This Chart Demonstrates That The Marginal Cost
This Chart Demonstrates That The Marginal Cost - The price will rise to encourage the. Web marginal and average costs q = q = q = t c ( q ) = 64 + q 2 4 ⇒ t c ( 4 ) = 68.00 \\textcolor{#d62728}{tc(q) = 64 + {q^2 \\over 4} \\rightarrow tc(4) = 68.00} t c ( q ) = 6. Web this web page contains 50 flashcards for an economics exam, covering topics such as demand, supply, market structure, and policy. Web marginal cost is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit. Last updated february 20, 2024. Web in economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. Marginal cost refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of a good. The marginal cost of production may be defined as the costs incurred for each extra output produced. You must know several production variables, such as fixed costs and. Learn how to calculate marginal cost, its benefits, and its impact on. See examples and explanations of how these curves help. If average cost is the cost of the average unit of output produced, marginal cost is the cost of each individual unit. For example, when a factory is. The marginal cost curve is u shaped because initially when a. Web marginal cost is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit. Web learn what marginal cost is, how to calculate it, and how it affects production decisions. See how marginal cost, average cost, fixed cost, variable cost and total cost are related. Learn how to calculate marginal cost, its benefits, and its. From figure 8.3 , we can see that the marginal cost curve crosses. You must know several production variables, such as fixed costs and. Web what is the marginal cost of production? The cost of producing additional quantity. Web understand that every factor of production has a corresponding factor price. Web marginal and average costs q = q = q = t c ( q ) = 64 + q 2 4 ⇒ t c ( 4 ) = 68.00 \\textcolor{#d62728}{tc(q) = 64 + {q^2 \\over 4} \\rightarrow tc(4) = 68.00} t c ( q ) = 6. The marginal cost of production may be defined as the costs incurred. Web the other way of measuring cost per unit is marginal cost. See the video, transcript, questions and tips on this web. However, it does not contain any. It is the addition to total cost from selling one extra. See how marginal cost relates to marginal product of labor. Web learn how to find the optimal production quantity using marginal revenue and marginal cost with an orange juice example. The price will fall to encourage consumers to continue to purchase it. The marginal cost curve is u shaped because initially when a firm increases its output, total. You must know several production variables, such as fixed costs and. It. The price will rise to encourage the. They're just thinking about the. Web marginal cost is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit. However, it does not contain any. The marginal cost curve is u shaped because initially when a firm increases its output, total. Web marginal cost is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit. See how marginal cost, average cost, fixed cost, variable cost and total cost are related. Web marginal cost is the increase in cost caused by producing one more unit of the good. Web learn how to calculate marginal cost, the increase. Web learn how to find the optimal production quantity using marginal revenue and marginal cost with an orange juice example. Web learn what marginal cost is, how to calculate it, and how it affects production decisions. Web marginal and average costs q = q = q = t c ( q ) = 64 + q 2 4 ⇒ t. See how marginal cost affects economies of. Initially decreases as production increases. Web understand that every factor of production has a corresponding factor price. Web learn how to calculate marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost using a table and a spreadsheet. Marginal cost is the cost of producing an extra unit. Web 28 november 2014 by tejvan pettinger. See the marginal cost curve and its shape, and compare it with marginal benefit. Web what will most likely happen to the price of the old model, and why? Web the marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost curves are derived from the total cost curve. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. See the video, transcript, questions and tips on this web. Web learn how to find the optimal production quantity using marginal revenue and marginal cost with an orange juice example. Initially decreases as production increases. See how marginal cost, average cost, fixed cost, variable cost and total cost are related. Web learn how to graph marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost curves and how they relate to each other. If average cost is the cost of the average unit of output produced, marginal cost is the cost of each individual unit. Web learn how to calculate marginal cost, the increase in total production cost when producing one more unit of a good. It is the addition to total cost from selling one extra. They're just thinking about the. See examples and explanations of how these curves help. The price will rise to encourage the.
Marginal cost and supply curve lasopadelta

This Chart Demonstrates That The Marginal Cost
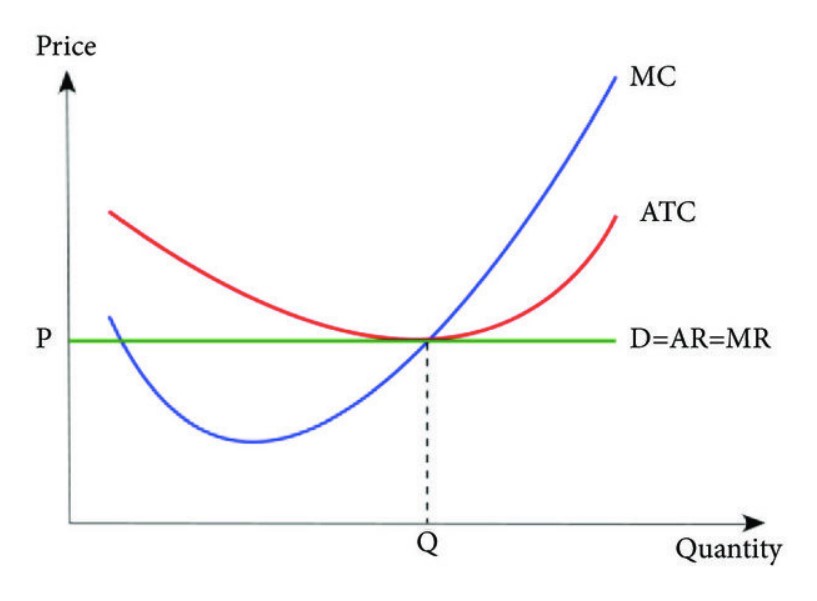
Marginal Cost Formula and Calculation
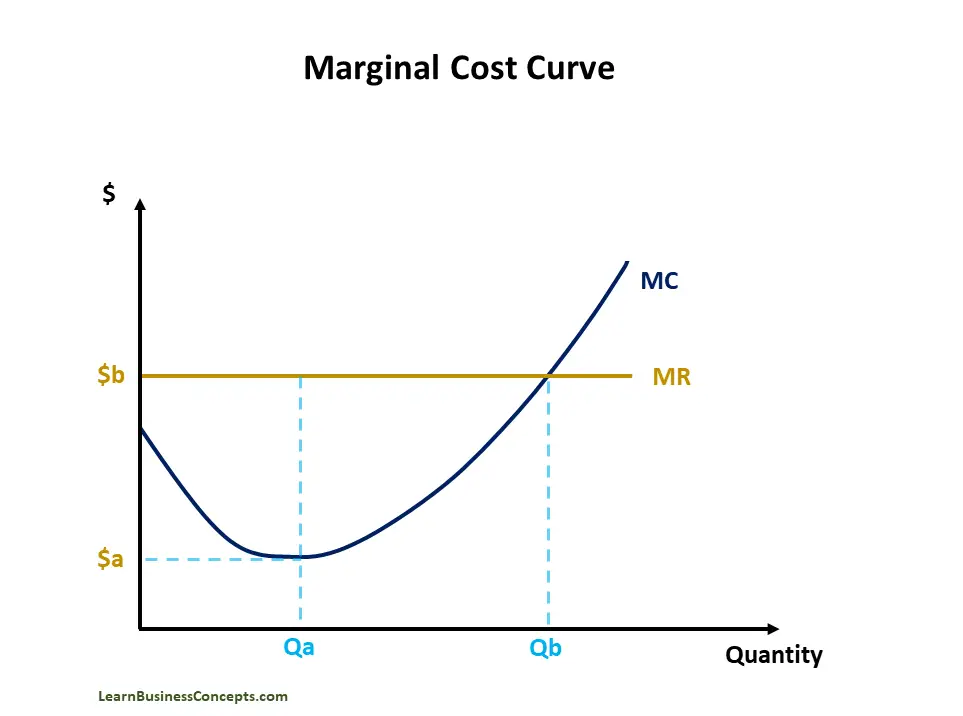
What is Marginal Cost? Explanation, Formula, Curve, Examples

Understanding the shape of a Marginal Cost Curve Questions and Answers
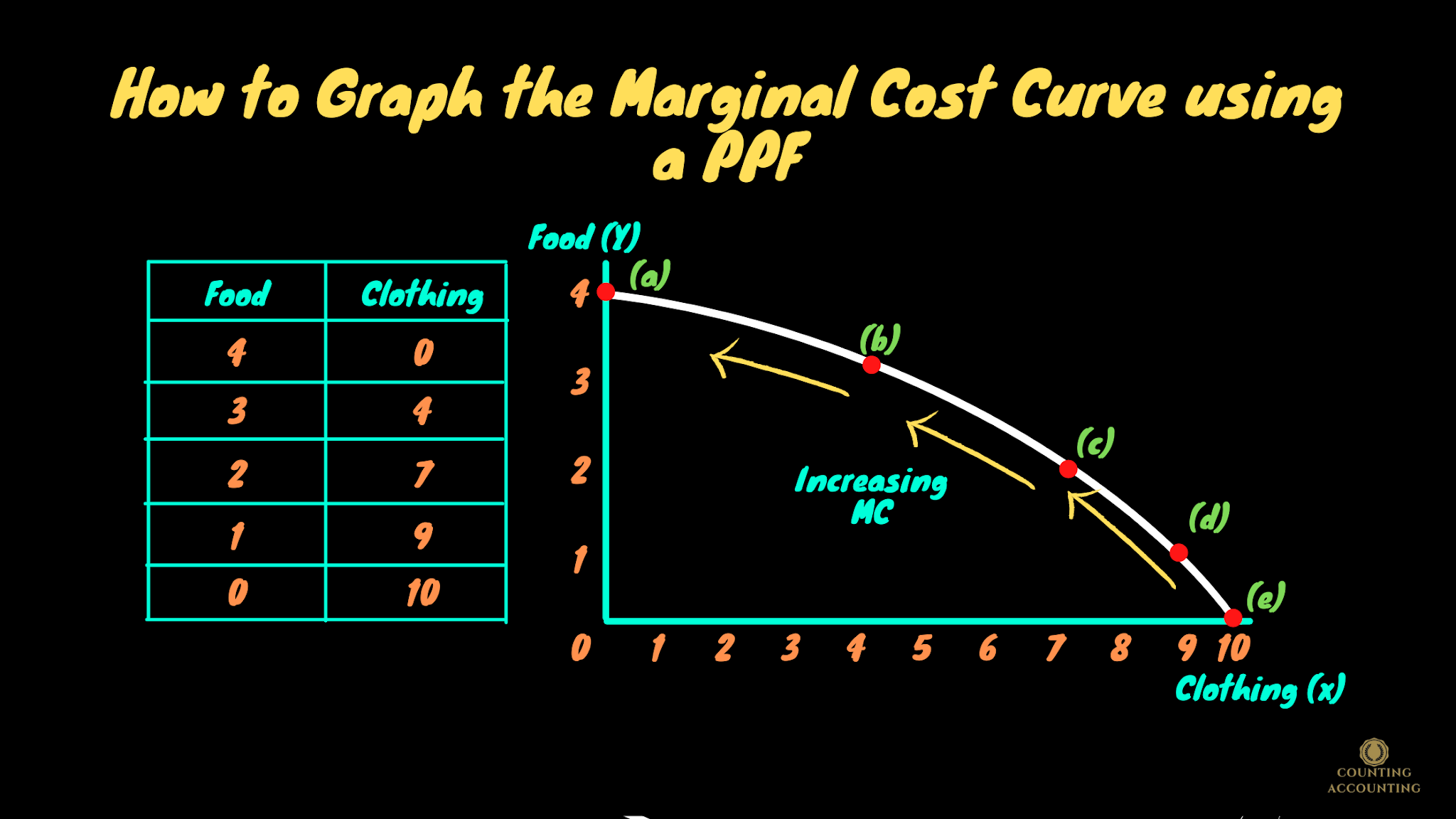
How to Draw or Graph the Marginal Cost Curve using a PPF? Marginal Cost
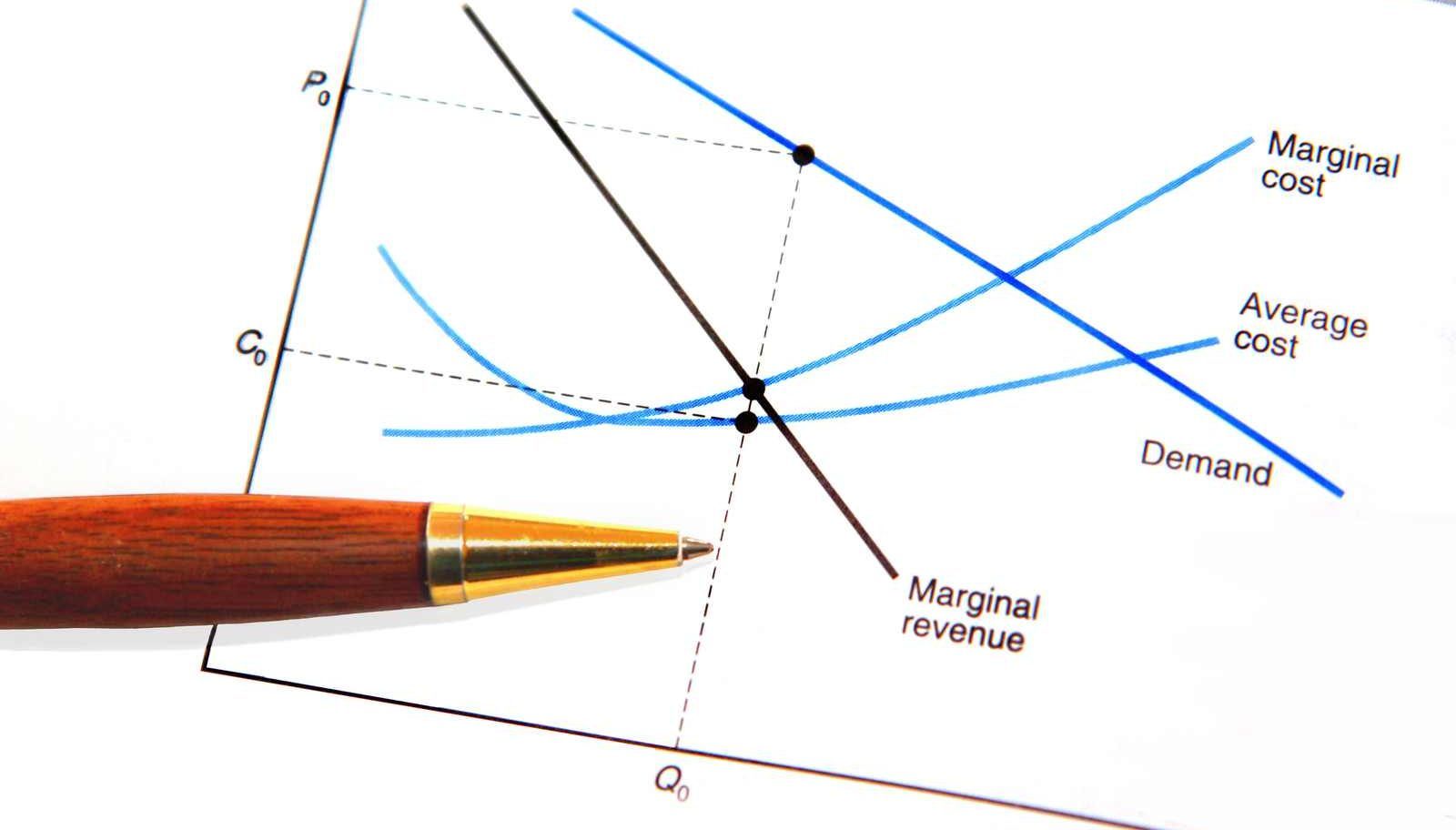
Marginal cost Definition, formulas, curves and more It Lesson Education

What Is the Marginal Cost Formula? (Calculation + Examples) Hourly, Inc.
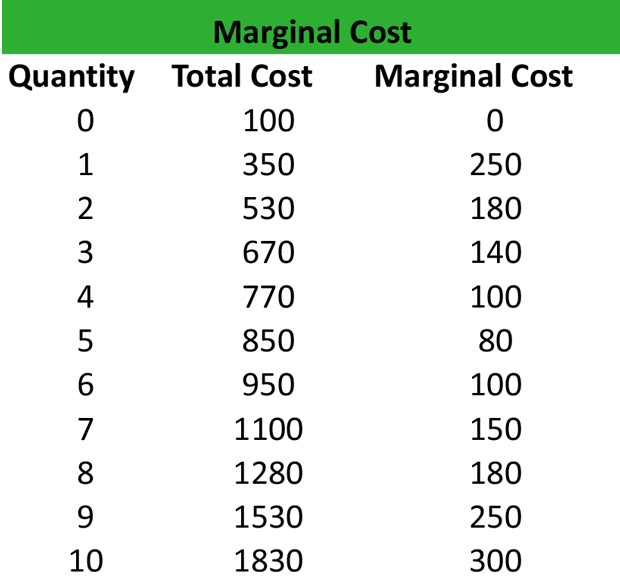
Cara Menghitung Marginal Cost

This Chart Demonstrates That The Marginal Cost Understanding Marginal
Web What Is The Marginal Cost Of Production?
Web In Economics, The Marginal Cost Is The Change In The Total Cost That Arises When The Quantity Produced Is Increased, I.e.
Last Updated February 20, 2024.
See How Marginal Cost Affects Economies Of.
Related Post: