The Skateboarder In The Drawing Starts Down The Left Side
The Skateboarder In The Drawing Starts Down The Left Side - Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 3.85 m/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4 m/s. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on. Now for the solution for the step to what done by gravity will increase the kinetic energy working by gravity, that is w is equal to mg sine 18 degree multiplied by six. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and fin As shown in the figure below, a skateboarder starts at point a on the ramp and rises to point b, a maximum height of h = 2.55 m above the top of the ramp. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side fthe ramp with an initial speed of 5.4 m/s. Given that, initial speed = 5.7 m/s. Web go the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4m/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 3.85 m/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 3.85 m/s. It is mg mg cause 18 degrees. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 6.3 ft/s. Given that, initial speed = 5.7 m/s. Web the skateboarder in. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and fin Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. If. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of $5.4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. This is a 40 body diagram. If nonconservativeforces, such as kinetic friction and air resistance, arenegligible, what would be the height h of the highestpoint reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp? It. It is mg mg cause 18 degrees. Web go the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4m/s. Now for the solution for the step to what done by gravity will increase the kinetic energy working by gravity, that is w is equal to mg sine 18 degree multiplied by. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. As shown in the figure below, a skateboarder. The skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}. Now for the solution for the step to what done by gravity will increase the kinetic energy working by gravity, that is w is equal to mg sine 18 degree multiplied by six. Solution verified answered 4 months. This is a very stevie um design 18 degree. Given that, initial speed = 5.7 m/s. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. Web he skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.0 m/s. This is a 40 body diagram. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 6.3 ft/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of. If nonconservative forces, such as kinetic friction and air resistance, are negligible, what would be the height $h$ of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp? As shown in the figure below, a skateboarder starts at point a on the ramp and rises to point b, a maximum height of h = 2.55. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 3.85 m/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4 m/s. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. If nonconservativeforces, such as kinetic friction and air resistance, arenegligible, what would be the height h of the highestpoint reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp? The skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.7 m/s. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp. Web go the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.4m/s. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 6.3 ft/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side fthe ramp with an initial speed of 5.4 m/s. Web the skateboarder in the drawing starts down the left side of the ramp with an initial speed of 5.0 m/s. The height of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp is 1.657 m. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached. If nonconservative forces, such as kinetic friction and air resistance, are negligible, what would be the height $h$ of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp? This is a 40 body diagram. Neglect nonconservative forces, such as friction and air resistance, and find the height h of the highest point reached by the skateboarder on the right side of the ramp.
How to Draw a Skateboarder Illustration Live with Frank Rodgers YouTube
How To Draw A Skateboard Step By Step 🛹 Skateboard Drawing Easy YouTube
Skateboard Drawing How To Draw A Skateboard Step By Step

How to Draw a Boy Riding a Skateboard Easy Skater Boy Drawing For

Learn how to draw a skateboarder doing a kickflip. This lesson is meant
How to draw a SkateBoard Step by Step Drawings Tutorials
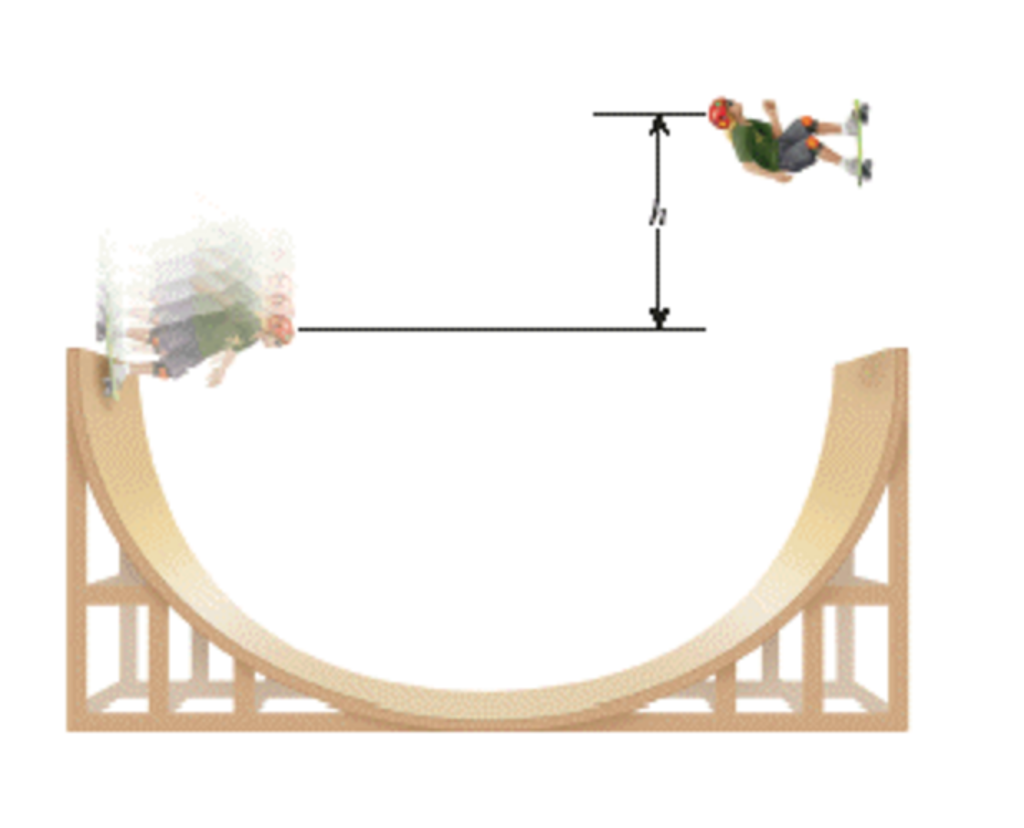
Solved The Skateboarder In The Drawing Starts Down The Le...

Learn How to Draw a Skateboarder (Skateboarding) Step by Step Drawing

how to draw a skateboarderdrawings for children YouTube
Learn How to Draw a Skateboarder (Skateboarding) Step by Step Drawing
Web The Skateboarder In The Drawing Starts Down The Left Side Of The Ramp With An Initial Speed Of 7.03 M/S.
Given That, Initial Speed = 5.7 M/S.
Web The Skateboarder In The Drawing Starts Down The Left Side Of The Ramp With An Initial Speed Of 3.85 M/S.
This Is A Very Stevie Um Design 18 Degree.
Related Post: