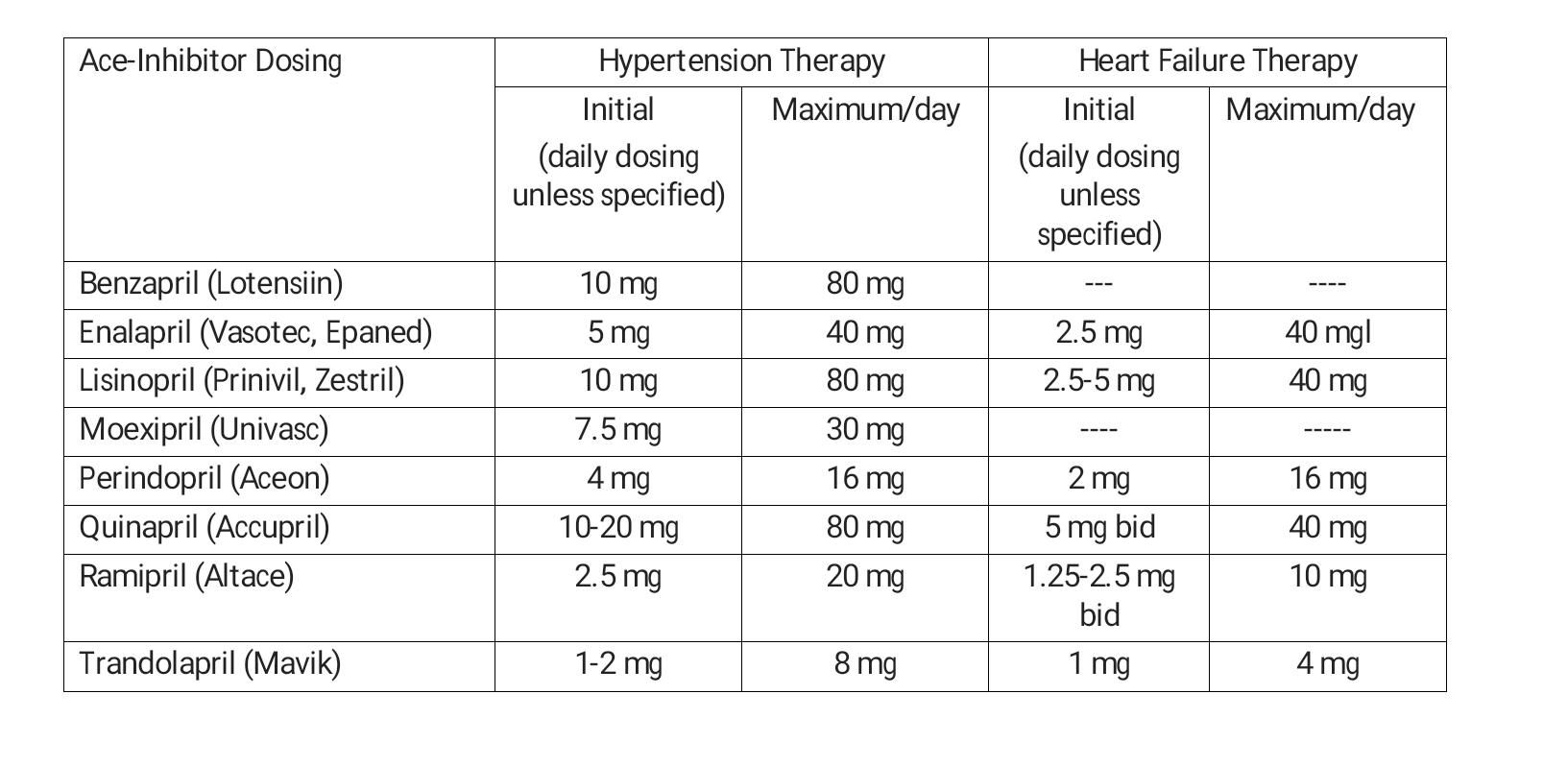
Acei Comparison Chart
Acei Comparison Chart - Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure. Web the purpose of this review is to compare the efficacy and adverse effects of different ace inhibitors. Ace inhibitor (acei)/angiotensin ii receptor blocker (arb): Web ace inhibitor antihypertensive dose comparison. Web the number and type of adverse effects observed were greater with ace inhibitors compared to arbs, although some differences still need further exploration. Slow titration up to the. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Web however, major clinical trials showing reductions in mortality have used somewhat larger target doses (see acei comparison chart: 160mg (160mg bid evaluated in heart failure studies) the table. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse effects can be observed. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure: Web comparison of angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) inhibitors. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey solution for proactive training in the. Various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey solution for proactive training in the. Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure: Lisinopril (prinivil, zestril) 2.5 mg once daily. Web angiotensin ii receptor blocker comparison. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse effects can be observed. Web angiotensin ii receptor blocker comparison. Web 10 mg once daily. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey solution for proactive training in the. Web comparison of angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) inhibitors. Web angiotensin ii receptor blocker comparison. Lisinopril (prinivil, zestril) 2.5 mg once daily. Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey solution for proactive training in the. High affinity for angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) competing with. Various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse effects can be observed. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Web regier l, jensen b. Slow titration up to the. Web arbs are now commonly prescribed in new zealand due to removal of funding restrictions and increasing clinical trial evidence supporting their similar efficacy. Slow titration up to the. 160mg (160mg bid evaluated in heart failure studies) the table. Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure. Web the number and. Drug comparisons based on potency. Web the purpose of this review is to compare the efficacy and adverse effects of different ace inhibitors. Web regier l, jensen b. Web arbs are now commonly prescribed in new zealand due to removal of funding restrictions and increasing clinical trial evidence supporting their similar efficacy. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based. Web arbs are now commonly prescribed in new zealand due to removal of funding restrictions and increasing clinical trial evidence supporting their similar efficacy. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted.. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse effects can be observed. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based. Web ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial effects on patients with cardiovascular risk factors only (hypertension, diabetes) and with several heart diseases. Dry, irritant cough in about 15% (10% men and 20% women) attributable to.. Web arbs are now commonly prescribed in new zealand due to removal of funding restrictions and increasing clinical trial evidence supporting their similar efficacy. Drug comparisons based on potency. Web the purpose of this review is to compare the efficacy and adverse effects of different ace inhibitors. Lisinopril 2.5 mg once daily. 160mg (160mg bid evaluated in heart failure studies) the table. Lisinopril (prinivil, zestril) 2.5 mg once daily. Ace inhibitor (acei)/angiotensin ii receptor blocker (arb): High affinity for angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) competing with. Ace inhibitors are generally well tolerated but some adverse effects can be observed. Our controlled substances & diversion training is your turnkey solution for proactive training in the. Web 10 mg once daily. Web comparison of the efficacy and safety of different ace inhibitors in patients with chronic heart failure: Web the number and type of adverse effects observed were greater with ace inhibitors compared to arbs, although some differences still need further exploration. Web however, major clinical trials showing reductions in mortality have used somewhat larger target doses (see acei comparison chart: Web ace inhibitor antihypertensive dose comparison. Various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted.
Comparison of ACEI in combination with ARB vs. highdose ACEI or ARB
Acei Conversion Chart Pharmacist Letter

Acei Comparison Chart

Acei Comparison Chart
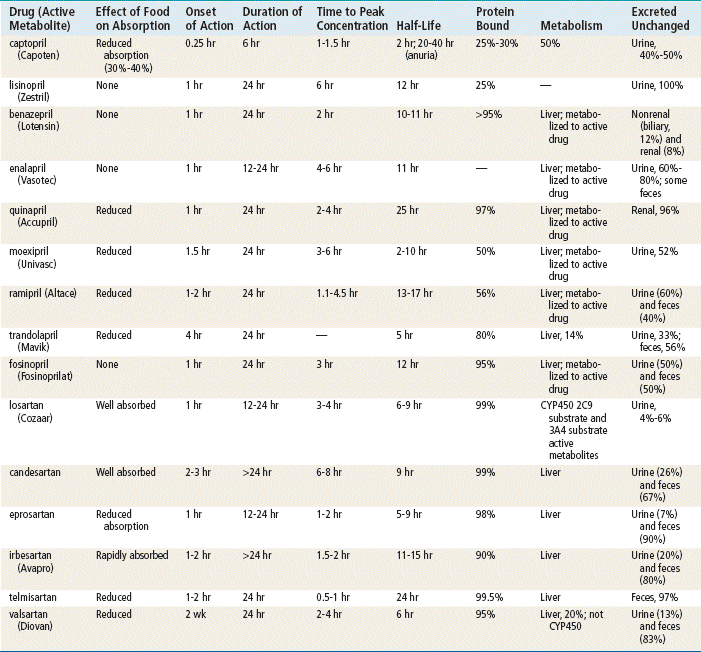
ACE Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Basicmedical Key

Ace Inhibitor Comparison Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
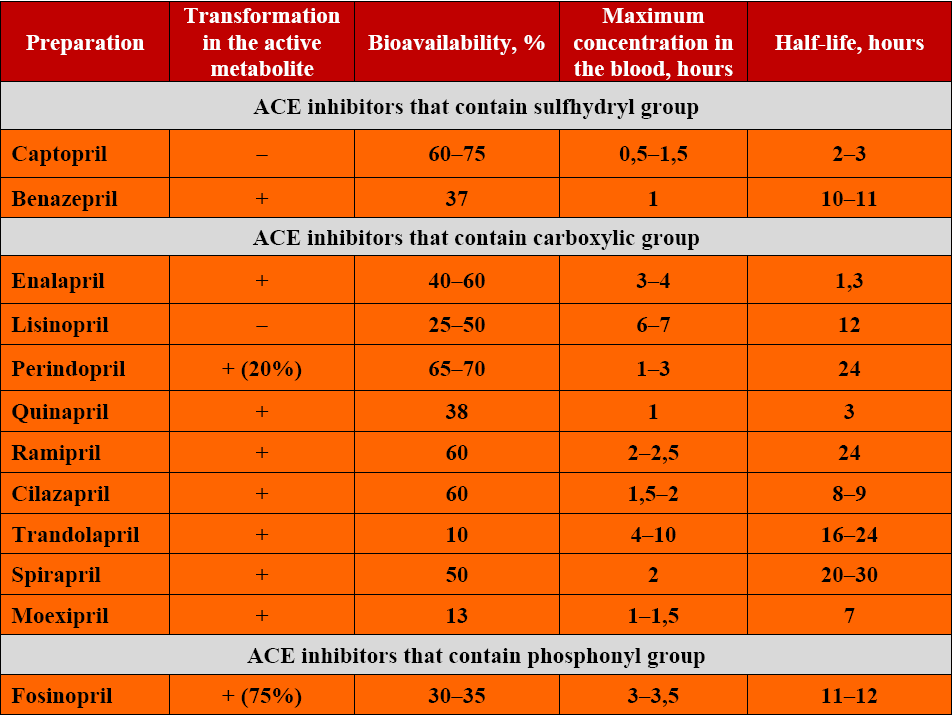
Ace Inhibitor Equivalent Dose Chart

From ACE Inhibitors/ARBs to ARNIs in Coronary Artery Disease and Heart
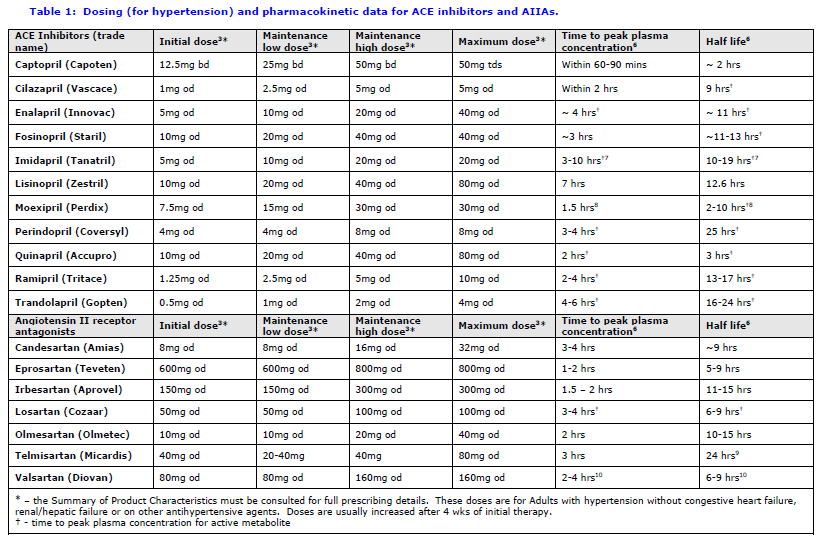
Ace Inhibitor Equivalent Dose Chart

Acei Conversion Chart Pharmacist Letter LETTER RTS
Web Regier L, Jensen B.
Web Angiotensin Ii Receptor Blocker Comparison.
Web Ace Inhibitors And Arbs Act By Blocking Raas With Beneficial Effects On Patients With Cardiovascular Risk Factors Only (Hypertension, Diabetes) And With Several Heart Diseases.
Dry, Irritant Cough In About 15% (10% Men And 20% Women) Attributable To.
Related Post: