Grain Size Chart Astm
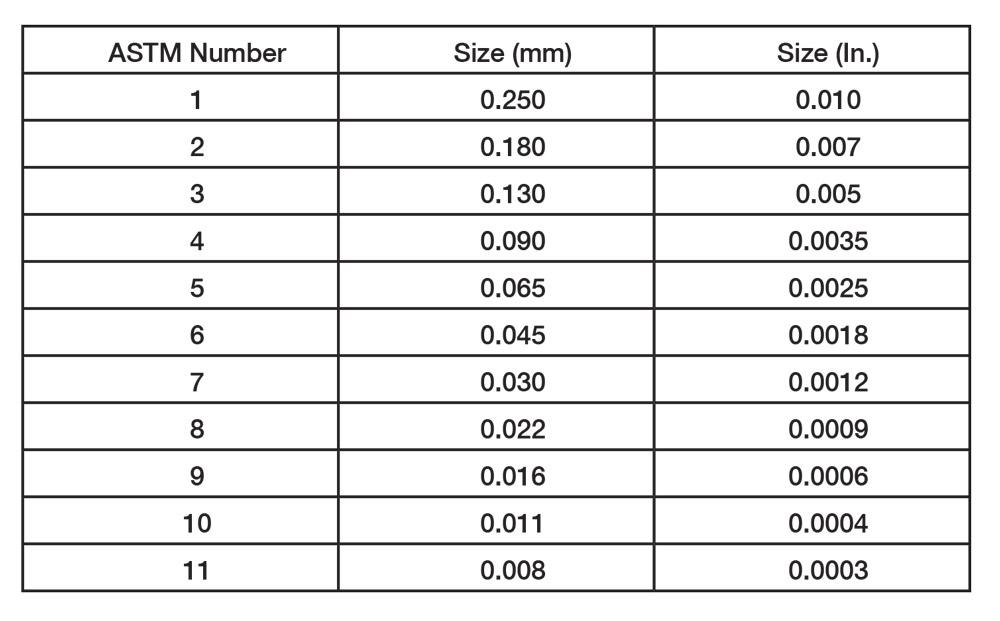
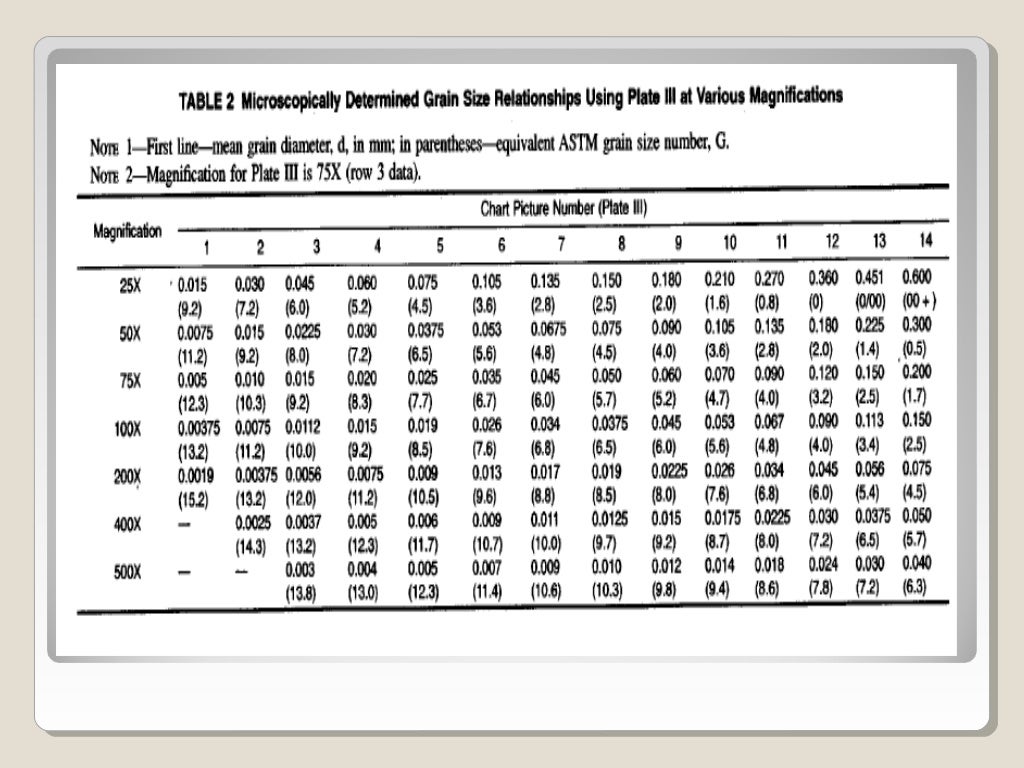
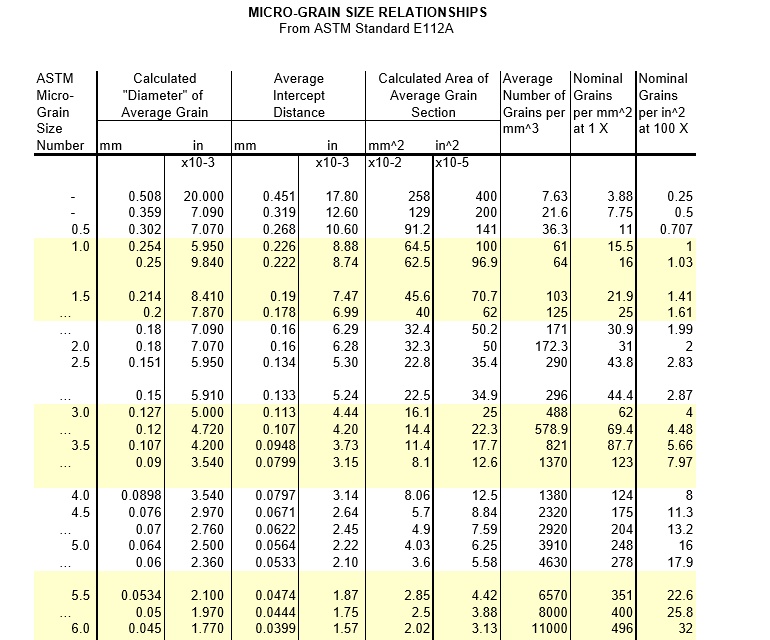
Grain Size Chart Astm - Web grain size considerably influences a material’s structural properties like elasticity and durability. N ae 52g21 (1) where n ae is the number of grains per square inch at 100x magnification. Web these methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. Web these test methods cover procedures for estimating and rules for expressing the average grain size of all metals consisting entirely, or principally, of a single phase. Web standard test methods for determining average grain size 1. In fact, the basic procedures may also be used for. These test methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. Web this article contains a conversion table, which assists in the conversion of astm number to average grain intercept length. 1.1 these test methods cover the measurement of average grain size and include the comparison procedure, the planimetric (or jeffries) procedure, and the intercept procedures. The methods discussed include comparison techniques employing standard charts or the shepherd fracture grain size standards; Web rules for expressing the average grain size of all metals consisting entirely, or principally, of a single phase. The three basic procedures for grain size estimation are: To obtain the number per square millimetre at 1x, multiply by 15.50. Web standard test methods for determining average grain size 1. Web 3.2.1 astm grain size number—the astm grain size number,. Web rules for expressing the average grain size of all metals consisting entirely, or principally, of a single phase. 1.1 these test methods cover the measurement of average grain size and include the comparison procedure, the planimetric (or jeffries) procedure, and the intercept procedures. These test methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures. These test methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. N ae 5 2 g21 (1) where n ae is the number of grains per square inch at 100x magnification. This thorough guide probes the intricacies of astm e112.. Web this article contains a conversion table, which assists in the conversion of astm number to average grain intercept length. The test methods may also be used for any structures having appearances similar to those of the metallic structures shown in the comparison charts. N ae 5 2 g21 (1) where n ae is the number of grains per square. Web these test methods apply chiefly to single phase grain structures but they can be applied to determine the average size of a particular type of grain structure in a multiphase or multiconstituent specimen. The methods discussed include comparison techniques employing standard charts or the shepherd fracture grain size standards; N ae 52g21 (1) where n ae is the number. These test methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. Standard test methods for determining average grain size. Web sieve grain size analysis is capable of determining the particles’ size ranging from 0.075 mm to 100 mm. Web methods. N ae 5 2 g21 (1) where n ae is the number of grains per square inch at 100x magnification. Web these test methods apply chiefly to single phase grain structures but they can be applied to determine the average size of a particular type of grain structure in a multiphase or multiconstituent specimen. Web these test methods cover procedures. The test methods may also be used for any structures having appearances similar to those of the metallic structures shown in the comparison charts. N ae 52g21 (1) where n ae is the number of grains per square inch at 100x magnification. The three basic procedures for grain size estimation are: Standard test methods for determining average grain size. To. Web this was the first chart (eight pictures) to define grain size in terms of the now familiar astm grain size numbers (1 to 8 in this chart). The test methods may also be used for any structures having appearances similar to those of the metallic structures shown in the comparison charts. N ae 52g21 (1) where n ae is. Web these test methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. Web sieve grain size analysis is capable of determining the particles’ size ranging from 0.075 mm to 100 mm. This thorough guide probes the intricacies of astm e112.. Web standard test methods for determining average grain size 1. This thorough guide probes the intricacies of astm e112. Any categorization of grains larger than 100mm will be conducted visually whereas particles smaller than 0.075 mm can be distributed using the hydrometer method. Web these test methods apply chiefly to single phase grain structures but they can be applied to determine the average size of a particular type of grain structure in a multiphase or multiconstituent specimen. To obtain the number per square millimetre at 1x, multiply by 15.50. Web 3.2.1 astm grain size number—the astm grain size number, g, was originally defined as: In fact, the basic procedures may also be used for. Web these test methods cover procedures for estimating and rules for expressing the average grain size of all metals consisting entirely, or principally, of a single phase. Web 3.2.1 astm grain size number—the astm grain size number, g, was originally defined as: Web these methods of determination of average grain size in metallic materials are primarily measuring procedures and, because of their purely geometric basis, are independent of the metal or alloy concerned. Web grain size considerably influences a material’s structural properties like elasticity and durability. Methods e 89 also marked the first detailed description of the heyn intercept method with equations and a conversion approach to yield astm grain size numbers. It also includes a table that lists european and u.s. From aerospace to construction, describing the grain size of materials accurately is important for engineers across numerous industries. Web rules for expressing the average grain size of all metals consisting entirely, or principally, of a single phase. For the measurement of austenite grains developed by other means (see annex a3), measure by comparing the microscopic image with the plate.
ASTM Grain Size Chart

Astm Grain Size Number Chart
Grain size control for successfully fabricating stainless and INCONEL
Astm Grain Size Chart
ASTM E 112 GRAIN SIZE MEASURING METHODS full standard, mecanical

ASTM Grain Size Chart
Astm Grain Size Number and Grain Diameter

Astm Grain Size Number Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
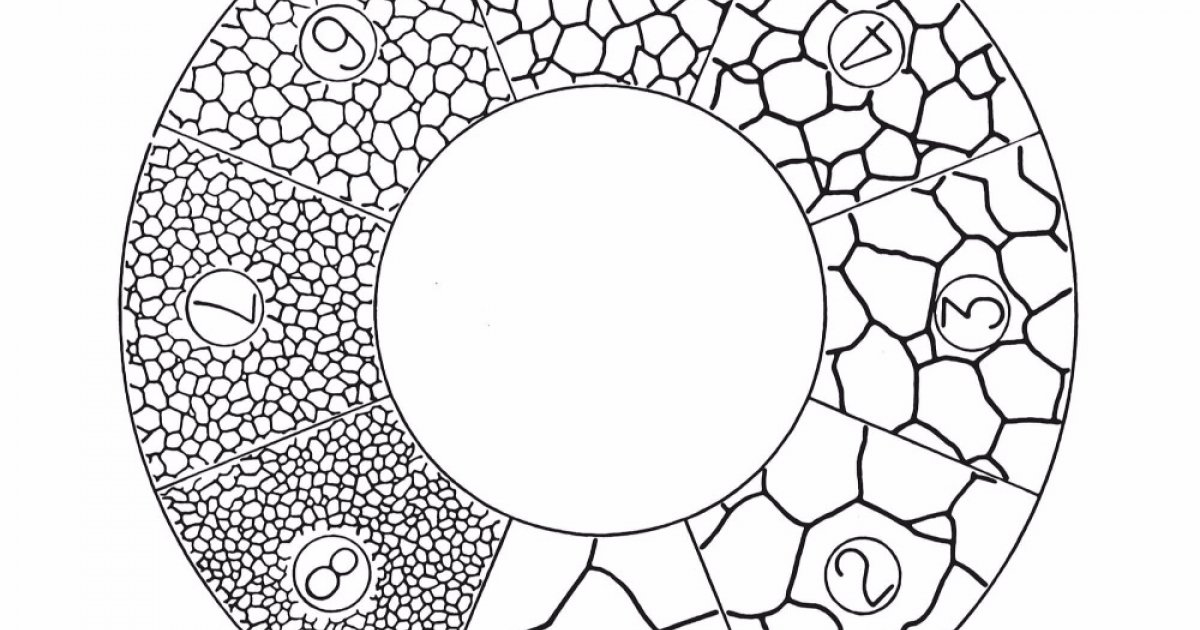
G41 ASTM Grain Sizing Austenite

ASTM Grain Size Chart
The Three Basic Procedures For Grain Size Estimation Are:
You Only Have To Look On The Eyepiece And Compare The Image You See There With The Standard Charts, That´s It.
The Test Methods May Be Applied To Specimens With Equiaxed Or Elongated Grain Structures With Either Uniform Or Duplex Grain Size Distributions.
Web These Test Methods May Be Used To Determine The Mean Grain Size, Or The Distribution Of Grain Intercept Lengths Or Areas, In Metallic And Nonmetallic Polycrystalline Materials.
Related Post: