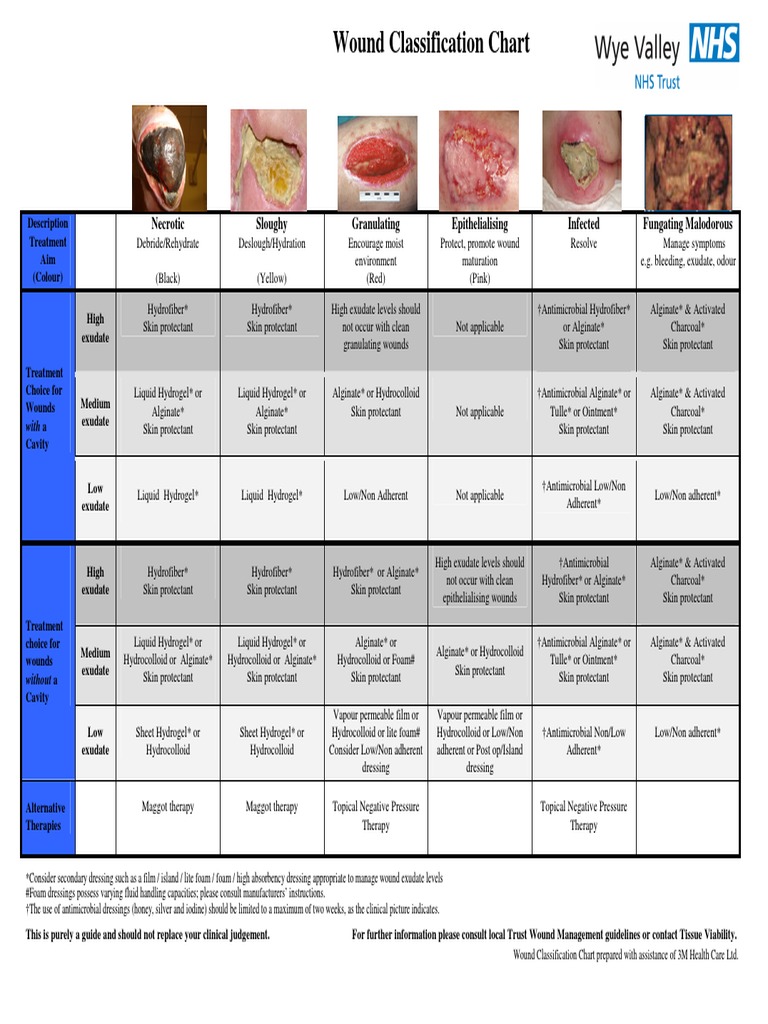
Wound Exudate Chart
Wound Exudate Chart - Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment for the patient. Maintaining a moist wound healing environment. The production of serous drainage is a typical response from the body during the normal inflammatory healing stage. Completing a holistic assessment improves continuity of care and can enhance communication with the patient (and / or carers) regarding their wound. Table 1 shows an example of descriptions of exudate levels. Web a better gauge of volume is to assess the dressing type and its wear time. Use alginate dressings, or hydroactive dressings, or foam dressings. Exudate production forms part of the normal wound healing process and can be beneficial to healing, by: Explain the potential complications in wound care. Web this activity addresses protocol for wound assessment for the interprofessional team during initial and subsequent wound assessments to best classify and treat a wound to enhance outcomes. Additional considerations include presence of pain and/or infection. Yet, if there is a large amount of serous drainage, it can be the result of a high bioburden count. Web exudate is a good indicator of the state of the wound. Web clinicians have described wound exudate as ‘fluid coming out of the wound’, ‘wound fluid’ and ‘an excess of normal. Web any alteration in exudate levels and characteristics may indicate a change in wound status and as such wound management should be reassessed as necessary. Completing a holistic assessment improves continuity of care and can enhance communication with the patient (and / or carers) regarding their wound. Maintain moist environment, absorb exudate, and promote epithelialisation. Web exudate consists of fluid. This may include infection, inflammation, or oedema. Web how to classify and document wound exudate. However, exudate can delay healing when in the wrong amount, in the wrong place, or of the wrong composition. Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment. Web wound assessment requires a multifaceted approach; Skin erosion due to prolonged exposure to moisture (caused by its components) masd: Describe the initial assessment of a wound. Additional considerations include presence of pain and/or infection. Softening or breakdown of the skin due to prolonged exposure to moisture excoriation: Maintain moist environment, absorb exudate, and promote epithelialisation. Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment for the patient. Explain the potential complications in wound care. Web superficial granulating wound with high exudate aim: Skin erosion due to prolonged exposure to moisture. Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment for the patient. Web when assessing and documenting a wound, it is important to note the amount and type of wound exudate (drainage). Serous drainage is clear, thin, and watery. Web it is mandatory. Exudate plays a key role in wound healing. Web exudate consists of fluid that has leaked out of blood vessels and closely resembles blood plasma (wuwhs, 2019). Web when assessing and documenting a wound, it is important to note the amount and type of wound exudate (drainage). Use alginate dressings, or hydroactive dressings, or foam dressings. Web proper assessment includes. There may be diabetes and pressure characteristics. Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment for the patient. Each color and consistency of wound drainage has specific significance with regard to wound management. There are 3 overall areas of wound assessment and. Serous drainage is clear, thin, and watery. Web how to classify and document wound exudate. The goal of wound management is to understand the different stages of wound healing and treat the wound accordingly. Skin erosion due to prolonged exposure to moisture (caused by its components) masd: Wound exudate is produced as a natural and essential part of the healing. There may be diabetes and pressure characteristics. Explain the potential complications in wound care. Web when assessing and documenting a wound, it is important to note the amount and type of wound exudate (drainage). Understanding what causes changes in its amount, colour, consistency and odour enables more effective wound management which promotes quicker healing, and minimises maceration, discomfort and embarrassment. The production of serous drainage is a typical response from the body during the normal inflammatory healing stage. Web superficial granulating wound with high exudate aim: If exudate changes in colour, smell, viscosity or volume then its time to reassess the wound. Web how to classify and document wound exudate. Each color and consistency of wound drainage has specific significance with regard to wound management. The frequency of dressing changes, how saturated the dressing is on removal, and the condition of the surrounding skin at each dressing change are good indicators of exudate volume. Maintaining a moist wound healing environment. Consider the reasons for the change in exudate production and treat the underlying cause. Skin erosion due to prolonged exposure to moisture (caused by its components) masd: Web clinicians have described wound exudate as ‘fluid coming out of the wound’, ‘wound fluid’ and ‘an excess of normal wound fluid’. This may include infection, inflammation, or oedema. When do wounds need to be documented? Web wound healing occurs in four stages, haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and remodelling, and the appearance of the wound will change as the wound heals. If your primary treatment aim is to manage high volumes of exudate consideration should be paid to the treatment options available. Web it is mandatory to complete a wound chart for all wounds requiring ongoing interventions. Fluid that comes from the wound periwound:![20100728_Wound_Assessment_Tool_Guide_Final[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3c80de9e-a70c-4984-a340-b57a7b841cd4-150129125750-conversion-gate01/95/20100728woundassessmenttoolguidefinal2-2-638.jpg?cb=1422557894)
20100728_Wound_Assessment_Tool_Guide_Final[2]

Wound dressing in Lubbock TX Southwest Regional Wound Care Center

Table 1 from Wound exudate a survey of current understanding and
Wound Classification Chart And Wound Care Management vrogue.co

Wound Management and Nutrition for Optimal Wound Healing Atlas of the

Types of Wound Exudate Cheat Sheet NCLEX Quiz

12 stages of healing pdf mininanax
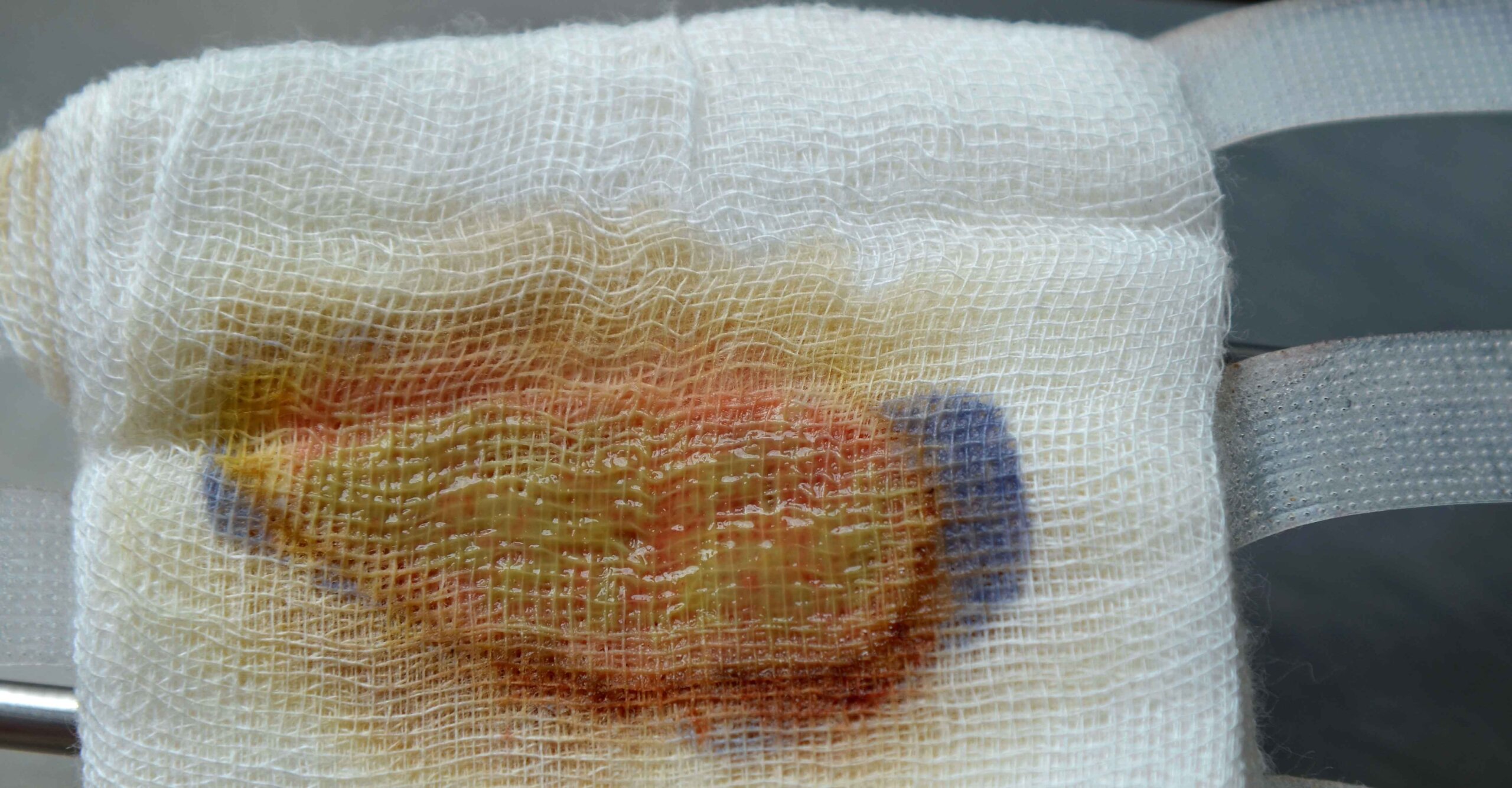
Purulent Drainage Characteristics, Treatments, and Challenges WCEI WCEI

Exudate definition, types and difference between transudate and exudate

Types of wound exudate Nursing school tips, Nursing assessment
Understanding What Causes Changes In Its Amount, Colour, Consistency And Odour Enables More Effective Wound Management Which Promotes Quicker Healing, And Minimises Maceration, Discomfort And Embarrassment For The Patient.
Serous, Sanguineous, Serosanguinous, And Purulent.
Web This Activity Addresses Protocol For Wound Assessment For The Interprofessional Team During Initial And Subsequent Wound Assessments To Best Classify And Treat A Wound To Enhance Outcomes.
Use Alginate Dressings, Or Hydroactive Dressings, Or Foam Dressings.
Related Post: