Levels Of Thinking Chart
Levels Of Thinking Chart - Both students and educators can make use of this chart. Web costa’s levels of thinking to better understand the content being presented in their core subject areas, it is essential for students to learn to think critically and to ask higher levels of questions. The ability to use visual imagery and or linguistic imagery comes in a wide variety of strengths. Provides a way to organise thinking skills into six levels, from the most. Edited november 1, 2023 by lordfall. Because it is for her portfolio, unlike with the s&p 500. Similar to bloom’s taxonomy , costa’s lower level prompts students to use more basic faculties; Higher order thinking questions help students explore and express rigor in their application of knowledge. Why does cathie wood think investors' fear about stocks is at great depression levels? Level 2 (knowledge application) are skills and concepts. This is the most fundamental level of understanding that involves remembering basic information regarding a subject matter. Below are the six question categories as defined by bloom. Web this framework consists of 4 levels, level 1 being the simplest and level 4 being the most complex. Web bloom's taxonomy is a hierarchical classification of the different levels of thinking, from. Learn how to apply it to create course objectives, assess learning outcomes, and revise the taxonomy for teaching and learning. Applying and evaluating actions, solutions, and connections made in order to predict. Level 2 (knowledge application) are skills and concepts. Both students and educators can make use of this chart. This means that students will be able to define concepts,. Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool. Web questions are not bad, but using them all the time is. Why does cathie wood think investors' fear about stocks is at great depression levels? Web bloom's taxonomy is a hierarchical classification of the different levels of thinking, from simple to complex and concrete to abstract. Level 1 (acquired knowledge). Web bloom’s 2 highest levels requires investigation, complex reasoning, planning, developing, and thinking‐probably over an extended period of time. *longer time period is not an applicable factor if work is simply repetitive and/or does not require higher‐order thinking. Web overview of the levels of thinking: Below are the six question categories as defined by bloom. 2 thinking strategies for student. Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory, used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material. This is the most fundamental level of understanding that involves remembering basic information regarding a subject matter. He made this simplified chart too, overall probably some of the best consciousness video i've seen outside of leo's work. Below are the six. By asking higher levels of questions, students deepen their knowledge and create connections to the material being presented. Web overview of the levels of thinking: These questions require much more brain power and a more extensive and elaborate answer. Applying and evaluating actions, solutions, and connections made in order to predict. Learn how to use bloom’s taxonomy to approach your. As students move up in levels, the questions prompt them to use more. Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool. Vocabulary words levels of thinking. By asking higher levels of questions, students deepen their knowledge and create connections to the material being presented. The ability to use visual imagery and or linguistic imagery comes in a wide variety. Thus, a student has achieved a high level of thinking skills. Web overview of the levels of thinking: Try to utilize higher order level of questions. Web costa’s levels of thinking to better understand the content being presented in their core subject areas, it is essential for students to learn to think critically and to ask higher levels of questions.. Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking. This is the most fundamental level of understanding that involves remembering basic information regarding a subject matter. Below are the six question categories as defined by bloom. Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory, used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material. Been adapted for classroom use as. There are 5 main areas of higher order thinking that promote rigor: Web this framework consists of 4 levels, level 1 being the simplest and level 4 being the most complex. As students move up in levels, the questions prompt them to use more. Vocabulary words levels of thinking. Higher order thinking questions help students explore and express rigor in. Below are the six question categories as defined by bloom. Thus, a student has achieved a high level of thinking skills. Vocabulary words levels of thinking. Because it is for her portfolio, unlike with the s&p 500. Learn how to apply it to create course objectives, assess learning outcomes, and revise the taxonomy for teaching and learning. Web 6 levels of understanding 1. Find study methods, questions, and resources to help you master higher order thinking and improve your academic performance. Higher order thinking questions help students explore and express rigor in their application of knowledge. 2 thinking strategies for student achievement bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives (1956) level of thinking knowledge comprehension application analysis. Try to utilize higher order level of questions. Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory, used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material. Level 2 (knowledge application) are skills and concepts. Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking. These questions require much more brain power and a more extensive and elaborate answer. Web bloom’s 2 highest levels requires investigation, complex reasoning, planning, developing, and thinking‐probably over an extended period of time. Both students and educators can make use of this chart.
Bloom's Vs. DOK// Instructional Coaching, Instructional Strategies
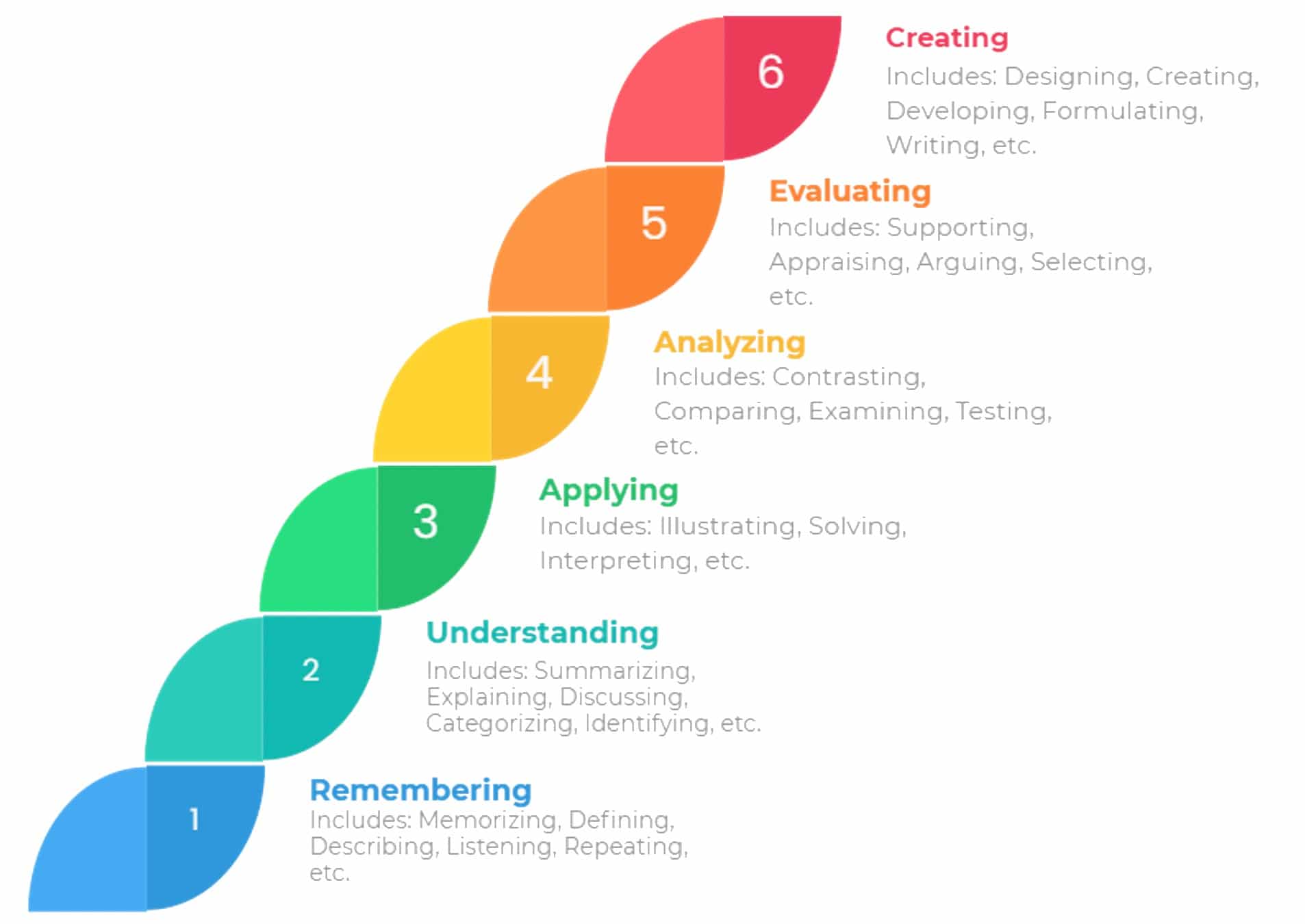
Bloom's Taxonomy Levels Chart

Bloom's Taxonomy Chart Current book status Natural Sciences and

Challenges Charts Thinking Skills Chart Thinking skills, Critical

Pin on Teaching ️

levels of questioning chart AVID Education Pinterest Student
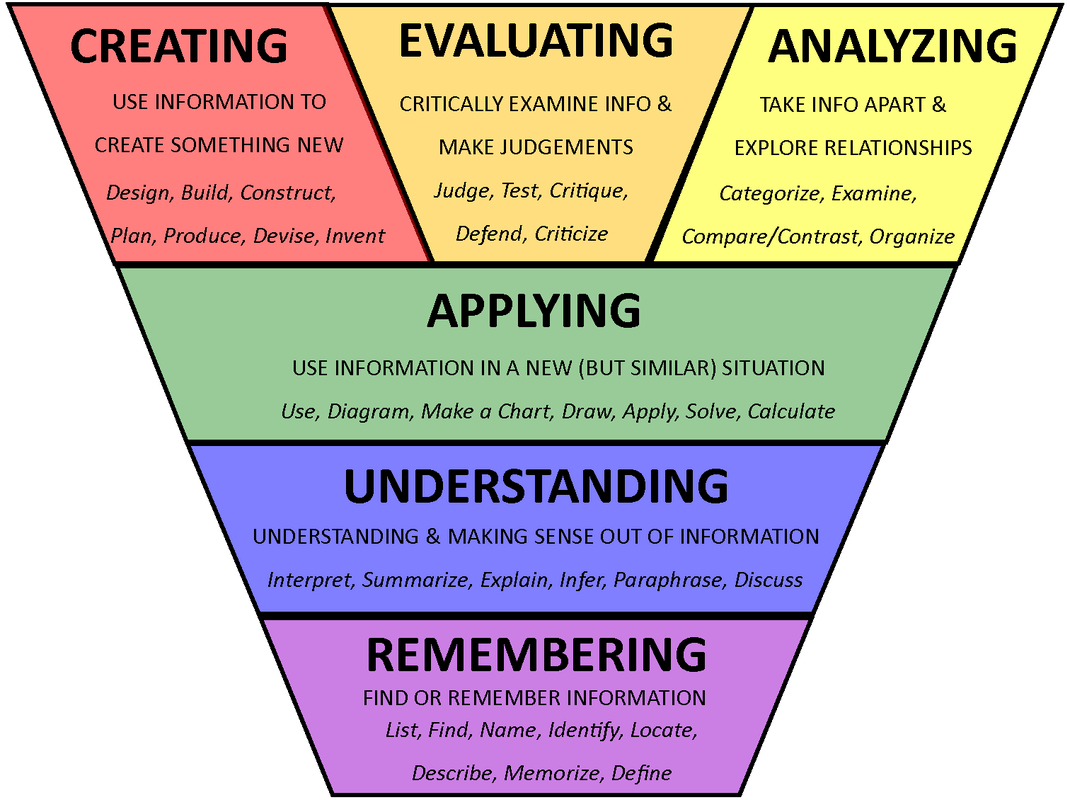
Blog iTHINK SMKCS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS

Higher Level Thinking Chart

Higher Order Thinking Skills CobykruwFrank

Levels Indigo and Group 9/10 Levels of consciousness, Understanding
By Asking Higher Levels Of Questions, Students Deepen Their Knowledge And Create Connections To The Material Being Presented.
Similar To Bloom’s Taxonomy , Costa’s Lower Level Prompts Students To Use More Basic Faculties;
Web Bloom's Taxonomy Is A Hierarchical Classification Of The Different Levels Of Thinking, From Simple To Complex And Concrete To Abstract.
There Are 5 Main Areas Of Higher Order Thinking That Promote Rigor:
Related Post: