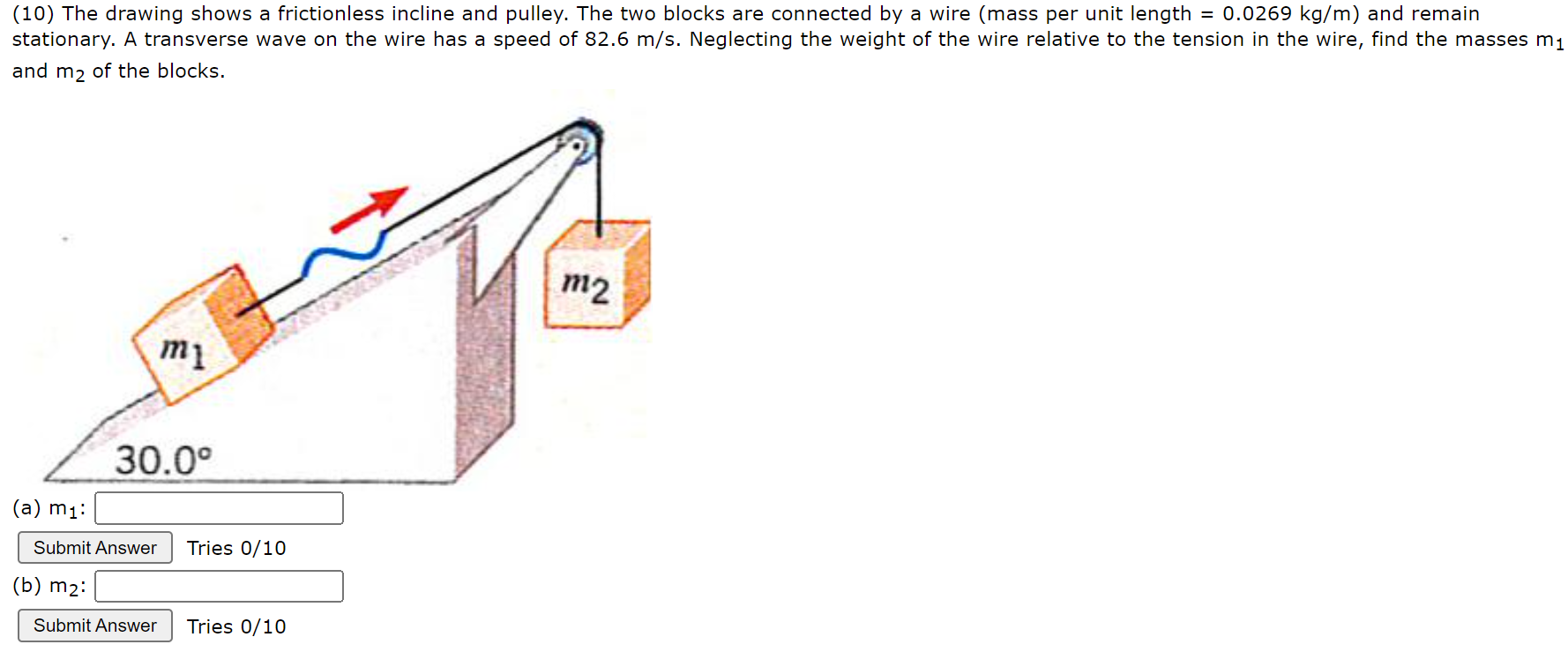
The Drawing Shows A Frictionless Incline And Pulley
The Drawing Shows A Frictionless Incline And Pulley - A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. A transcerse wave on the wire has a speed of 60m/s relative to it. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, find the masses m1 and m2 of the blocks. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length = 0.0250 kg/m) and remain stationary. Applying newton's second law and substituting the numerical value yields \begin{gather*} f_{net}=ma_x \\\\ mg\sin\theta=ma_x \\\\ \rightarrow a_x=g\sin\theta \\\\ a_x=(9.8) \sin 15^\circ \\\\ \rightarrow \boxed{a_x=2.6\,\rm m/s^2}. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The mass per unit length of the cord is 1.12×10−2 kg/m, so the mass of the cord is negligible compared to the mass of the block. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length = 0.0199 kg/m) and remain stationary. This is the ideal pully at the top of the plane of wire passing over the pulley holding another block of mass m M2 in 1 30.0 (a. And this incline is at 30 degrees, and let's step it up let's make it hard, let's say the coefficient of kinetic friction between the incline and the 4kg mass is 0.2. M2 in 1 30.0 (a. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. Web the free body diagrams for the two masses are shown in figure 2. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length = 0.0199 kg/m) and remain stationary. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, find the masses (a) m1 and (b) m2 of the blocks. Web physics question the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The cord is being vibrated at a frequency of 154 hz. Web the drawing shows a. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length, `mu = 25 g//m` ) and remain stationary. Web we've got a 9kg mass hanging from a rope that rope passes over a pulley then it's connected to a 4kg mass sitting on an incline. This is the plane which is inclined at an angle and it is. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length = 0.0199 kg/m) and remain stationary. It is equal to 30.0 degree. A transcerse wave on the wire has a. And this incline is at 30 degrees, and let's step it up let's make it hard, let's say the coefficient of kinetic friction between the incline and the. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. Neglect the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 75.0 m/s. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. A transcerse wave on the wire has a speed of `60 m//s` relative to it. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length, μ = 25g/m ) and remain stationary. A transverse. The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 72.4 m/s. Neglect the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire. This is the ideal pully at the top of the plane of wire passing over the pulley The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, find the masses (a) m1 and (b) m2 of the blocks. The degree is 30.0 degrees. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, find the masses m1 and m2 of the blocks. And this incline is at 30 degrees, and let's. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. This is a plane that is inclined at an angle. The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 75.0 m/s. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 75.0 m/s. We will use the airtrack to create a frictionless plane and also assume that the pulley is frictionless with uniform tension in the string. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 75.0 m/s. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, find the masses (a) m1m1 and (b) m2m2 of the blocks. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. Web the drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. A transverse wave on the wire has a speed of 60m/s relative to it. The two blocks are connected by a wire (mass per unit length, μ = 25 g/m μ = 25 g / m) and remain stationary. The mass per unit length of the cord is 1.12×10−2 kg/m, so the mass of the cord is negligible compared to the mass of the block. Neglect the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire. This is the ideal pully at the top of the plane of wire passing over the pulley holding another block of mass m This is the plane which is inclined at an angle and it is a given problem. A transcerse wave on the wire has a speed of `60 m//s` relative to it. Neglecting the weight of the wire relative to the tension in the wire, f i nd the masses m1 and m2 of the blocks. Web we've got a 9kg mass hanging from a rope that rope passes over a pulley then it's connected to a 4kg mass sitting on an incline. So there's going to be. Blocks 1 and 2 were kept over the inclined plane.
The figure shows a frictionless incline plane and sm... Physics

SOLVED The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The two
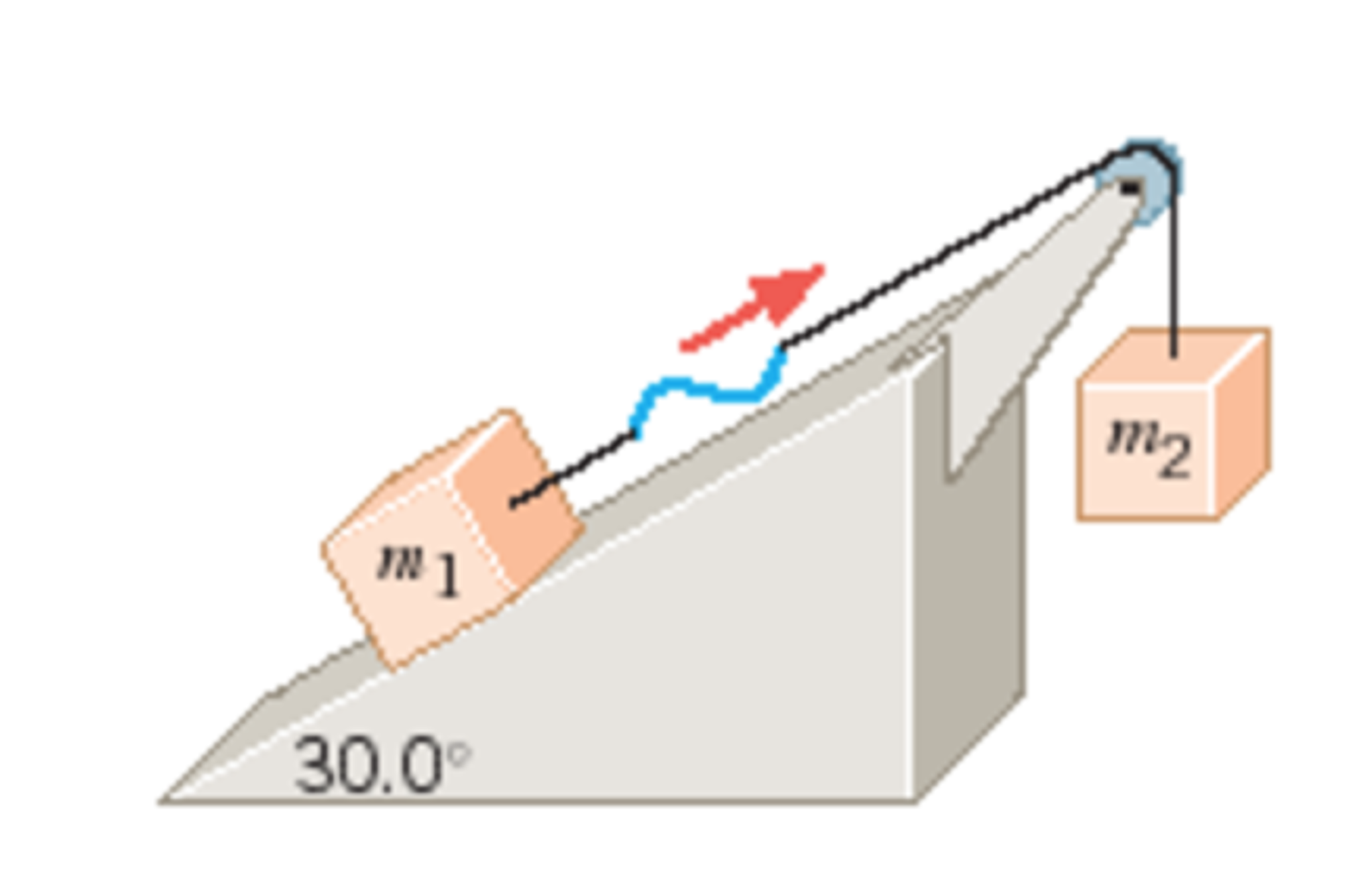
Solved The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley.
[Solved] . The following drawing shows two frictionless inclines that

Science compound machine pulley and inclined plane diagrams

SOLVED The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley The two
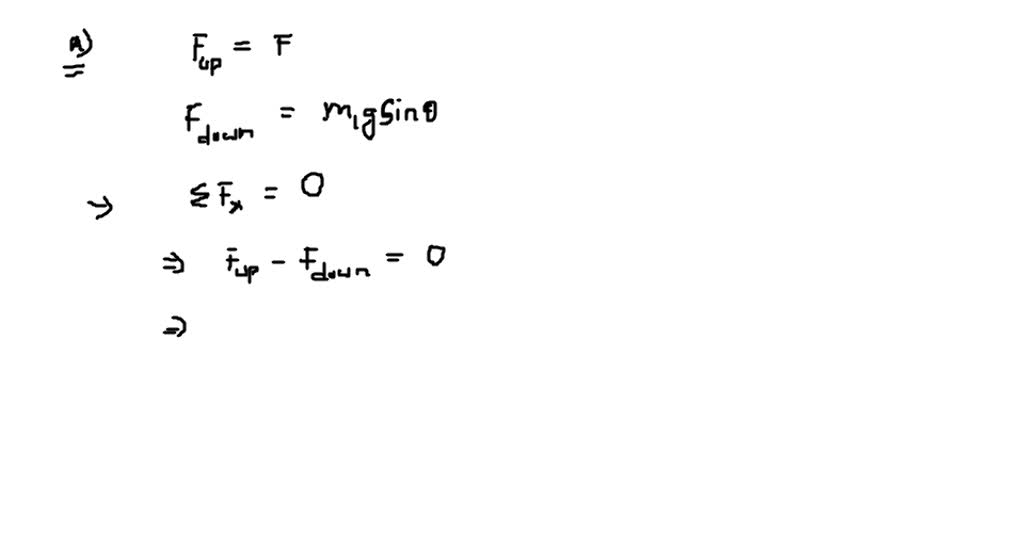
SOLVEDThe drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The two
Solved (10) The drawing shows a frictionless incline and
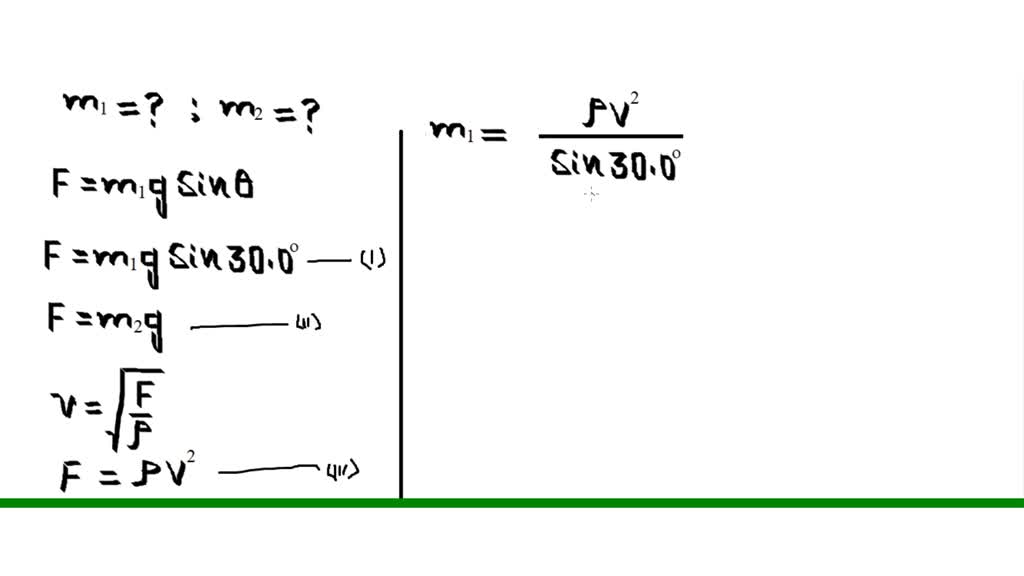
SOLVEDThe drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The two

The drawing shows a frictionless incline and pulley. The two blocks ar
Neglecting The Weight Of The Wire Relative To The Tension In The Wire, Find The Masses (A) M1 And (B) M2 Of The Blocks.
Neglecting The Weight Of The Wire Relative To The Tension In The Wire, Find The Masses (A) M1 And (B) M2 Of The Blocks.
The Two Blocks Are Connected By A Wire (Mass Per Unit Length = 0.0367 Kg/M) And Remain Stationary.
A Transverse Wave On The Wire Has A Speed Of 65.1 M/S.
Related Post: