Power Line Minimum Approach Distance Chart
Power Line Minimum Approach Distance Chart - Performing minor building work using hand tools held by a person. Web minimum approach distances for the voltage ranges are provided in column a of table 1 in appendix a. Over 1,000 kv, the utility/owner or a registered engineer must establish it. Please see the chart below to determine these distances for the above identified voltages and greater: The lab and rab vary depending on voltage present. Web 4 until march 31, 2015, employers may use the minimum approach distances in table 6 through table 13 in appendix b to this section. As with other articles in this series, we must begin with the hazard. * for nominal voltages not listed use the next higher voltage in the table. Web determine if any part of the equipment, load line or load (including rigging and lifting accessories), while operating up to the equipment's maximum working radius in the work zone, could get closer than the minimum approach distance of the power line permitted under table a (see § 1926.1408). Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have donned rated rubber gloves. In meters) shall conform to the following equations. Over 37 kv, not over 87.5 kv: Operating cranes and their loads or mobile plant. Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body. Web 4 until march 31, 2015, employers may use the minimum approach distances in table 6 through table 13 in appendix b to this section. 230 kv is 4.52 p. Web a safe approach distance is the minimum separation in air from an energised overhead electric line that should be maintained by a machine, person, or object held by or. Web determine if any part of the equipment, load line or load (including rigging and lifting accessories), while operating up to the equipment's maximum working radius in the work zone, could get closer than the minimum approach distance of the power line permitted under table a (see § 1926.1408). The approach distance for each work zone (see figures 3 and. Best practice is to keep any unqualified person 10’ or more away from the hazard. 1 mad = m + d, where: Web table 1 shows general approach distances for unauthorised persons working near low voltage service lines when: Web 4 until march 31, 2015, employers may use the minimum approach distances in table 6 through table 13 in appendix. Minimum approach distances ensure that workers do not approach or take any conductive object closer to the energized parts. Scaffolding, roofing materials, ladders and guttering. Voltage range (phase to phase, rms) approach distance (inches) 300 v and less (1) over 300v, not over 750v: Web limits of approach are the safe distances that people or equipment must maintain from exposed. The approach distance for each work zone (see figures 3 and 4) will vary depending on the voltage of the overhead electric line and the level of authorisation of each person carrying out the work. Web limits of approach are the safe distances that people or equipment must maintain from exposed energized power lines or equipment, which vary depending on. Altitude correction factor for minimum approach distances. Please see the chart below to determine these distances for the above identified voltages and greater: Voltage range (phase to phase, rms) approach distance (inches) 300 v and less (1) over 300v, not over 750v: Web limits of approach are the safe distances that people or equipment must maintain from exposed energized power. Minimum clearance distances based on voltage. Over 15 kv, not over 37 kv: 1 mad = m + d, where: Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3. Altitude correction factor for minimum approach distances. The approach distance for each work zone (see figures 3 and 4) will vary depending on the voltage of the overhead electric line and the level of authorisation of each person carrying out the work. Web the word is actually an acronym that stands for minimum approach distance, which is the calculated safe. Over 15 kv, not over 37 kv: 1 mad = m + d, where: Web osha refers to mad as “the closest distance a qualified employee may approach an energized conductor or object.” osha mad requirements in 2014, osha updated the 29 cfr 1910.269 and 1926 subpart v standards with requirements for all employers to establish mads. Web the word. 345 kv is 4.93 p.u. Altitude correction factor for minimum approach distances. 1 mad = m + d, where: Web the calculator will output the minimum approach distance. The minimum approach distance (mad; Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have donned rated rubber gloves. Over 37 kv, not over 87.5 kv: Voltage range (phase to phase, rms) approach distance (inches) 300 v and less (1) over 300v, not over 750v: In meters) shall conform to the following equations. * for nominal voltages not listed use the next higher voltage in the table. The approach distance for each work zone (see figures 3 and 4) will vary depending on the voltage of the overhead electric line and the level of authorisation of each person carrying out the work. Web table 1 shows general approach distances for unauthorised persons working near low voltage service lines when: Over 750v not over 2 kv: Performing minor building work using hand tools held by a person. Over 1,000 kv, the utility/owner or a registered engineer must establish it. Web the word is actually an acronym that stands for minimum approach distance, which is the calculated safe working distance that provides worker protection when working on or in the vicinity of energized lines and equipment.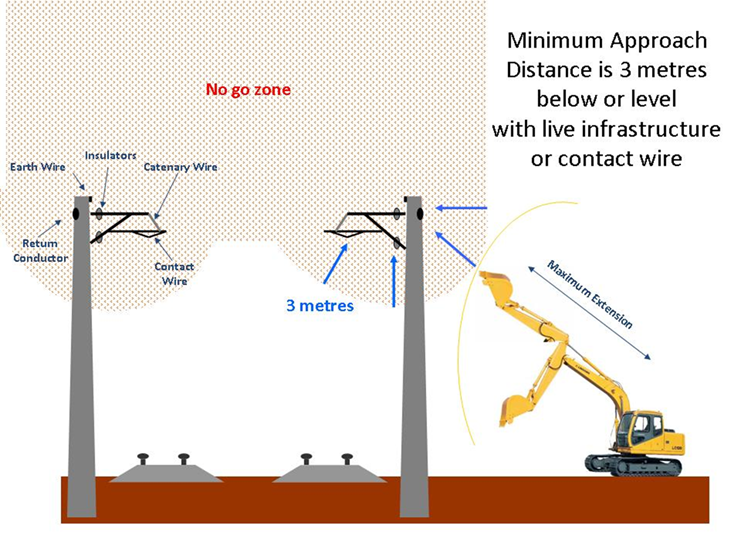
Electrical Safety Department for Infrastructure and Transport South
Minimum Approach Distances 220kV Lines on Towers Electric Power
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
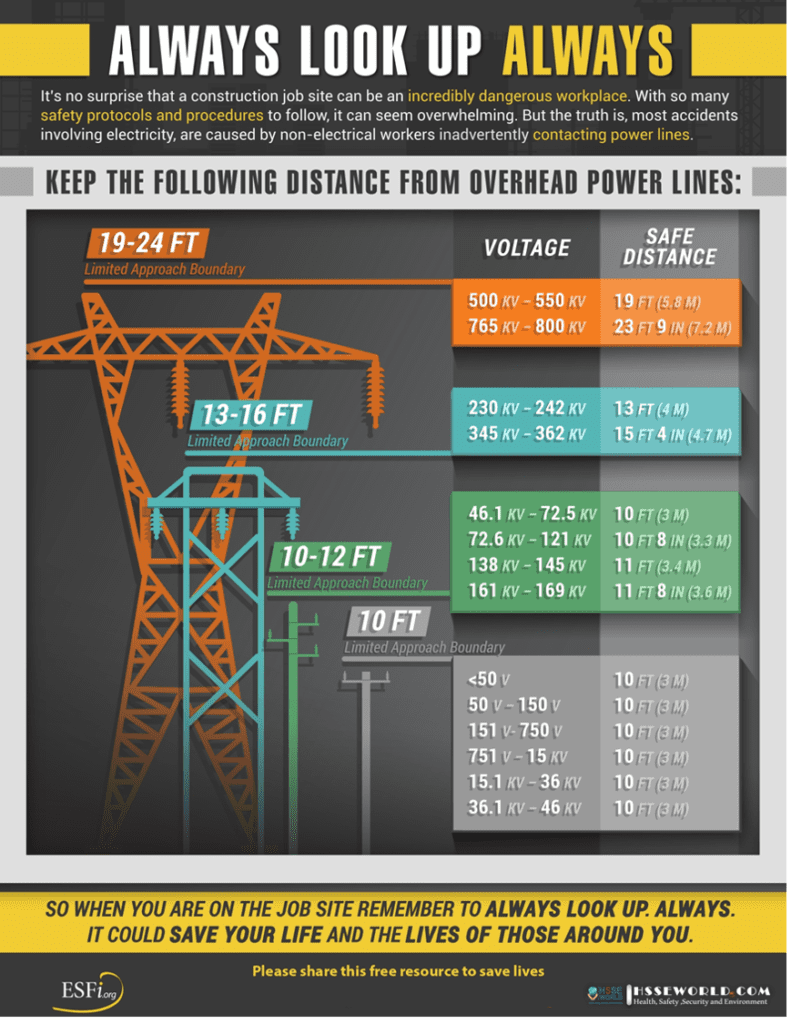
Over head power lines Clearance photo of the day HSSE WORLD
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum

Maintenance of trees around powerlines WorkSafe
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum

Overhead Powerline Safety Electrical Safety Foundation International
Limits of Approach Working in Close Proximity to Electrical Equipment
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
Minimum Clearance Distances Based On Voltage.
In Meters) Shall Conform To The Following Equations.
The Following Table Provides Minimum Approach Distances Grouped By Nominal Voltages.
230 Kv Is 4.52 P.
Related Post:
