Txv Subcooling Chart
Txv Subcooling Chart - Adjusting txv for subcooling is an essential skill for maintaining an efficient hvac system. Shroud on the outdoor ac unit, on the back side of the shroud, should have something like “target subcooling 12°f”. The indoor wet bulb reading reflects the total heat of the air and, therefore, the total loading on. A dirty or clogged filter drier is a potential culprit, especially since they are most often installed upstream from txvs. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll find every detail you need, explained in straightforward terms, to make this task as smooth as possible. General requirements for all long line set applications. Web as the thermostatic expansion valve regulates the rate at which liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator, it maintains a proper supply of refrigerant by matching this flow rate against how quickly the refrigerant evaporates (boils off) in the evaporator coil. Web txv’s control the superheat. Web this target superheat chart (r22, r410a, r134a examples) and this target subcooling temperature can also be useful. A decrease in liquid temperature (suction line). Superheat is the difference between the refrigerant vapor temperature and its saturation temperature. The indoor wet bulb reading reflects the total heat of the air and, therefore, the total loading on. Best practices and tips for adjusting the txv valve. These txvs incorporate a check valve for heat pump system applications. Web txv’s control the superheat. Adjusting txv for subcooling is an essential skill for maintaining an efficient hvac system. Best practices and tips for adjusting the txv valve. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll find every detail you need, explained in straightforward terms, to make this task as smooth as possible. To properly charge a system with an expansion valve (txv) you must charge by subcooling.. Web normally the charts will require an indoor wet bulb temperature reading as well as an outdoor dry bulb temperature reading. High superheat high subcooling caused by restriction in the liquid line (1st cause) Then take the temperature of the liquid line as close to evaporator as possible before the metering device. Do not use mercury or dial type thermometers.. Easy way to remember what superheat is: Do not use mercury or dial type thermometers. These txvs incorporate a check valve for heat pump system applications. A dirty or clogged filter drier is a potential culprit, especially since they are most often installed upstream from txvs. General requirements for all long line set applications. To properly charge a system with an expansion valve (txv) you must charge by subcooling. Web this 3d video shows setting a charge by subcool on a txv system in 3d. The method used to charge a system depends on the metering device. Web as the thermostatic expansion valve regulates the rate at which liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator,. Web check subcooling at both the condenser outlet and the txv inlet prior to adding any refrigerant. Take the high side pressure and convert it to temperature using chart or gauge. Web a txv is designed to maintain a constant superheat. Monitoring and recording system performance data. You can get a list of subcooling temperatures, depending on the outdoor temperature. Dealing with excessive or insufficient refrigerant charge. Shroud on the outdoor ac unit, on the back side of the shroud, should have something like “target subcooling 12°f”. Web the thermostatic expansion valve (tev) controls the flow of liquid refrigerant entering the direct expansion (dx) evaporator by maintaining a constant superheat of the refrigerant vapor at the outlet of the evaporator.. General requirements for all long line set applications. Maintaining a systematic approach during adjustments. Use a digital thermometer for all temperature measurements. Web subcooling on systems that use a thermostatic expansion valve (txv) should be approximately 10 ° f to 18 ° f. Web txv’s control the superheat. The indoor wet bulb reading reflects the total heat of the air and, therefore, the total loading on. Do not use mercury or dial type thermometers. To charge a fixed metering device system (piston) you must use superheat. The method used to charge a system depends on the metering device. Superheat is the difference between the refrigerant vapor temperature and. Web subcooling on systems that use a thermostatic expansion valve (txv) should be approximately 10 ° f to 18 ° f. Web this 3d video shows setting a charge by subcool on a txv system in 3d. Take the high side pressure and convert it to temperature using chart or gauge. Higher subcooling indicates excess refrigerant backing up in the. Many techs will say that subcooling is how you “set a charge” on a txv/tev/eev metering device system. In limited cases, the subcooling won’t be just one number. Dealing with excessive or insufficient refrigerant charge. Web this target superheat chart (r22, r410a, r134a examples) and this target subcooling temperature can also be useful. Easy way to remember what superheat is: The method used to charge a system depends on the metering device. Web however, you must look for the proper design subcooling for the particular system you are working on. The photo shows both sides of the tool. For any residential split system installed with a long line set, 3/8” liquid line size must be used. General requirements for all long line set applications. Web this 3d video shows setting a charge by subcool on a txv system in 3d. Web a txv is designed to maintain a constant superheat. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). To properly charge a system with an expansion valve (txv) you must charge by subcooling. Superheat is the difference between the refrigerant vapor temperature and its saturation temperature. Equivalent length must be used to determine acceptability of any long line set application.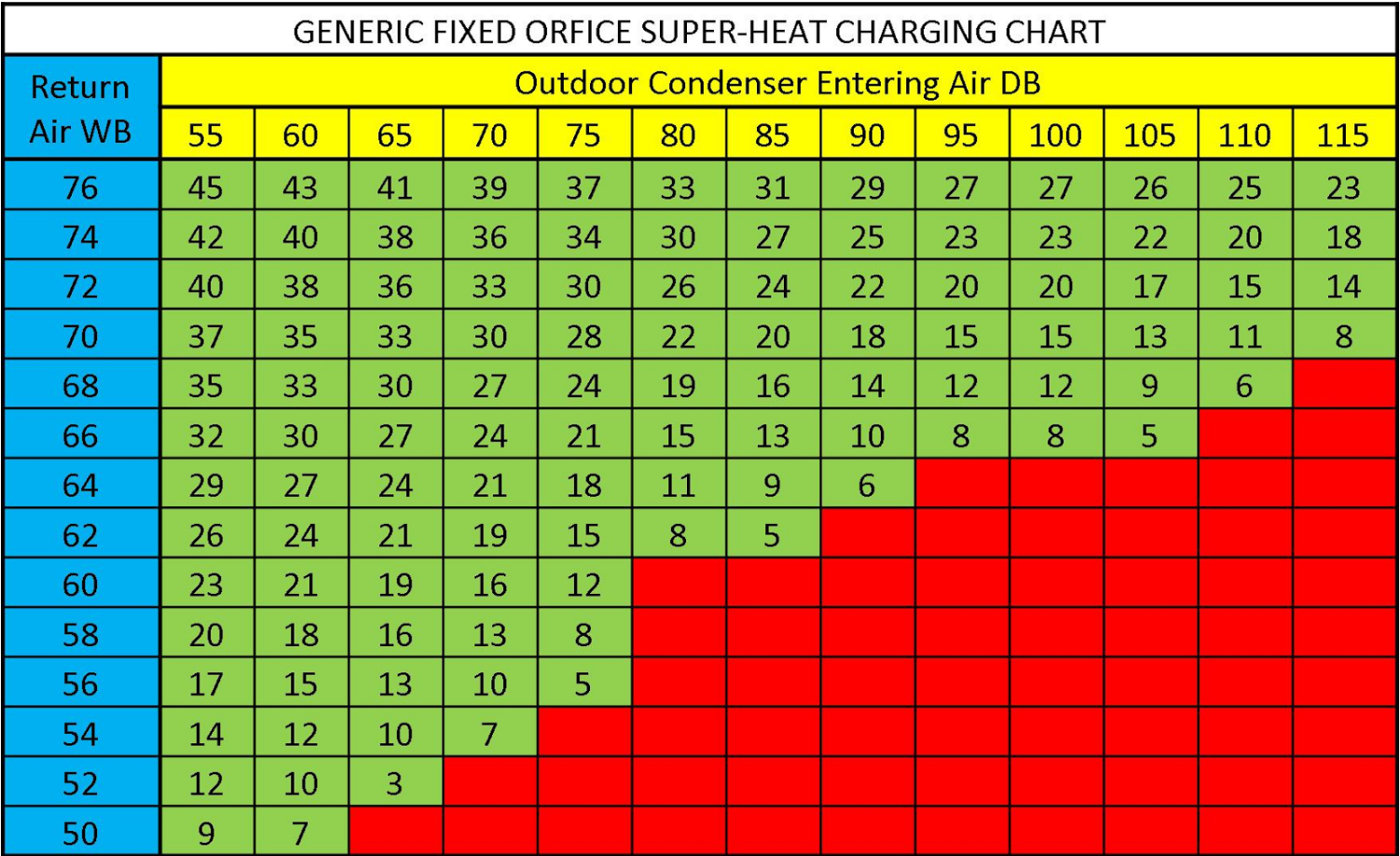
Subcool And Superheat Chart
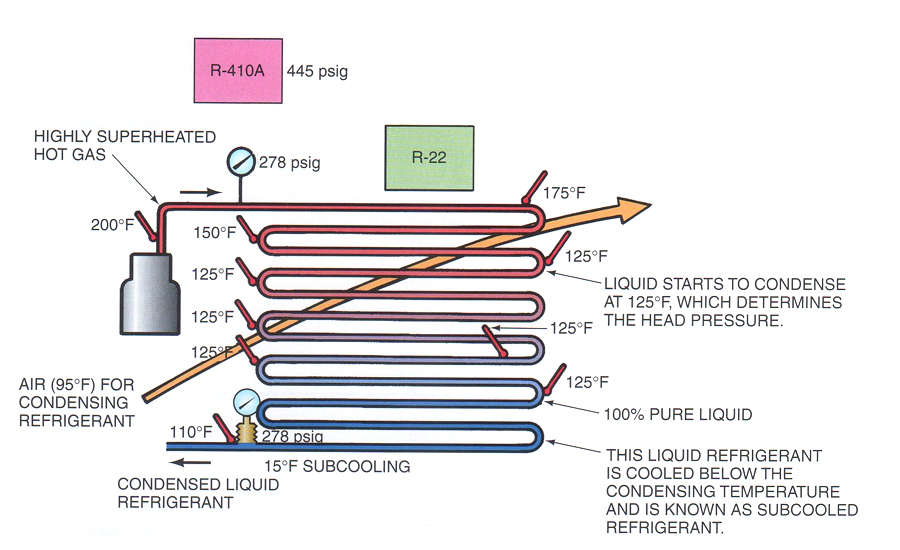
Btu Buddy 171 Charging a TXV System for Subcooling 20170619
R 22 Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart TXV TEV

R 22 Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart TXV TEV

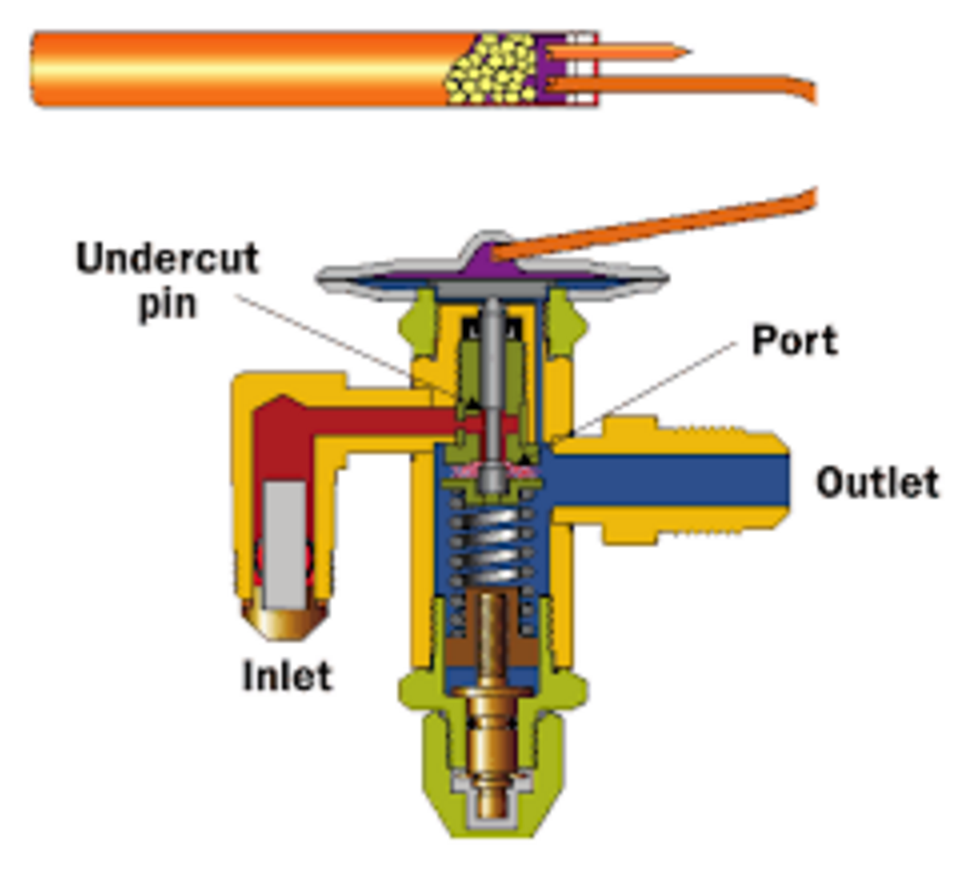
Piston vs. TXV Metering Devices HVAC School

Superheat And Subcool Chart

Hvac Piston Size Chart
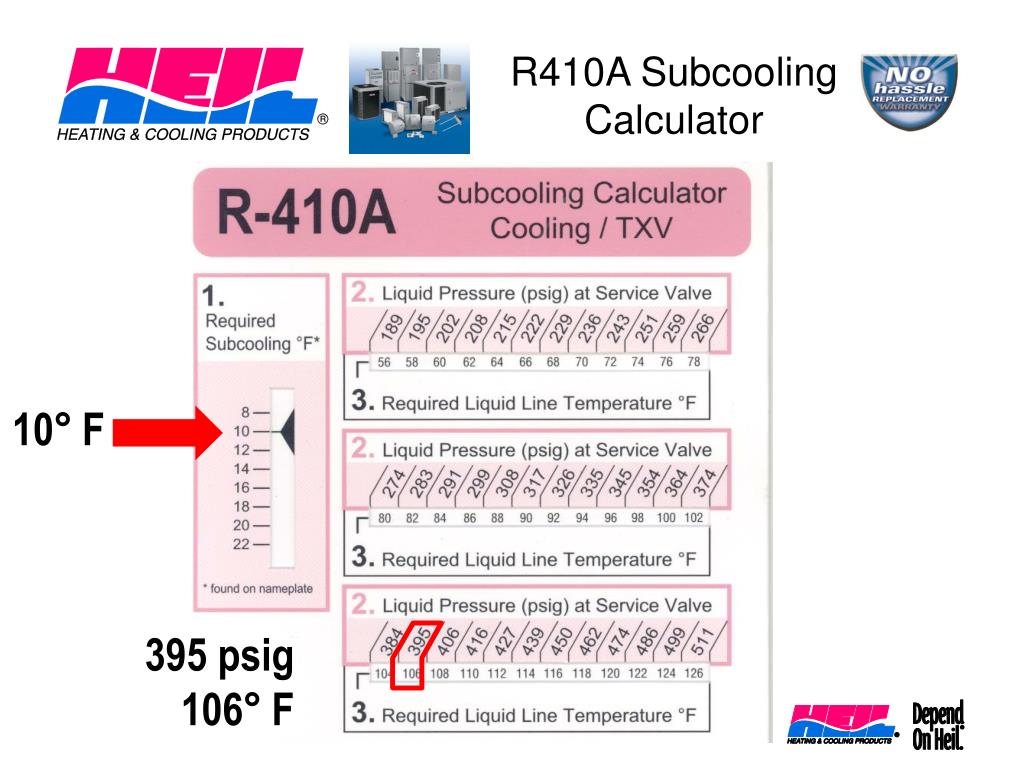
PPT TXV Devices PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3546979

R410a Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart for TXV Tev

R 22 Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart TXV TEV eBay
The Indoor Wet Bulb Reading Reflects The Total Heat Of The Air And, Therefore, The Total Loading On.
A Decrease In Liquid Temperature (Suction Line).
Seeking Professional Help When Necessary.
Best Practices And Tips For Adjusting The Txv Valve.
Related Post: