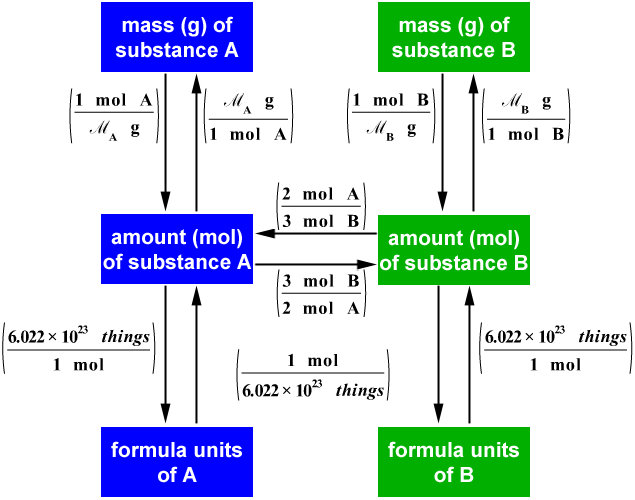
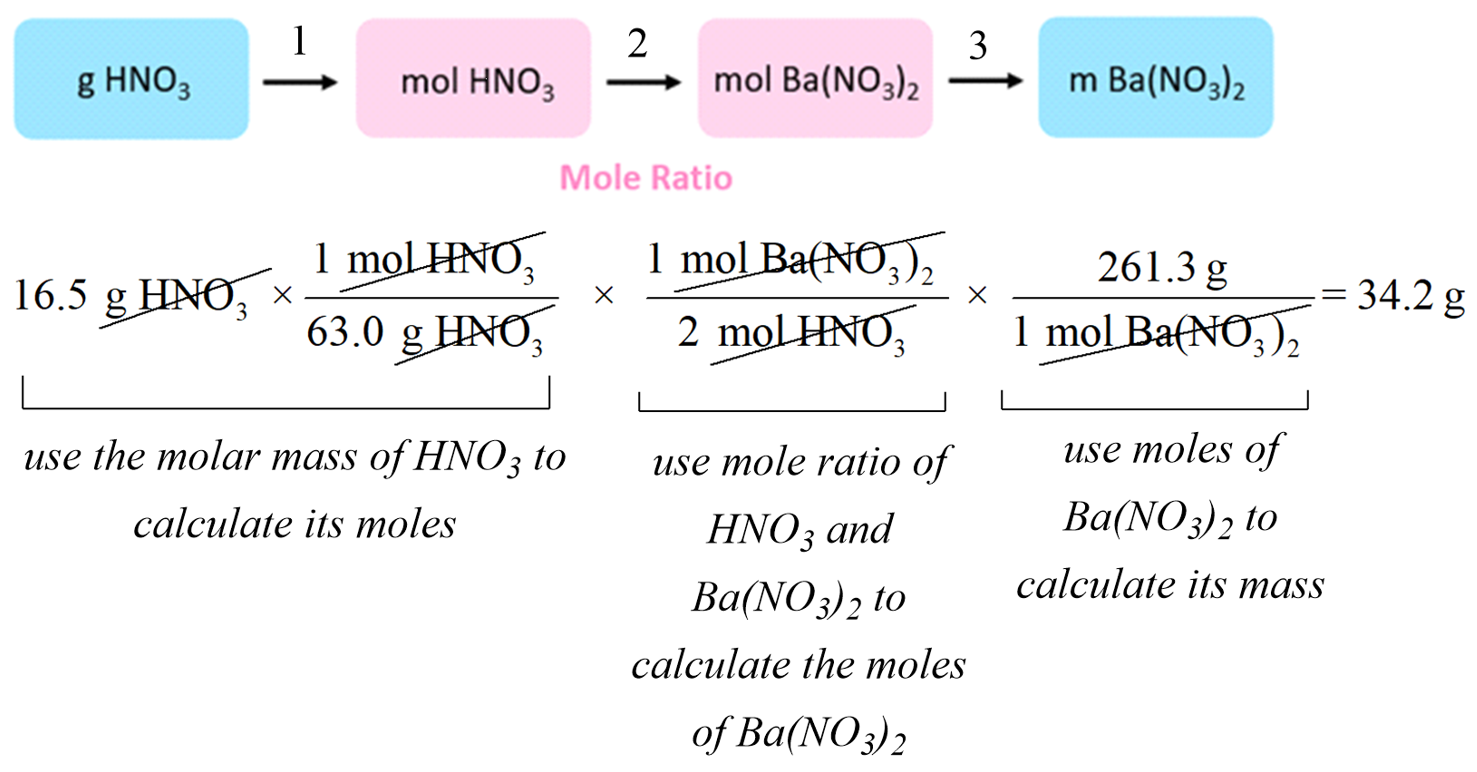
Stoichiometry Chart Conversions Chart - Web conversion table for problems below. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. N2(g) +3h2(g) → 2nh3(g) mole of n2 and 3 moles of h2 can make 2 moles of nh3. 1 gal = 3.7854 l. Web flow chart for solving stoichiometry problems: The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. The picture below is a representation of what i am saying. If you started with any unit other than moles, convert the amount to moles of “a” using dimensional analysis. Web apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a mass and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. Web you will see a selection of chart images that show different aspects of chemistry stoichiometry conversion chart, such as stoichiometry flowchart chemical conversions, how do you solve a stoichiometry problem example, smart exchange usa stoichiometry conversion chart, and more. Web you will see a selection of chart images that show different aspects of chemistry stoichiometry conversion chart, such as stoichiometry flowchart chemical conversions, how do you solve a stoichiometry problem example, smart exchange usa stoichiometry conversion chart, and more. Web stoichiometry is a set of calculations you perform to figure out how much stuff you can make in a. Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. Web the conversion factors are used to calculate the unknown quantity in the mole from the known quantity in the mole of any other reactant or product in the same chemical equation, as explained in the following examples. Volume particles particles 1 mole = molar mass (g) 1 mole = molar mass (g)) ). Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. The mass of a substance and its number of moles are related through the conversion factor of m, the molar mass expressed in g/mol. The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. Web stoichiometry tutorial for converting mass and moles using stoichiometric conversions, balanced reactions, and molecular weights. If your honors. In other words, stoichiometry is used to figure out if you’ve got enough crackers to make 30 sandwiches, or how much cheese you’ll need to make 15 sandwiches. Web apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a mass and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. The quantitative relationship between the amounts of reactants consumed. Web the conversion factors are used to calculate the unknown quantity in the mole from the known quantity in the mole of any other reactant or product in the same chemical equation, as explained in the following examples. The quantitative relationship between the amounts of reactants consumed and those of products formed in chemical reactions as expressed by the balanced. Web calculations involving conversions between moles of a substance and the mass of that substance can be done using conversion factors. 454 g = 1 lb; Web versions of conversion tables below: Web conversion table for problems below. Web common chemistry conversions english to metric conversions (mass, length, volume, and area. The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. The mass of a substance and its number of moles are related through the conversion factor of m, the molar mass expressed in g/mol. As you work your way through chemistry problems use the map to guide you. You are notified to consult an expert in case you consider. Then, you can use conversion factors to convert the grams and ml into mol and l if you want the answer in mol/l. Web conversion table for problems below. In ap/college you won't see these because we need students to be able to understand dimensional analysis (conversions) and stoichiometry. Web this means that the mole conversions for stoichiometry are the. Web calculations involving conversions between moles of a substance and the mass of that substance can be done using conversion factors. Students are given a balanced chemical equation, the amount of a reactant, and the unknown (usually the amount of a product). If you started with any unit other than moles, convert the amount to moles of “a” using dimensional. Web apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a mass and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. In general, mole ratios can be used to convert between amounts of any two substances involved in a chemical reaction. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. Web conversion table for problems below. N2(g) +3h2(g) → 2nh3(g) mole of. 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. You can use the conversion aids listed in parentheses to help. 2.54 cm = 1 inch (exact) mass: Convert the units of the given substance (a) to moles. Web mass and grade conversion factors 1 troy oz 31.1035g 1g 0.03215 troy oz 1 short ton 2000lb 907.2kg 0.9072t 1 long ton 2240lb 1016kg 1.016t 1t 2204.6lb 1.1023 short ton 0.9842 long ton 1g/t 1ppm 1mg/kg 1% 10,000 ppm 1ppm 1,000 ppb 1ppb 1,000 ppt st= short ton lt = long ton t = metric tonne. The mass of a substance and its number of moles are related through the conversion factor of m, the molar mass expressed in g/mol. As you work your way through chemistry problems use the map to guide you. Use the mole ratio to calculate the moles of wanted substance (b). To calculate a concentration, you need to divide the mass of the solute by the volume of the solvent. N2(g) +3h2(g) → 2nh3(g) mole of n2 and 3 moles of h2 can make 2 moles of nh3. The moles of a substance and the number of entities per mole are related by the conversion factor, avogadro’s number. 1 gal = 3.7854 l. Web in chemistry the most common way to describe concentration is with molarity (mol/l). 454 g = 1 lb; Web chemistry english to metric conversion chart bmpo. Web the conversion factors are used to calculate the unknown quantity in the mole from the known quantity in the mole of any other reactant or product in the same chemical equation, as explained in the following examples.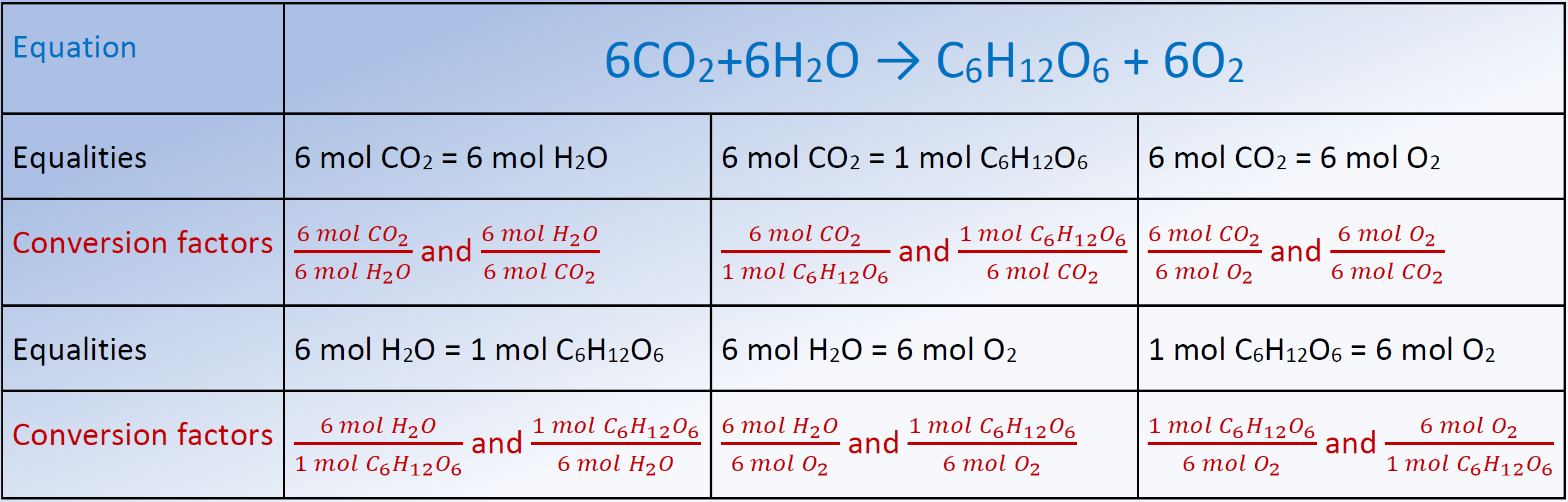
Chemistry Conversion Chart Moles

Stoichiometry Lessons TES chemistry & physics Pinterest

The Stoichiometric Chart YouTube
Stoichiometry Conversions Chart chegos.pl
C&J&S&B's Class Chemisty ) What is Stoichiometry?

Chem Gas Stoichiometry Scientific Tutor

Extended Reaction Stoichiometry Road Map — Examples Expii

Molecular Weight and Stoichiometry Explained in Simple Steps

Stoichiometry Introduction Using Stoich Tables YouTube
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions Chemistry Steps
Students Are Given A Balanced Chemical Equation, The Amount Of A Reactant, And The Unknown (Usually The Amount Of A Product).
1 Inch = 2.54 Centimeters.
Volume Particles Particles 1 Mole = Molar Mass (G) 1 Mole = Molar Mass (G)) ) 1 Mole = 6.02E23 (Particles) Molecules/Atoms 1 Mole = 6.02E23 (Particles) Molecules/Atoms.
Web Chose Your Starting Point (“A”) By What Units You Have To Start With:
Related Post: