Emerald Ash Borer Drawing
Emerald Ash Borer Drawing - It was first introduced into prince georges county in 2003 and was confirmed to be infesting ash trees on the eastern. Its confirmed presence in wyandotte, johnson, and leavenworth counties and potential losses to valuable landscape and municipal trees have prompted state agencies to join a national. Dwg (ft) dwg (m) svg. Elizabeth barnes when emerald ash borer swept through the midwest it left three kinds of ash trees in its wake: Near detroit, michigan in 2002. Females lay eggs in bark crevices on ash trees, and larvae feed underneath the bark of ash trees to emerge as adults in one to two years. Follow the dead ash trees. It kills all species of ash trees (including white, green and blue ash) as its larvae burrow beneath the bark, leaving tunnels that prevent the tree from drawing nutrients up from its roots. Shaw | jul 2022 | educational gallery. About the size of president. The dead, the dying, and the diligently protected and thriving. Eab lays its eggs in the bark crevices of ash trees. Follow the dead ash trees. Department of agriculture, walked to a. Web for jian duan, the answer is simple: Eab lays its eggs in the bark crevices of ash trees. Web the emerald ash borer ( agrilus planipennis) is a beetle native to russia, china, japan, and korea. It was first detected in detroit in 2002 and was found in boulder, co, in september 2013. What is the emerald ash borer? Exit holes are sometimes found low in the. Web the emerald ash borer ( agrilus planipennis) is a beetle native to russia, china, japan, and korea. The adults will cause slight damage to the leaves of trees but the larvae cause significant damage, eating the inner portion of the bark of ash trees. It is an invasive insect that is native to asia. Females lay eggs in bark. The eab was first found in north america in 2002 near detroit and since has spread to 13 states and two canadian provinces. It was first detected in detroit in 2002 and was found in boulder, co, in september 2013. It is often abbreviated as eab. Web may 24, 2022 usda. Web emerald ash borer. First detected in north carolina in 2013, it has already spread to 61 of our 100 counties, making it one of the fastest spreading invasive forest pests our state has ever seen. It kills all species of ash trees (including white, green and blue ash) as its larvae burrow beneath the bark, leaving tunnels that prevent the tree from drawing. Web emerald ash borer (eab) is a serious threat to maryland ash trees. The adults will cause slight damage to the leaves of trees but the larvae cause significant damage, eating the inner portion of the bark of ash trees. The hunt was on for ways to stop this insect and save north america’s ash trees. Web the emerald ash. The dead, the dying, and the diligently protected and thriving. Lincoln's image on a penny). This feeding behavior can affect the xylem and phloem. In its native range, the species is found at low densities, and it does not cause significant damage to trees native to the area. Follow the dead ash trees. 60 minutes background/setting the stage: Web may 24, 2022 usda. Web emerald ash borer photo gallery. Elizabeth barnes when emerald ash borer swept through the midwest it left three kinds of ash trees in its wake: Lincoln's image on a penny). Use questions to get youth thinking about biodiversity: It kills all species of ash trees (including white, green and blue ash) as its larvae burrow beneath the bark, leaving tunnels that prevent the tree from drawing nutrients up from its roots. Web what is the emerald ash borer (eab)? Web the emerald ash borer (eab) agrilus planipennis fairmaire is an. After pupating within the ash host, eab adults emerge in the spring. Its confirmed presence in wyandotte, johnson, and leavenworth counties and potential losses to valuable landscape and municipal trees have prompted state agencies to join a national. The dead, the dying, and the diligently protected and thriving. The adults will cause slight damage to the leaves of trees but. Select an image to see a larger photo. Hosts are species (and cultivars) of ash in the genus fraxinus. The hunt was on for ways to stop this insect and save north america’s ash trees. It is not native to the united states and was first found in the u.s. First detected in north carolina in 2013, it has already spread to 61 of our 100 counties, making it one of the fastest spreading invasive forest pests our state has ever seen. Web the emerald ash borer is a devastating invasive beetle that has already killed millions of ash trees in the us. About the size of president. 60 minutes background/setting the stage: Emerald ash borer temporary quarantine adopted in washington county effective dec. Elizabeth barnes when emerald ash borer swept through the midwest it left three kinds of ash trees in its wake: It was first introduced into prince georges county in 2003 and was confirmed to be infesting ash trees on the eastern. Web recognizing ash trees in oregon, washington and northern california. One pest, the emerald ash borer, has killed hundreds of millions of rural and urban ash trees. Emerald ash borer wounds ash trees by tunneling under the bark. Follow the dead ash trees. Females lay eggs in bark crevices on ash trees, and larvae feed underneath the bark of ash trees to emerge as adults in one to two years.
Drawing Made by the Insect the Emerald Ash Borer Under the Bark of a
Emerald Ash Borer University YouTube
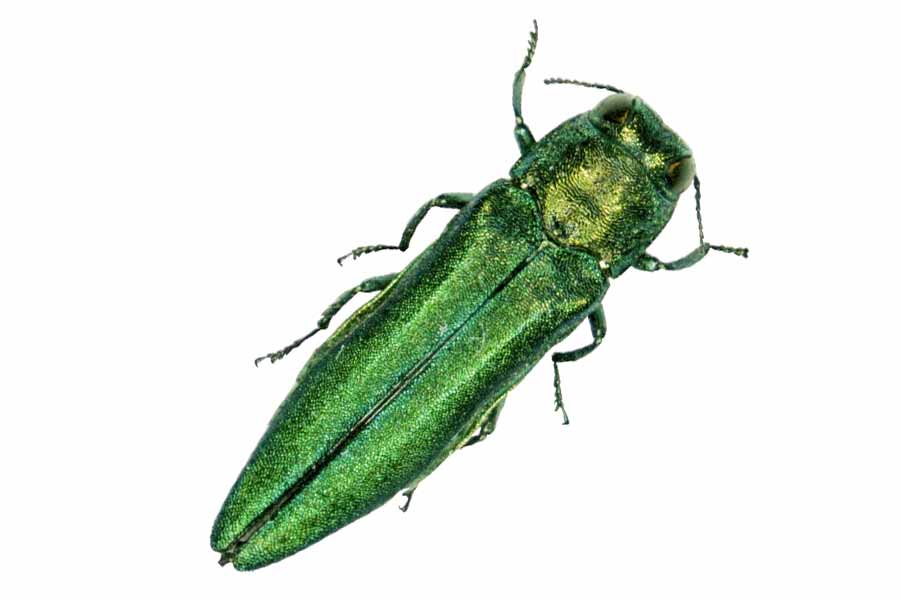

Emerald Ash Borer The Arbor Day Foundation
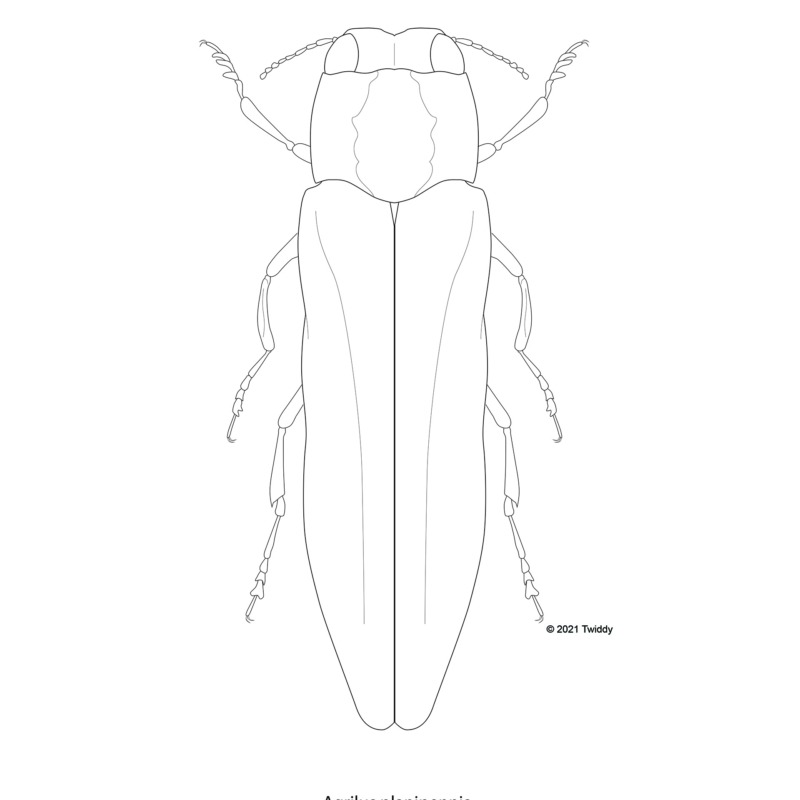
Scientific Illustration Sean Twiddy's Bughaus Productions

Emerald Ash Borer Is Here. What Can We Do? The Times Ink!

Emerald Ash Borer The Washington Post
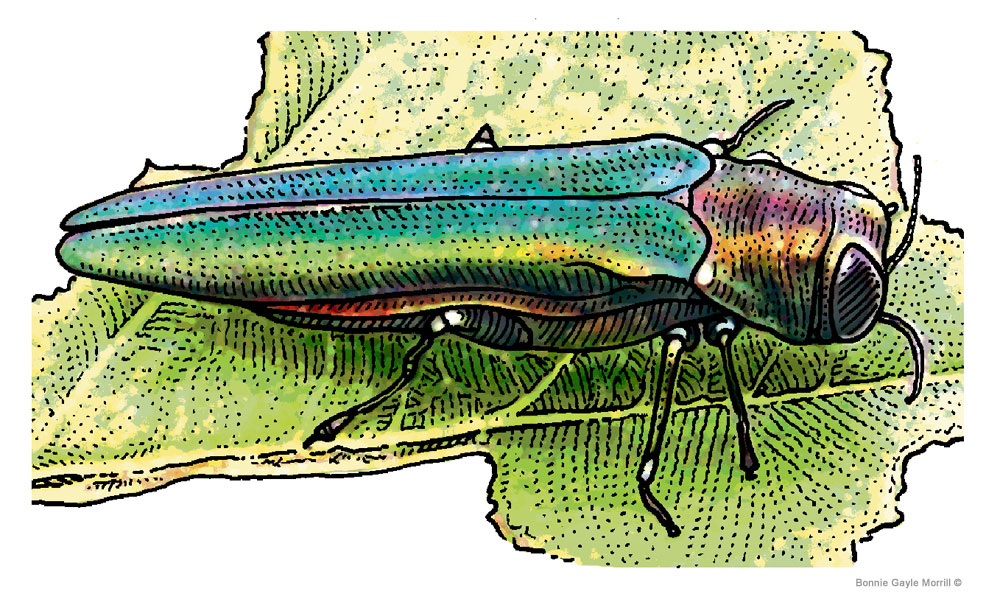
Emerald Ash Borer BGM Illustrations
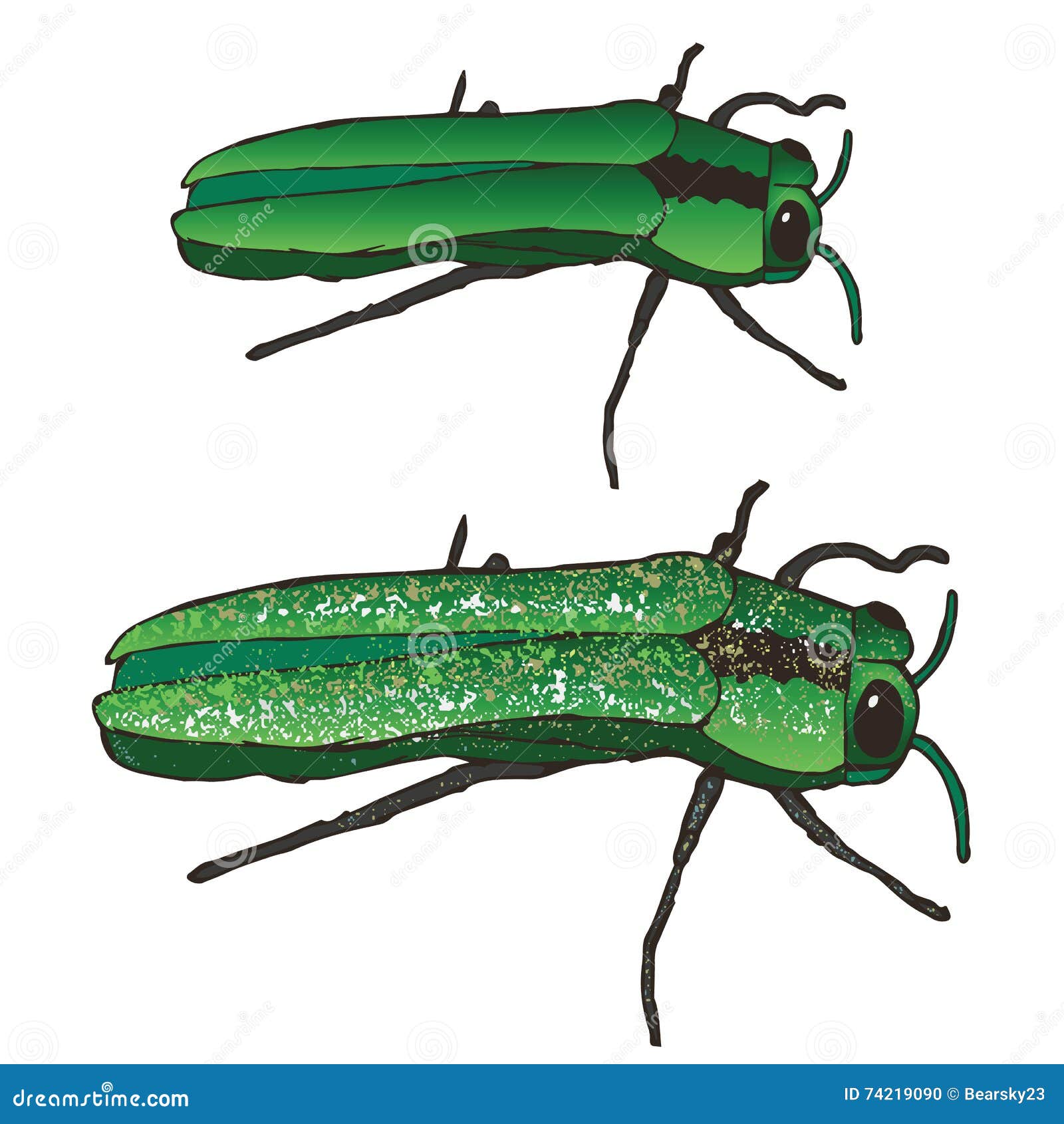

Emerald Ash Borer Stock Illustrations 2 Emerald Ash Borer Stock
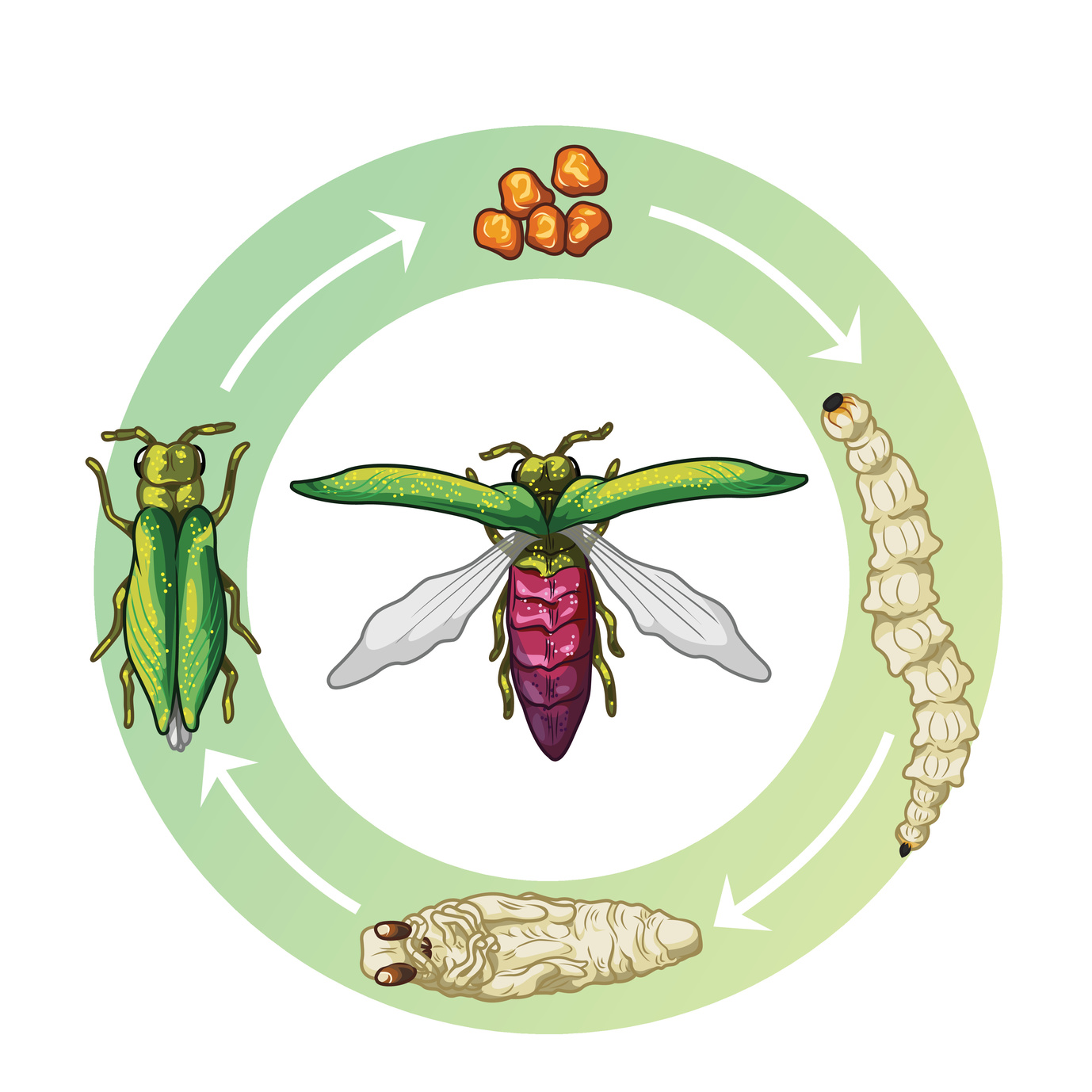
How To Identify Emerald Ash Borer Symptoms And Prevention

Emerald Ash Borer Stevenson Tree Care & Stevenson Lawn Care
Eab Lays Its Eggs In The Bark Crevices Of Ash Trees.
The Eab Was First Found In North America In 2002 Near Detroit And Since Has Spread To 13 States And Two Canadian Provinces.
It Was First Detected In Detroit In 2002 And Was Found In Boulder, Co, In September 2013.
In Its Native Range, The Species Is Found At Low Densities, And It Does Not Cause Significant Damage To Trees Native To The Area.
Related Post: